Abstract
Mosaicism refers to the presence of two or more populations of genetically distinct cells within an individual, all of which originate from a single zygote. Previous literature estimated the percentage of parental mosaicism ranged from 0.33 to 25.9%. In this study, parents whose children had previously been diagnosed with developmental disorders with an apparent de novo variant were recruited. Peripheral blood, buccal and semen samples were collected from these parents if available for the detection of potential parental mosaicism using droplet digital PCR, complemented with the method of blocker displacement amplification. Among the 20 families being analyzed, we report four families with parental mosaicism (4/20, 20%). Two families have maternal gonosomal mosaicism (EYA1 and EBF3) and one family has paternal gonadal mosaicism (CHD7) with a pathogenic/ likely pathogenic variant. One family has a paternal gonosomal mosaicism with a variant of uncertain significance (FLNC) with high clinical relevance. The detectable variant allele frequency in our cohort ranged from 8.7–35.9%, limit of detection 0.08–0.16% based on our in-house EBF3 assay. Detecting parental mosaicism not only informs family with a more accurate recurrence risk, but also facilitates medical teams to create appropriate plans for pregnancy and delivery, offering the most suitable care.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s40246-023-00535-y.
Keywords: Parental mosaicism, Gonadal mosaicism, Gonosomal mosaicism, De novo mutation, Recurrence risk, Droplet digital PCR
Introduction
Mosaicism refers to the presence of two or more genetically distinct cell populations within an individual, all derived from a single fertilized egg [1]. These cell populations arise from de novo variants (DNVs) that may occur at any developmental stage. Depending on the specific timing of such event, the level and location of mosaicism may be different. Mosaicism can be broadly classified as solely somatic, solely gonadal or gonosomal mosaicism [2]. Mosaicism is commonly found at a variety of levels with variant allele frequencies (VAF) of as low as 0.5% to 3% depending on the detection methods [3, 4]. Traditional Sanger sequencing can only detect mosaicism with a detection limit of 15–20% [5]. The common trio next generation sequencing (NGS) using blood may not be able to distinguish somatic mosaic mutation from gonosomal mosaic mutation, unless multiple sample types such as semen are being tested [6], or inferred from family history due to recurrence of disease. In both gonosomal and gonadal mosaicism, either parent could carry the DNV without any manifestation with the potential to be transmitted to the offspring. It is undetectable or barely detectable in routine genetic tests using blood.
Previous studies estimated the de novo mutation rate for single nucleotide variants (SNVs)/small indels to be approximately 1–1.8 × 10−8 per base pair per gamate generation. Therefore, the number of DNVs correlates with parental age at conception, increasing by 1–3 DNVs for every one year increase in age for father and 0.24 DNVs for mother [7]. The disparity primarily stems from the physiological process of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. In females, primordial germ cells (PGCs) arrest in the prophase of meiosis-I and only undergo one additional round of DNA replication during meiosis-II to mature into an ovum. By contrast, male spermatogonial stem cells undergo mitosis every 16 days. Thus, by age 20, a male would have experienced around 190 mitoses, and by age 40, around 660 mitoses. Each replication harbors the potential for incidental copying errors. Hence, approximately 80% of DNVs exhibit what is known as the paternal age effect (PAE) [8]. Although the effect is less severe than paternal age, advanced maternal age also presents a positive correlation with an increased number of apparent DNVs in offspring. Besides, aging oocytes are postulated to accumulate DNVs through alternate mechanism including meiotic gene conversions, crossovers or deficiency in double strand-breaks repair [6, 9].
A specific group of DNVs expand exponentially at significantly higher rates than other DNVs [10, 11]. These highly specific DNVs are observed in genes involved in the RAS-MAPK pathway, which controls cell growth. The mechanism is known as “selfish spermatogonial selection” [10], resulting in a higher risk of sporadic PAE disorders in the offspring of older fathers. Examples of recognized PAE disorders include Apert syndrome (FGFR2), Achondroplasia/ Thanatophoric dysplasia (FGFR3), Costello syndrome (HRAS), Endocrine neoplasia (RET) and Noonan syndrome (PTPN11) [11]. In addition to the classic PAE genes, there are candidate PAE genes which do not fully satisfy the PAE criteria (e.g., not involved in the RAS pathway) but may still exhibit some PAE features, such as CHD7 (CHARGE syndrome).
Parental mosaicism increases recurrence risk, and the actual risk depends on the level of parental mosaicism. In some cases, concealed parental mosaicism could be misinterpreted as a DNVs arising in the child. Such misinterpretations could obstruct the accurate estimation of recurrence risk, thereby limiting the options for prenatal or preimplantation genetic testing for families contemplating another child. Despite having a great implication on family planning, particularly for severe diseases with high penetrance and limited medical intervention, current routine practices do not often offer robust detection of low-level parental mosaicism. A recurrence risk of 1% is therefore commonly used when counseling parents whose child is carrying a disease-causing DNV, which may not be always reflecting the truth due to the possibility of hidden low level parental mosaicism that is hindered by current detection limit in terms of sample source and method used.
