Abstract
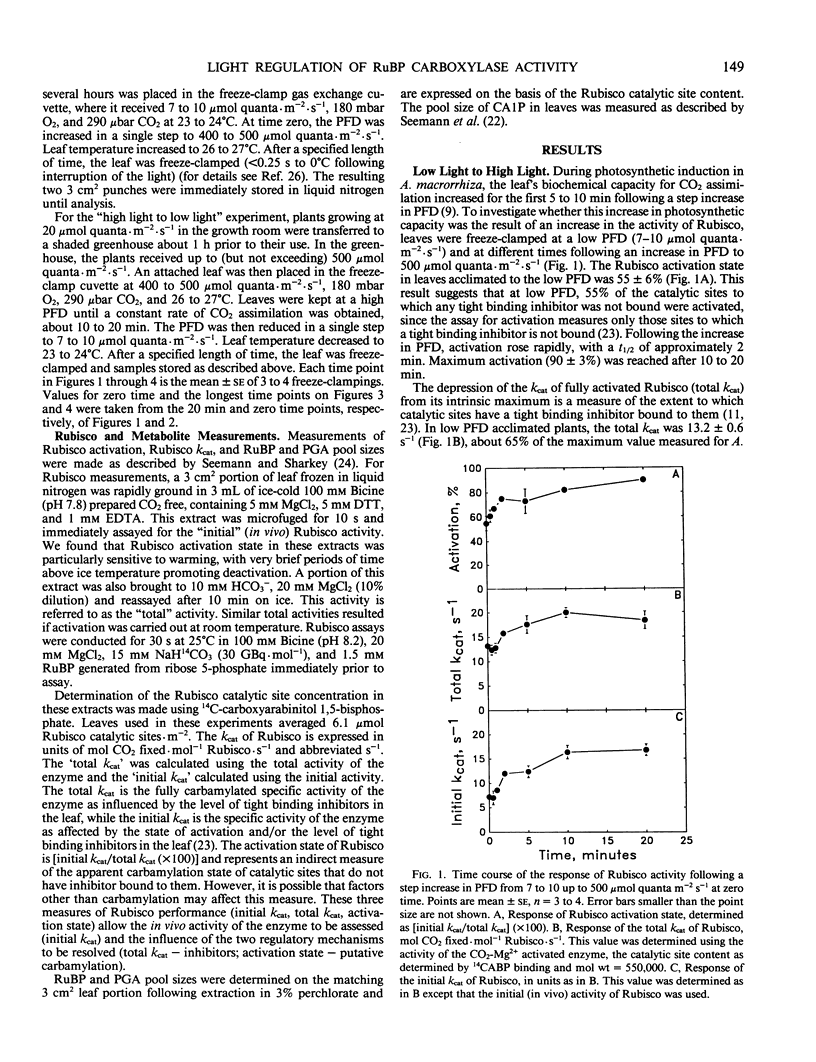
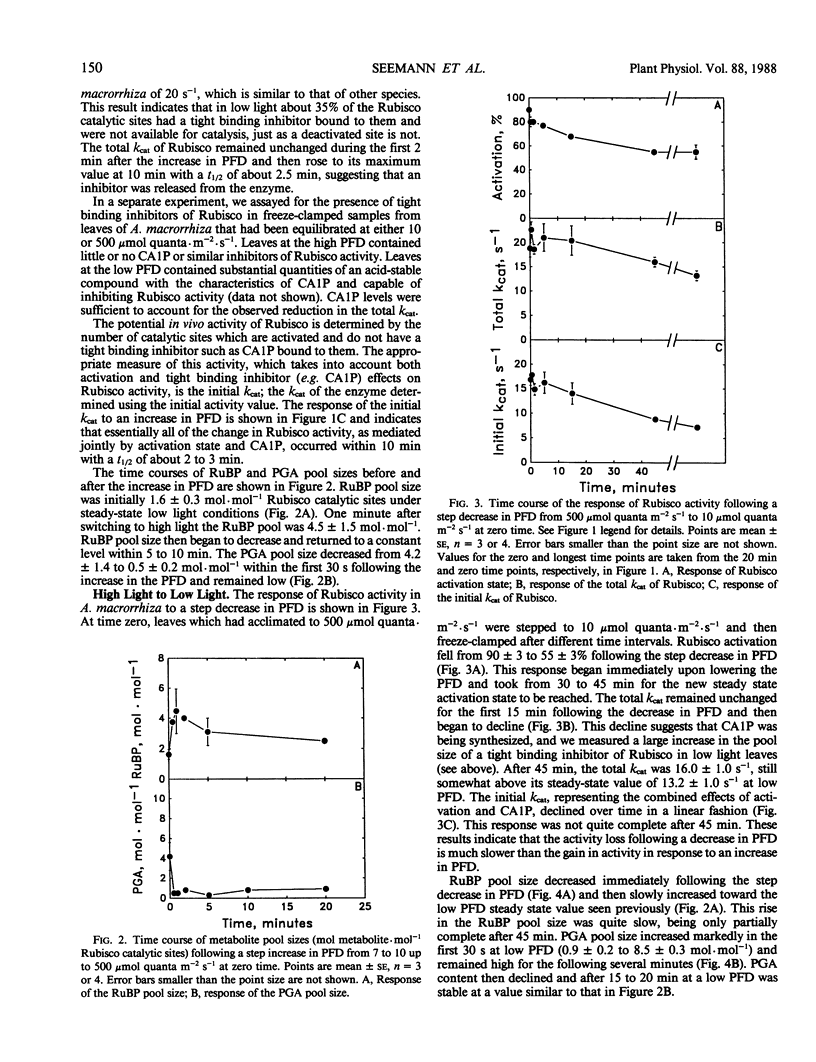
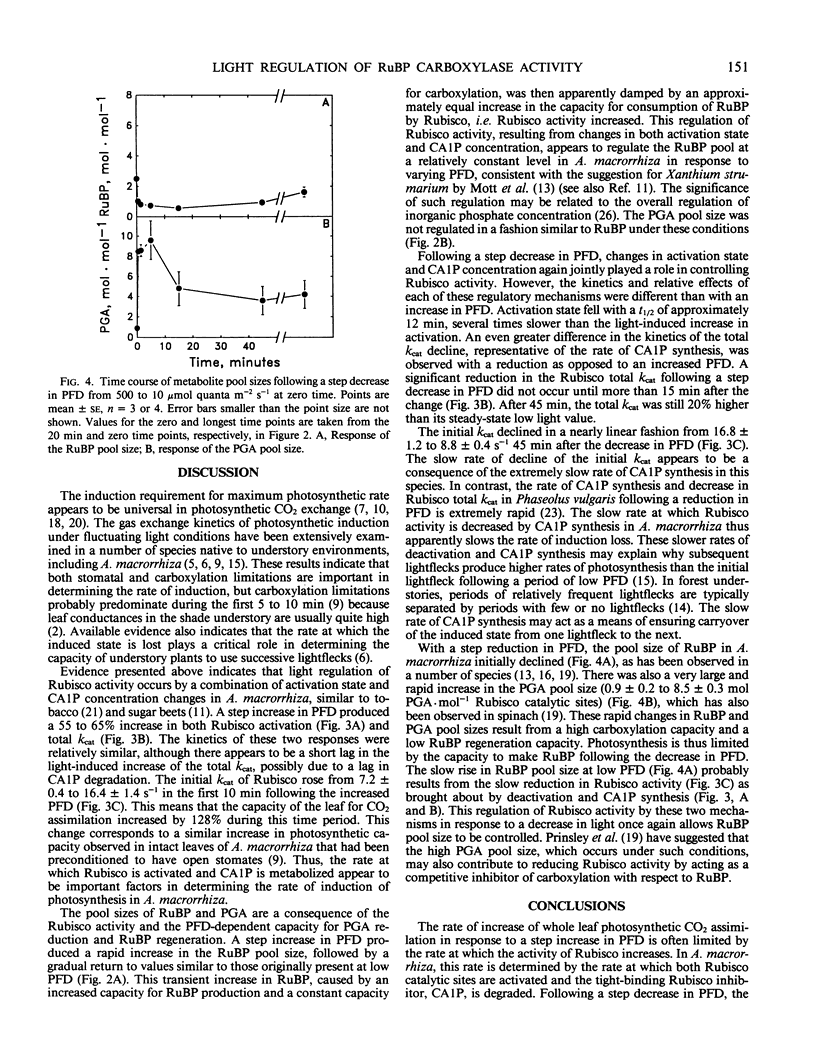
The regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase (Rubisco) activity and pool sizes of RuBP and P-glycerate were examined in the tropical understory species Alocasia macrorrhiza following step changes in photon flux density (PFD). Previous gas exchange analysis of this species following a step increase in PFD from 10 to 500 micromoles quanta per square meter per second suggested that the increase in photosynthetic rate was limited by the rate of increase of Rubisco activity for the first 5 to 10 minutes. We demonstrate here that the increase in photosynthetic rate was correlated with an increase in both the activation state of Rubisco and the total kcat (fully activated specific activity) of the enzyme. Evidence presented here suggests that a change in the pool size of the naturally occurring tight binding inhibitor of Rubisco activity, 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate, was responsible for the PFD-dependent change in the total kcat of the enzyme. RuBP pool size transiently increased after the increase in PFD, indicating that photosynthesis was limited by the capacity for carboxylation. After 5 to 10 minutes, RuBP pool size was again similar to the pool size at low PFD, presumably because of the increased activity of Rubisco. Following a step decrease in PFD from 500 to 10 micromoles quanta per square meter per second, Rubisco activity declined but at a much slower rate than it had increased in response to a step increase in PFD. This slower rate of activity decline than increase was apparently due to the slower rate