Abstract
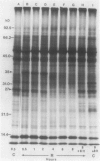
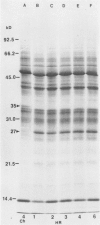
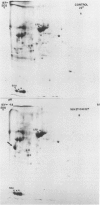
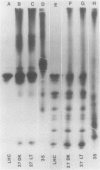
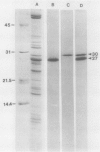
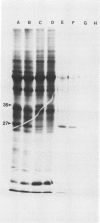
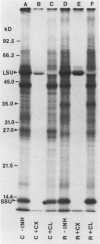
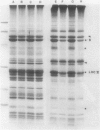
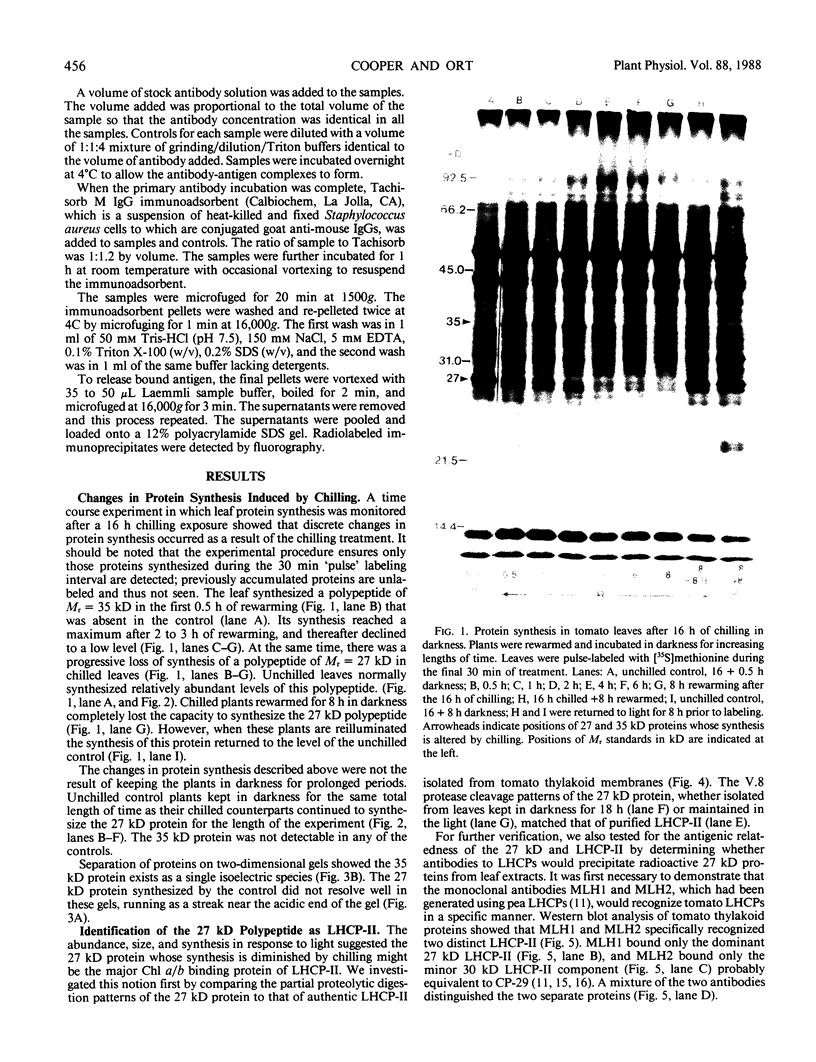
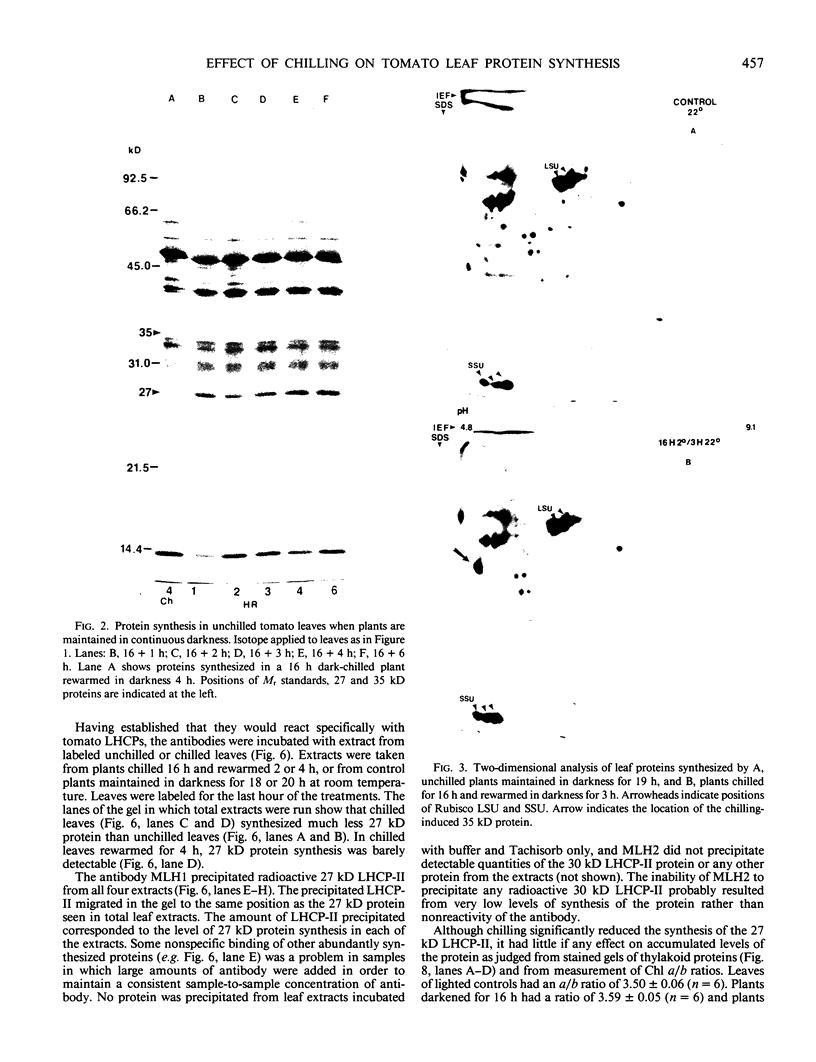
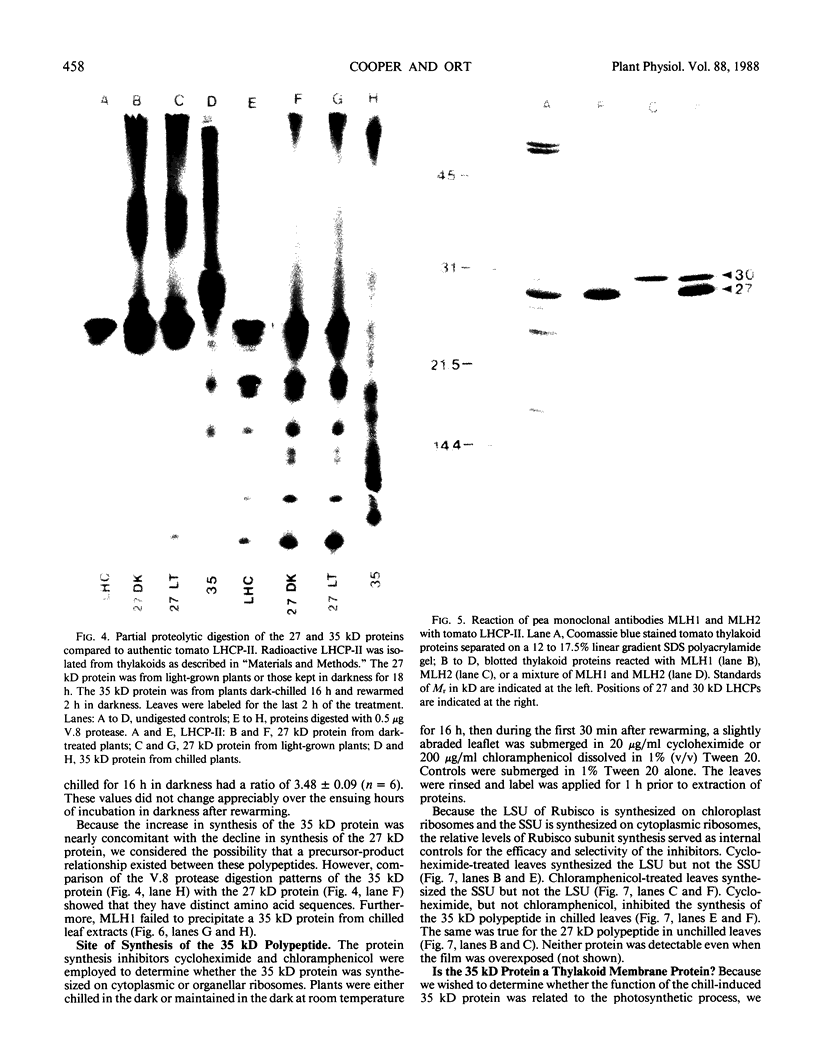
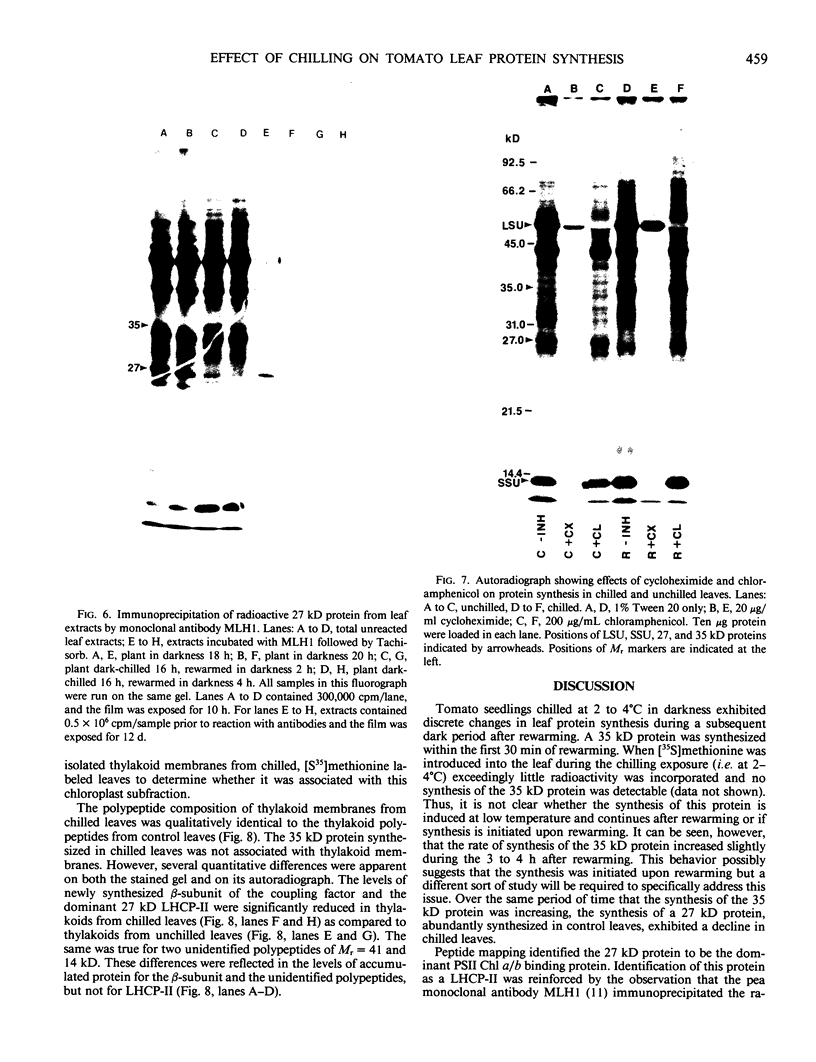
Impaired chloroplast function is responsible for nearly two-thirds of the inhibition of net photosynthesis caused by dark chilling in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Yet the plant can eventually recover full photosynthetic capacity if it is rewarmed in darkness at high relative humidity. As a means of identifying potential sites of chilling injury in tomato, we monitored leaf protein synthesis in chilled plants during this rewarming recovery phase, since changes in the synthesis of certain proteins might be indicative of damaged processes in need of repair. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins pulse labeled with [35S]methionine revealed discrete changes in the pattern of protein synthesis as a result of chilling. A protein of Mr = 27 kilodaltons (kD), abundantly synthesized by unchilled plants, declined to undetectable levels in chilled plants. Reillumination restored the synthesis of this protein in plants rewarmed for 8 hours. Peptide