Previous studies indicated the possibilities of low-level parental mosaicism in transmitting disease-causing variants to the offspring. Although an extensive review by Hancarova et al. [12] reported parental mosaicism from nearly 400 publications in a wide spectrum of diseases, majority of these studies utilized routinely collected samples such as peripheral blood. Zemet et al. [13] in a recent review suggested semen sample may help further stratifying variant with low- or high-risk of recurrence. Indeed, when using semen as the sample type, Bruess et al. [14] in a cohort of patients with Autism Spectrum Disease (ASD) and Frisk et al. [15] in a cohort of patients with intellectual disability (ID) revealed a parental mosaicism diagnostic rate of 21% and 4%, respectively. However, the detection of parental mosaicism using semen samples in other diseases categories remains scarce. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the percentage of parental mosaicism in a cohort of families with apparent DNVs associated with developmental disorders by analyzing the parental blood, semen/or buccal samples with droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) as the main detection method. We also determined the usefulness of parental mosaicism detection to the genetic counseling and management of patients and their families.
Methods
Patient recruitment
Parents of children who had previously received diagnoses of developmental disorders with apparent DNVs identified by trio sequencing using peripheral blood between September 2010 and June 2022 were recruited according to previous sequencing results. There were initially 93 families referred from the clinical genetics service at the Queen Mary Hospital and the Hong Kong Children's Hospital (the University of Hong Kong affiliated hospitals). After that, 42 families were selected according to the following inclusion criteria: i) the apparent DNV is of SNV type or small (< 20 bp) indels, and ii) parents were able to provide freshly obtained buccal and/or semen samples. Invitations were sent to these 42 families, 20 agreed to participate and provided samples. Majority of families (18/20, 90%) were first diagnosed by trio exome sequencing (ES), while 10% (2/20) of families were first diagnosed by trio NGS panel testing. Variant interpretation was based on the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) Variant Interpretation Guidelines [16]. The most frequent type of variant is missense (n = 10, 50%), followed by nonsense (n = 4, 20%), frameshift (n = 4, 20%), splice (n = 2, 10%), and in frame deletion (n = 1, 5%). Three genes were located on chromosome X, while the rest of the genes were located on autosomes. The PAE/candidate PAE genes were CHD7, COL1A1, RAF1, PTPN11. The median maternal age at conception was 34.0 years old (range: 25–41) and the median paternal age at conception was 35.5 years old (range: 28 to 44). Semen samples were collected from 18 fathers, and buccal swabs were collected from both mothers (n = 8) and fathers (n = 17) whenever possible. Written informed consent was obtained from these parents who agreed to participate. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong/Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster. (UW 12–211). Figure 1 shows the flowchart for patient recruitment and Additional file 1: table S1 lists the apparent de novo variants for all families in this study.
Fig. 1.
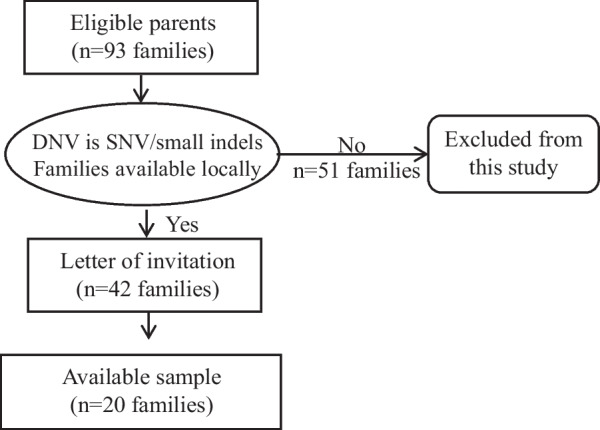
Flowchart for patient recruitment. The diagram shows the recruitment workflow. A total of 20 families are being recruited
Genomic DNA extraction from buccal mucosa and sperm
Genomic DNA was extracted from buccal mucosa within 24 h of collection using Gentra Puregene Buccal Cell Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Semen samples were also processed within 24 h using the Qiagen QIAamp® DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instruction with overnight incubation to lyse the sperm cells completely. Quantity and quality of the extracted DNA was measured by the Qubit 3.0 Fluorometer (Thermofisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA) and Nanodrop (Thermofisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA).
Sanger sequencing
DNA from buccal mucosa and semen samples was subjected to Sanger sequencing to screen for possible tissue specific mosaic variants. PCR was performed using Qiagen HotStarTaq Plus Master Mix Kit (Qiagen, Hilden,Germany) according to manufacturer instruction. Sanger sequencing was performed at the Center of PanorOmic Sciences (CPOS), The University of Hong Kong.