of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate synthesis than degradation and, to a lesser degree, to slower deactivation than activation. RuBP pool size initially declined following the decrease in PFD, indicating that RuBP regeneration was limiting photosynthesis. As Rubisco activity decreased, RuBP slowly increased to its original level at high PFD. The slow rate of activity loss by Rubisco in this species suggests a biochemical basis for the increased efficiency for CO2 assimilation of successive lightfleck use by species such as A. macrorrhiza.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. A., Lorimer G. H., Pierce J., Seemann J. R., Meek J., Freas S. Isolation, identification, and synthesis of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate, a diurnal regulator of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):734–738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum M. U., Pearcy R. W. Gas Exchange Analysis of the Relative Importance of Stomatal and Biochemical Factors in Photosynthetic Induction in Alocasia macrorrhiza. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):782–785. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobza J., Seemann J. R. Mechanisms for light-dependent regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity and photosynthesis in intact leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3815–3819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearcy R. W., Osteryoung K., Calkin H. W. Photosynthetic Responses to Dynamic Light Environments by Hawaiian Trees : Time Course of CO(2) Uptake and Carbon Gain during Sunflecks. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):896–902. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Salvucci M. E., Ogren W. L. Activation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase at Physiological CO(2) and Ribulosebisphosphate Concentrations by Rubisco Activase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):967–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Anderson J. C. Factors affecting the activation state and the level of total activity of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in tobacco protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):66–71. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Berry J. A., Freas S. M., Krump M. A. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Sharkey T. D. Salinity and Nitrogen Effects on Photosynthesis, Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Metabolite Pool Sizes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Oct;82(2):555–560. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C. Binding of a Phosphorylated Inhibitor to Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase during the Night. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):839–843. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Seemann J. R., Berry J. A. Regulation of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity in Response to Changing Partial Pressure of O(2) and Light in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):788–791. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Seemann J. R., Pearcy R. W. Contribution of Metabolites of Photosynthesis to Postillumination CO(2) Assimilation in Response to Lightflects. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):1063–1068. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