mapping analysis showed the 27 kD protein to be the major chlorophyll a/b binding protein of the photosystem II light-harvesting complex (LHCP-II). The identity of this protein was confirmed by its immunoprecipitation from leaf extracts by a monoclonal antibody specific for the major LHCP-II species. While chilling abolished the synthesis of the major LHCP-II species, it also induced the synthesis of an entirely new protein of Mr = 35 kD. The protein was synthesized on cytoplasmic ribosomes, and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophroesis showed it to exist as a single isoelectric species. This chilling-induced 35 kD protein is structurally distinct from the 27 kD LHCP-II and appears to be synthesized specifically in response to low temperature. While the 35 kD protein was found not to be associated with the chloroplast thylakoid membrane, chilling did cause selective changes in thylakoid membrane protein synthesis. The synthesis of two unidentified proteins, Mr = 14 and 41 kD, and the β-subunit of the chloroplast coupling factor were substantially reduced after chilling. These losses may provide clues as to the causes of the overall reduction in net photosynthesis caused by chilling.
Full text
PDF

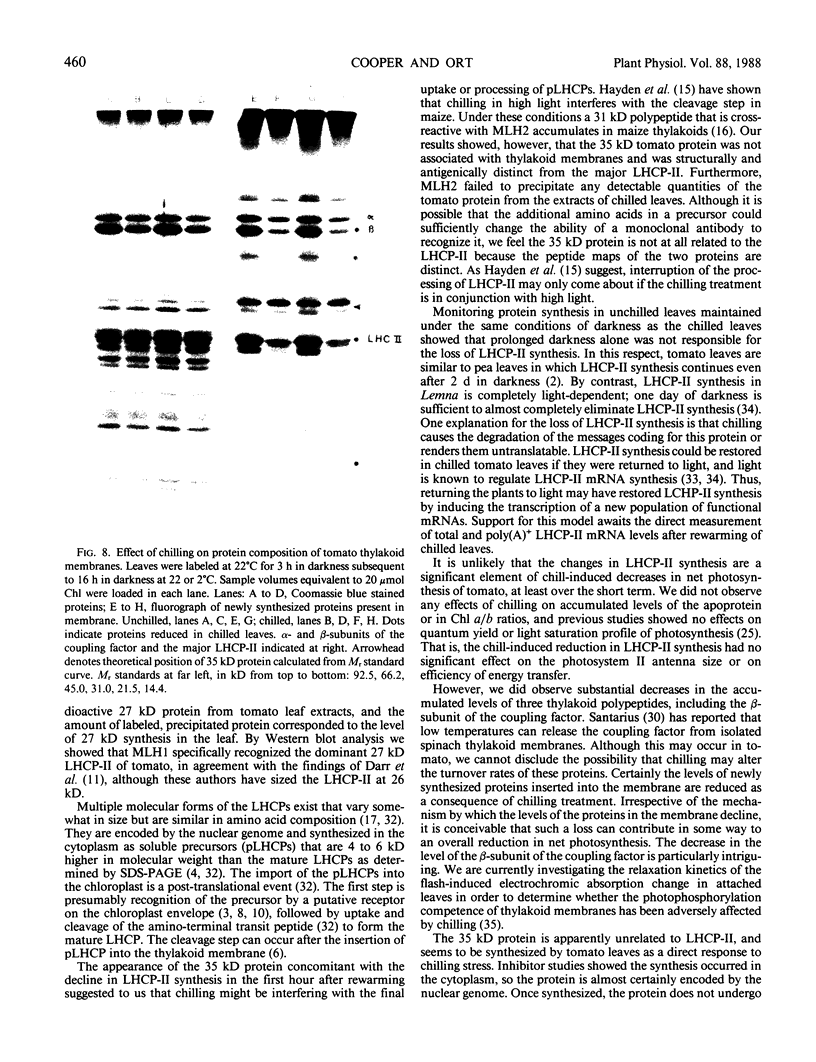