Blocker displacement amplification (BDA)/BDA quantitative PCR
BDA was performed for 18 families. Additional file 2: Table S2 lists all the primer pairs and blockers sequences for BDA. Primers to probe ratio were adjusted accordingly case by case during optimization. Parental samples were tested with blocker, while patient samples were tested with blocker and without blocker (with forward and reverse primers only) as the experimental control. Amplified products were Sanger sequenced for verification. BDA-qPCR was performed for Family 14. The reaction mixture contained 10X PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), 400 nM of each primer, an optimized amount of blocker and DNA per well. Final volume of 10uL/reaction was loaded on the 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Each reaction was repeated at least twice. Calculations were based on the previous studies by Karolak et al. [17] and Wu et al. [18]. Briefly, change in quantification cycle (∆Cq) values were calculated for each sample using Cq values obtained in both experiments (with and without blocker), i.e., ∆Cq sample = Cq sample (with blocker) − Cq sample (without blocker). VAF were then calculated using the following formula:
ddPCR technology
A custom TaqMan assay (with primers and probe at 40X concentration) was designed and ordered from ThermoFisher Scientific (Massachusetts, USA) for each individual case (Additional file 3: Table S3), where the reference and variant alleles were labeled as FAM or VIC, respectively. One µl of the above 20 × custom TaqMan assay was mixed with 10 µL of 2 × QX200 ddPCR Probe supermix (no dUTP) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Munich, Germany), together with 8.25 µl of genomic DNA at ≥ 20 ng/µl and 0.25µL (5U) of digesting enzyme. At least 250 ng of parental samples was used to maximize the chances for low-level mosaicism (< 0.01%) detection as per manufacturer’s guidelines. This 20 µl of ddPCR reaction mixture was then loaded on to the BioRad QX200 ddPCR system according to the manufacturers’ instruction and the analysis was performed as described by Hindson et al [19]. The ddPCR data were analyzed with the QuantaSoft™ analysis software version Pro 1.0.596 (Bio-Rad). Samples with total droplets count of > 8000 were used for subsequent analysis.
Results
Percentage of parental mosaicism
Among the 20 families, four families have parental mosaicism (4/20, 20%), in which two families have maternal gonosomal mosaicism (2/20, 10%), one family has paternal gonadal mosaicism (1/20, 5%). The maternal mosaicism in family 17 is a nonsense variant NM_000503.6:c.1081C > T p.(Arg361Ter) in EYA1, which has been previously reported [20]. The other maternal mosaic variant is a missense NM_001005463.3:c.488G > A p.(Arg163Gln) variant in the EBF3 gene. The father in family 14 has a mosaic paternal splice variant in CHD7 (NM_107780.3:c.7164 + 1G > A). In addition to the three families with parental mosaicism of pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants, the father in family 15 has a mosaic missense variant of uncertain significance (VUS) with high clinical relevance [NM_001458.4:c.4916G > A(p.Cys1639Tyr)] in the FLNC gene. Table 1 lists all the pathogenic/likely pathogenic/VUS parental mosaicism included in this study.
Table 1.
Details of all four families with parental mosaicism (pathogenic/likely pathogenic/variant of uncertain significance) in this study
| Family | Gene | Origin | Sample Type | Variant detected by trio ES with peripheral blood | Variant detected by Sanger | Variant detected by BDA/BDA-qPCR | Variant detected by dPCR/ddPCR | Type of Mosaicism | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference count | Variant count | Total count | VAF (%) | Enriched | VAF (%) | Total chambers/droplets | VAF (%) | ||||||
| 14 | CHD7 | Maternal | Blood | Unknown (ES by third party) | No | No | Not tested | Not tested | Paternal gonadal mosaicism | ||||
| Buccal | Not tested | No | No | Not tested | 10,286 | < 0.01 | |||||||
| Paternal | Blood | Unknown (ES by third party) | No | No | Not tested | 14,649 | < 0.01 | ||||||
| Buccal | Not tested | No | No | Not tested | 14,446 | < 0.01 | |||||||
| Semen | Not tested | Yes | Yes | Not tested | 41,644 | 13.9 | |||||||
| 15 | FLNC | Maternal | Blood | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0.0 | No | No | < 0.1 | 16,628 | < 0.01 | Paternal gonosomal mosaicism |
| Buccal | Not tested | No | No | Not tested | 17,538 | < 0.01 | |||||||
| Paternal | Blood | 8 | 2 | 10 | 20.0 | Yes | Yes | 12.7 | 17,905 | 22.2 | |||
| Buccal | Not tested | Yes | Yes | 8.7 | 36,218 | 21.3 | |||||||
| Semen | Not tested | Yes | Yes | 22.7 | 17,510 | 35.9 | |||||||
| 17 | #EYA1 | Maternal | Blood | 24 | 4 | 28 | 14.3 | Yes | Not tested | Not tested | 17,284 | 21.7 | Maternal gonosomal mosaicism |
| Paternal | Blood | 17 | 0 | 17 | 0.0 | No | Not tested | ||||||
| 18 | EBF3 | Maternal | Blood | 117 | 17 | 134 | 12.7 | Yes | Not tested | Not tested | 10,203 | 18.4 | Maternal gonosomal mosaicism |
| Buccal | Not tested | Yes | 12,506 | 29.6 | |||||||||
| Paternal | Blood | 107 | 0 | 107 | 0.0 | No | Not tested | ||||||
#Previously reported family. VAF: Variant allele frequency; BDA: blocker displacement amplification; ES: exome sequencing; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; dPCR: digital PCR; ddPCR: droplet dPCR
Families with parental mosaicism
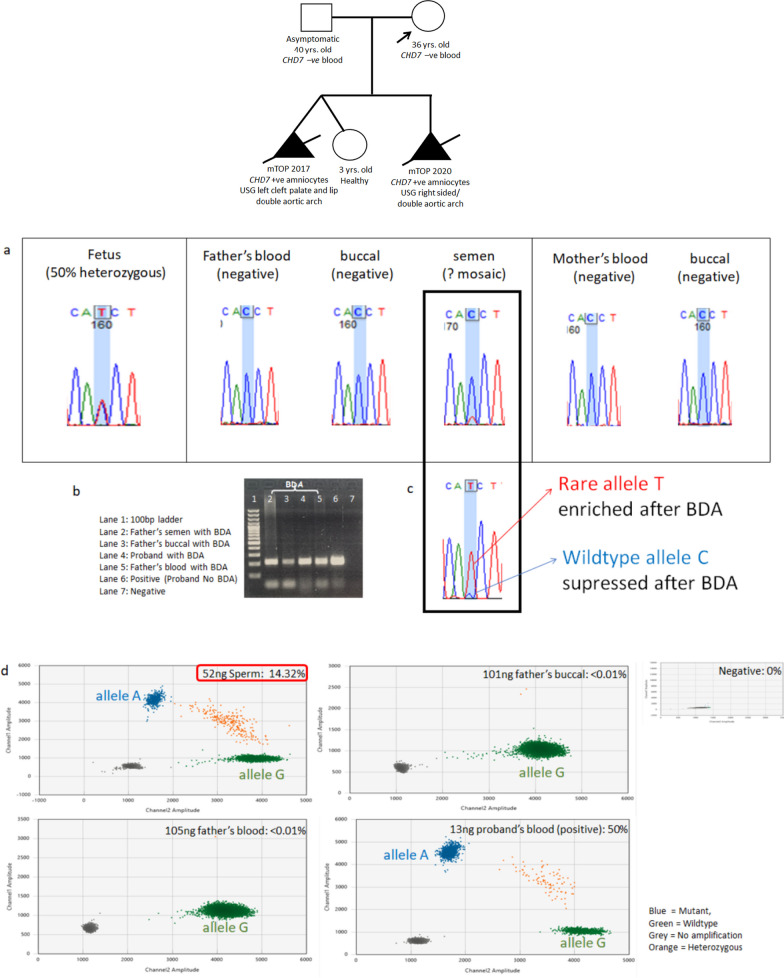
Paternal mosaicism 1: Family 14 with paternal gonosomal mosaicism in CHD7
Family 14 is previously reported by our team for another RNA study [21] (Fig. 2). Though the variant was not detected in parental blood and buccal cells via Sanger sequencing, a potential mosaic variant was suspected in the father’s semen DNA. With blocker displacement amplification, the rare allele T is enriched and the wildtype allele C is suppressed. DdPCR corroborated the results obtained from Sanger sequencing and BDA, identifying 14.32% of the rare allele in the father’s semen DNA. The detection is highly precise as demonstrated by our three internal serial dilutions with a total input of 52 ng, 26 ng and 13 ng of the same sperm sample, the detectable VAF ranges from 13.6%-14.3% (CV = 0.13 and SD = 0.36).
Fig. 2.
Sanger sequencing and ddPCR results for family 14 with paternal mosaic CHD7 variant. a Sanger sequencing showed ambiguous small peak for father’s semen at variant position (black rectangle in bold). b Gel electrophoresis with and without BDA. Noted bands with BDA are lighter than that without BDA, demonstrating the suppression of wildtype allele. c Sanger sequencing confirmed rare allele T enriched after BDA. d DdPCR confirmed paternal gonadal mosaicism with a VAF of 14.32%
This confirms the presence of paternal gonadal mosaicism. CHD7 is a candidate PAE gene with a prevalence of 1/12–15,000 [22]. The detected paternal mosaicism signifies that this family’s risk of recurrence is considerablyhigher than the general prevalence. This is also reflected by the recurrent mutation found in the two affected siblings. Therefore, options such as preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disease (PGT-M) and prenatal diagnosis for future pregnancy would be beneficial for this family.
Paternal mosaicism 2: family 15 with paternal gonosomal mosaicism in FLNC (VUS with high clinical relevant)
Family 15 is a non-consanguineous Chinese family. The first child was presented with restrictive cardiomyopathy and a dilated left atrium at 23 months old. He had a deceased younger brother who passed away at 7 months old due to idiopathic restrictive cardiomyopathy. Trio WES using parental blood revealed a VUS in FLNC (NM_001458.4:c.4916G > A p.(Cys1639Tyr)), which is suspected to be a paternally inherited mosaic variant due to low coverage with 6 reference reads and two variant reads at 25% VAF. FLNC is associated with restrictive cardiomyopathy (MIM: 617,047) which aligns well with the phenotype observed in our patient. The variant is absent in control population (gnomAD v 2.1.1) and software prediction indicates a damaging effect on this variant. Segregation analysis using Sanger sequencing revealed the same variant in the younger brother, which warranted further investigation.