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. Biosynthesis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Polypeptide turnover in darkness. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):61–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broglie R., Bellemare G., Bartlett S. G., Chua N. H., Cashmore A. R. Cloned DNA sequences complementary to mRNAs encoding precursors to the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and a chlorophyll a/b binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7304–7308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis P. R., Harel E., Kohorn B. D., Tobin E. M., Thornber J. P. Assembly of the precursor and processed light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of Lemna into the light-harvesting complex II of barley etiochloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):982–988. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Lubben T. H., Keegstra K. Precursors to two nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins bind to the outer envelope membrane before being imported into chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3691–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):215–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell K. L., Keegstra K. Evidence that a Chloroplast Surface Protein Is Associated with a Specific Binding Site for the Precursor to the Small Subunit of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Nov;85(3):780–785. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.3.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darr S. C., Somerville S. C., Arntzen C. J. Monoclonal antibodies to the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex of photosystem II. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):733–740. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson M. C., Alfinito S. H. Proteins Produced during Salt Stress in Tobacco Cell Culture. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):506–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graan T., Ort D. R. Quantitation of the rapid electron donors to P700, the functional plastoquinone pool, and the ratio of the photosystems in spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14003–14010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. L., Niemi K. J., Brambl R. Altered gene expression during cold acclimation of spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Millington R. H., D'Angelo L. P. Structural similarities between the major polypeptides of thylakoid membranes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jun;202(1):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen G., Thach R. E. Inhibition of host translation in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected L cells: a novel mechanism. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.250-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanabus J., Pikaard C. S., Cherry J. H. Heat Shock Proteins in Tobacco Cell Suspension during Growth Cycle. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):639–644. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Freeling M. Anaerobic expression of maize fructose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14180–14183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B., Ort D. R., Boyer J. S. Impairment of photosynthesis by chilling-temperatures in tomato. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):329–334. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B., Ort D. R. Insensitivity of Water-Oxidation and Photosystem II Activity in Tomato to Chilling Temperatures. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):689–694. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Bartlett S. G., Grossman A. R., Cashmore A. R., Chua N. H. Biosynthetic pathways of two polypeptide subunits of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):468–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Tobin E. M. Demonstration of transcriptional regulation of specific genes by phytochrome action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin E. M. White Light Effects on the mRNA for the Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll a/b-Protein in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jun;67(6):1078–1083. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.6.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurfluh L. L., Guilfoyle T. J. Auxin-induced changes in the population of translatable messenger RNA in elongating sections of soybean hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):332–337. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]