Using Sanger sequencing, BDA-qPCR and ddPCR, we confirmed an average of 29.3% of the rare allele in the father’s semen DNA, and an average of 17.5% and 15.1% of the rare allele in the father’s blood and buccal sample, respectively, which confirmed paternal gonosomal mosaicism (Fig. 3). Should there be functional evidence of the pathogenicity of the FLNC variant, cardiac screening might be necessary for the father. As risk of recurrence may be as high as 29.3%, the option of PGT-M and prenatal diagnosis for future pregnancy would be helpful for the family.
Fig. 3.
ES, Sanger sequencing, BDA and ddPCR results for family 15 with a paternal mosaic FLNC variant. a ES showing low coverage at variant position by. b Sanger sequencing showing ambiguous small peak for father’s blood, buccal and semen at variant position (highlighted in blue). c Gel electrophoresis with and without BDA. Noted bands with BDA are lighter than that without BDA, demonstrating the suppression of wildtype allele. d Sanger sequencing confirmed rare allele T enriched after BDA. e BDA-qPCR showing VAF of father’s sperm, buccal and blood at 22.7%, 8.7% and 12.7%, respectively. f DdPCR confirmed paternal gonosomal mosaicism with VAF of father’s sperm, buccal and blood at 35.9%, 21.4% and 22.2%, respectively
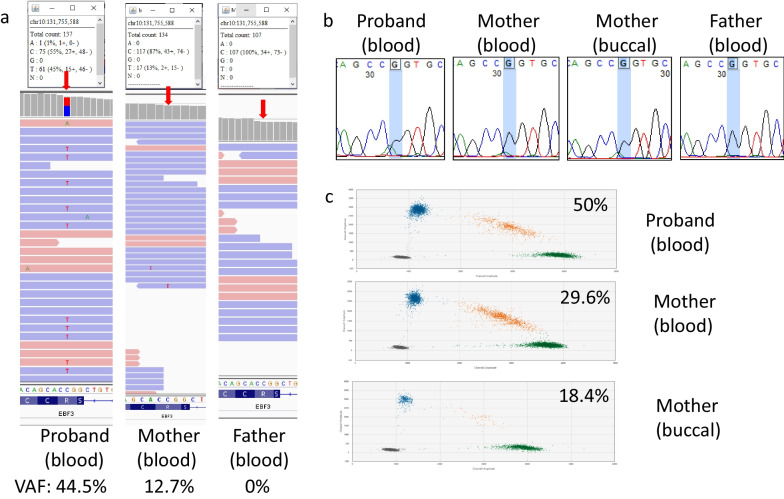
Maternal mosaicism: family 18 with maternal gonosomal mosaicism in EBF3
A 15-year-old Nepalese girl was found to have paraplegia, ataxia and strabismus since birth. She also experienced neurogenic bladder with reflux nephropathy which required intermittent catheterization since age of six. At age 13, she was diagnosed with end stage renal disease and started on hemodialysis. She was referred to our genetic clinic from nephrology due to sudden onset of seizure. Previous trio ESusing peripheral blood revealed a pathogenic heterozygous EBF3 missense variant in NM_001005463:c.488G > A p.(Arg163Gln), associated with hypotonia, ataxia and delayed development syndrome (MIM: 617,330). The variant is suspected to be inherited from her unaffected mother in a mosaic form as the VAF is skewed at 12.7% with 117 of the reference reads and 17 reads with the variant. Buccal mucosa was then collected for further investigation. Sanger results on both blood and buccal sample showed ambiguous small peak at the variant position, and ddPCR confirmed maternal gonosomal mosaicism with 29.6% of the variant allele detected in buccal and 18.4% of the variant allele detected in blood (Fig. 4). The maternal mosaicism indicated that an increase in risk of recurrence for this family, so, PGT-M and prenatal diagnosis is useful for this family.
Fig. 4.
ES, Sanger and ddPCR results for family 18 with maternal mosaic EBF3 variant. a IGV showing location of the EBF3 variant in NM_001005463:c.488G > A p.(Arg163Gln) with a red arrow. Maternal mosaicism was initially suspected. b Sanger sequencing showed ambiguous small peak for mother at variant position (highlighted in blue). c DdPCR confirmed maternal gonosomal mosaicism with 29.6% of the variant allele detected in the buccal sample and 18.4% of the variant allele detected in blood
In-house ddPCR limit of detection (LOD) was determined using the EBF3 assay, in which the detected VAF were comparable with the expected VAF when VAF was expected to be 0.08–0.16% (Figure S2). Theoretically LOD should be systemically determined on per assay based; however, with limited resources and control DNA, EBF3 assay was used and results were comparable with manufacturer’s guideline and other similar studies [19, 23, 24].
Discussion
This study investigated parental mosaicism in 20 families, in which the children had been previously diagnosed with developmental disorders with apparent de novo variants identified through trio sequencing. Utilizing family history, additional biological samples including buccal mucosa and semen samples, coupled with sensitive technologies including ddPCR and BDA, we illustrated that 20% (4/20) of the families have parental mosaic variants which is previously regarded as DNVs in the patients.
Cohort characteristics
The median maternal age at conception in our cohort was 34.0 years, ranging from 25–41 years of age. Excluding the three families without an affected first child, the median maternal age at first childbirth for our cohort was 34.4 years old (ranging from 26–40 years old), slightly higher than the data reported by the Census and Statistics Department Hong Kong in 2021 [25], where the maternal median age at first childbirth was 32.6 years. The median paternal age at first childbirth for our cohort is 36.0 years old (ranging from 29–44 years old). There was a lack of Census data for paternal median age at first childbirth for a similar comparison, highlighting that discussions regarding parental age at childbirth tend to focus predominantly on females, despite the significant role of paternal age [22]. According to Census data [25], both the median age at first marriage for female and male has been steadily increasing, from 27.5 and 30.2, respectively, in 2001 to 30.6 and 32.2, respectively, in 2021, which can be inferred that maternal and paternal age at first childbirth may also be on a steady increase. While our current societal focus revolves around maternal age as a public health concern, it is equally important to educate the public about the potential risk of advanced paternal age and the burdens it may bring.
Percentage of parental mosaicism and clinical implications
Despite the significant differences in inclusion criteria, detection methods and sample types used, the diagnostic yield of 4/20 (20%) disease-causing parental mosaicism found in our cohort with diverse Mendelian diseases was comparable with previous studies, where parental mosaicism were found between 0.3%-26.5% [4, 26, 27] in cohorts that focused on similar diverse Mendelian disease. Among the families with detected parental mosaicism, half had two affected siblings. This suggests that parental mosaicism should be strongly considered in families where the disease recurs. Moreover, our data suggest that the empirical VAF obtained from laboratory tests may further help predict recurrence risk. A higher VAF in multiple tissues indicates an earlier occurrence during embryonic development leading to a higher recurrence risk. This is exemplified in family15 with paternal gonosomal mosaicism, in which both affected offspring inherited the FLNC variant from the father. We identified the paternal mosaic variant in tissues representing ectoderm (buccal), intermediate mesoderm (sperm) and mesoderm (blood). The average VAF in sperm was higher (29.3%) compared to blood and buccal samples (average VAF of 14.5% and 15.0%, respectively). These results imply that low level parental mosaicism is prone to be missed if only blood or buccal samples are tested.
The mutational event in family 14 with the paternal gonadal CHD7 variant would have occurred later after differentiation of PGCs since the mosaic variant is confined in the semen at 13.9% and not found in blood and buccal. The recurrence risk in this family appears to be smaller than that of family 15, as demonstrated by the presence of two affected and one healthy offspring. However, as CHD7 is a candidate PAE gene associated with proliferation advantages; the recurrence risk may increase with the father’s age. Although Pauli et al. [28] did not find any PAE in their cohort of affected children carrying CHD7 variants of paternal origin (n = 12), earlier studies by Tellier et al [29] (n = 41) and Blake et al [30] (n = 39) suggested an association between CHD7 mutation and PAE.
Although PAE may increase the prevalence of paternal mosaicism, and previous studies report a ratio of paternal to maternal DNVs is at 4:1 [8, 31, 32], our observations confirm that maternal mosaicism still exist, as demonstrated by two families in our study. To increase the sample size, we reviewed parental mosaicism studies with more than ten families since 2009 (Table 2). Among those with a known positive parental mosaic variant affecting non-sex chromosome, the incidence of paternal mosaicism and maternal mosaicism were comparable at 59% (47/80) and 41% (33/80), respectively. On the other hand, X-linked recessive diseases (e.g., DMD) have a higher maternal mosaicism rate and it is not surprising because males are more likely to have an X-linked recessive diseases as their X-chromosome can only be inherited from their mother. Besides, X-linked dominant diseases seems to show a higher rate of paternal mosaicism (e.g., MECP2 and PCDH19 in Rett Syndrome and Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 9, respectively, as shown in Table 2), however, a more thorough literature search that includes all cases using an unbiased approach is required to confirm these preliminary findings.
Table 2.
Literature review on parental mosaicism since 2009 for cohort studies with more than 10 families
| Disease | Author | Year | Sample Size | Sample Type | Detection Method | Parental Mosaicism | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paternal | Maternal | Unknown | Total | Percentage | Detectable %VAF | ||||||
| AHC | Yang et al | 2019 | 80 families | Blood/Saliva/Buccal mucosa/Hair/Skin/Urine/Sperm | Deep sequencing/SS/mddPCR | 4 | 2 | 0 | 6/80 | 7.5% | 0.03–33.03% |
| Autism | Krupp et al | 2017 | 2264 families | Blood | ES | 63* | 49* | 0 | NA | 6.80% | 7.9–36.1% |
| Breuss et al | 2020 | 14 families | Sperm | GS | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3/14 | 21.43% | 0.6–14.5% | |
| Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy | Liu et al | 2019 | 22 families | Blood/Buccal mucosa/Hair/Nails/Urine | Targeted sequencing/SS/MLPA/mddPCR | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2/22 | 9.09% | 1.2–-37.38% |
| Diverse Mendelian Disease | Cao et al | 2019 | 12,000 samples (120 candidate parental mosaic variants) | Blood | ES/Deep sequencing/Sanger Sequencing | 14 | 25 | 1 | 40/12,000 | 0.33% | 3.1–67.8% |
| Gambin et al | 2020 | 2000 families (102 candidate parental mosaic variant) | Blood/Saliva/Buccal mucosa/Hair/Urine | ES/Deep sequencing/ddPCR/BDA | 0 | 0 | 27 | 27/102 | 26.47% | 0.3–18.2% | |
| Shu et al | 2021 | 237 families | Blood/Saliva/Buccal mucosa/Hair/Urine | Deep sequencing/ddPCR | 4 | 10 | 0 | NA | 3.00% | 0.22–34.0% | |
| This study | 2022 | 21 families | Blood/Buccal mucosa/Sperm | ES/SS/BDA/ddPCR | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4/21 | 19.00% | 8.7–35.9% | |
| DMD | Helderman-van den Enden et al | 2009 | 318 families | Blood | Haplotyping | 0 | 19 | 0 | 19/318 | 5.97% | NA |
| Zhong et al | 2019 | 74 families | Blood | Targeted sequencing/MLPA | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2/74 | 2.70% | NA | |
| Epilepsy | Depienne et al | 2010 | 177 families | Blood/Sperm | SS,QAS-PCR, haplotyping | 6 | 7 | 0 | 13/177 | 7.34% | 0.04–24% |
| Xu et al | 2015 | 174 families | Blood/Saliva/Buccal mucosa/Hair/Urine | Deep sequencing/SS/MLPA/dPCR | 13 | 7 | 0 | 20/174 | 11.49% | 1.1–32.6% | |
| Yang et al | 2017 | 112 families | Blood/Sperm | Deep sequencing/SS /MLPA/mddPCR | 18 | 11 | 0 | 29/112 | 25.89% | 0.01–39.04% | |
| Myers et al | 2018 | 120 families | Blood/Saliva | smMIP | 6 | 4 | 0 | 10/120 | 8.33% | 1.4–3.6% | |
| de Lange et al | 2019 | 80 families | Blood | Deep sequencing/ddPCR | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4/80 | 5.00% | 0.5–8.0% | |
| Rikke S Møller | 2019 | 75 families | Blood/Buccal mucosa/Urine | Gene panel sequencing | 4 | 1 | 0 | 5/75 | 6.67% | 0.8–29% | |
| Holoprosencephaly | Paulussen et al | 2010 | 86 families | Blood/Sperm | SS/haplotyping | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1/86 | 1.16% | NA |
| Hu et al | 2019 | 136 families | Blood | Targeted sequencing/ddPCR | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5/136 | 3.68% | 0.1–13% | |
| ID | Acuna-Hidalgo et al | 2017 | 50 families | Blood | GS | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4/50 | 8.00% | 0.22–6.15% |
| Wright et al | 2019 | 420 families | Blood/Saliva | ES/Deep sequencing | 13 | 8 | 0 | 21/420 | 0.50% | 0.5–33.0% | |
| Frisk et al | 2022 | 44 families | Blood/Sperm | ES/ddPCR | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2/44 | 4.55% | 1.1–20.24% | |
| Malformation of cortical development | Zillhardt et al | 2016 | 18 families | Blood | ES/ddPCR/SS | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4/18 | 22.22% | 4.31–4.57% |
| Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly | Huang et al | 2016 | 94 families | Blood | Sanger Sequencing/Haplotyping | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1/94 | 1.06% | NA |
| Marfan and Ehlers-Danlos syndromes | Chesneau et al | 2021 | 333 families | Blood | Targeted sequencing/SS/HRMA | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3/62 | 4.84% | 1.1–13.6% |
| MPSII | Alcantara-Ortigoza et al | 2016 | 25 families | Blood//Buccal mucosa/Hair/Urine | SS | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1/25 | 4.00% | NA |
| OI | Pyott et al | 2011 | 37 families | Blood | SS | 2 | 4 | 0 | 6/37 | 16.22% | NA |
| Shaheen et al | 2012 | 13 families | Blood | SS | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2/13 | 15.38% | NA | |
| PID | Mensa-Vilaro et al | 2019 | 92 families | Blood//Buccal mucosa/Hair/Urine/Sperm | Gene panel/SS | 1 | 5 | 1 | 7/92 | 7.61% | 2.7–21.2% |
| Rett syndrome | Zhang et al | 2018 | 21 families | Blood/Saliva/Sperm | ddPCR | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5/21 | 23.81% | 0.03–7.55% |
| X-linked ALD | Wang et al | 2011 | 489 families | Blood | SS | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4/489 | 0.82% | NA |
AHC: Alternating hemiplegia of childhood; ALD: adrenoleukodystrophy; ES: exome sequencing; VAF: Variant allele frequency; BDA: blocker displacement amplification; DMD: Duchenne muscular dystrophy; dPCR: digital polymerase chain reaction; ddPCR: droplet dPCR; HRMA: high-resolution melting analysis; mddPCR: micro ddPCR; MLPA: Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification; ID: intellectual disability; MPSII: Mucopolysaccharidosis type II; OI: Osteogenesis imperfecta; PID: Primary immunodeficiency diseases; SS: Sanger Sequencing. *Numbers extracted from best practice filter
Indeed, the most accurate method for detecting gonadal mosaicism should involve direct observation of germ cells. While sperm can be sued to detect paternal gonadal mosaicism, maternal gonadal mosaicism would require an invasive biopsy of ovaries [33], which is impractical in most cases. Therefore, known cases of maternal gonadal mosaicism are likely to be underestimated. Notably for the same reason, the absence of detectable mosaicism in paternal semen does not necessarily stratify low recurrence risk unless the DNV of interest is known to phase to paternal allele, which usually requires long-read sequencing that is not commonly accessible in routine clinical laboratories [14]. Caution is required to completely rule out maternal mosaicism. Nonetheless, the use of blood and saliva analysis could possibly pick up both maternal and paternal gonosomal mosaicism [34].
Comparison with previous studies
Although the first few reported parental mosaicism cases in the late 1980s and early 1990s mainly focused on isolated families with genetic disorders such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy and osteogenesis imperfecta [35, 36] with limited molecular evidence available. However, the rapid advancement of molecular technologies, particularly NGS, has accelerated the identification ofparental mosaicism in a broader range of disorders, for example epilepsy [37–39], ASD [14, 40, 41] and developmental delay (DD) [3], as well as a wide spectrum of genetic disorders including Marfan [42], Noonan [43], polycystic kidney [44], primary immunodeficiency diseases [45] and congenital heart diseases [46] (Table 2).Earlier studies, such as Myers et al. [37] showed that among 120 children having epilepsy with an apparently DNV, approximately 10% of them had a parent with mosaicism. Krupp et al. [41] also showed that parental mosaicism was found to range from 7–11% in a large ASD cohort with 2300 families using blood as the sample type. Using semen as the sample type, Breuss et al. [14] showed that 29% (4/14) fathers were mosaic for the causative DNVs transmitted to their ASD-affected children. For intellectual disability (ID) caused by DNVs, paternal mosaicism was found in 4.7–6.5% of the families in cohorts of around 50 patients [7, 15]. In a cohort of 237 patients with a DNVs among a wide spectrum of developmental disorders, Shu et al. [27] also found 3% parental mosaicism using ES as the detection method at read depth of 2000X.
Based on the above studies, it can be concluded that parental mosaicism can be found in 3–29% of various developmental disease cohorts. Diagnostic yield for parental mosaicism is much lower at 0.3–0.5% if a non- targeted approach was used, as demonstrated in two large cohort studies using ES at a read depth of 50-130X as the initial detection method. Wright et al. [3] examined trio ES data of 4,293 probands at ~ 50 X average depths from the Deciphering Developmental Disorders (DDD) Study and only 0.5% of parental mosaicism was found. Similar study performed by Cao et al. [4] based on ES data of 11,992 probands at 130X average depth from Baylor Genetics identified only 0.3% parental mosaicism in the analyzed families. While only seven mosaic variants were identified directly by trio ES, 33 mosaic variants could be found during Sanger confirmation. These larger cohort studies with > 4000 patients indicated that parental mosaicism may have been underestimated unless a more targeted approached is implemented in clinical settings. Despite its increasingly strong association with many disorders and great clinical impact, detection of mosaicism is still mostly passive and technically challenging. This underscores the need for continued research and development of more sensitive and targeted detection methods.
Technical advice
Our study, in line with previous studies, had demonstrated that the detection of parental mosaicism is challenging as mosaicism maybe tissue-specific or tissue-limited [2, 3, 12, 14, 20, 26, 47]. Using Sanger sequencing as a golden standard and blood as the most clinically accessible sample type may miss the detection of low- level parental mosaicism. While isolated study demonstrated that LOD of Sanger sequencing could go as low as 0.25% [48], such LOD require thorough optimization of the whole Sanger sequencing procedure, and depends on the particular location of the mosaic variants. BDA-qPCR is a valuable tool in determining low-level mosaicism although the experimental conditions need to be extensively optimized and technically more demanding than Sanger sequencing and ddPCR. The robustness coupled with high sensitivity and precision of ddPCR provides a reliable alternative for the detection of low-level parental mosaicism. Based on the EBF3 assay, in-house ddPCR LOD is determined to be 0.08%-0.16%, which is comparable to manufacturer’s guideline (Figure S2). Therefore, our data demonstrated the feasibility of routine clinical analysis for parental mosaicism evaluation in families in need, using buccal and/or semen samples. With the increased accessibility and affordability of NGS technology, high depth sequencing may also help reveal more cases of parental mosaicism [3, 14]. While GS is not yet offered as the first-tier genetic testing in routine clinical setting, with increased throughput and lower costs, universal GS-based clinical genetic testing is within reach. Once this becomes routine, the chances of detecting these low-level mosaic variants through massive parallel sequencing at the current 30X read depth might diminish. Recent advancements in bioinformatics such as DeepMosaic [49] may have the potential to reveal mosaic SNVs with GS at 50X; however, an orthogonal method may still be needed to validate these potential mosaic findings [50]. Consequently, we recommend careful examination of the potential for parental mosaicism in instances where an apparent de novo variant has been identified through either routine exome sequencing or genome sequencing, particularly for families contemplating a second child. It is crucial for diagnostic laboratories to thoroughly validate their methodologies, including assessment of sensitivity, precision, and accuracy, to ensure reliable findings that can effectively inform both healthcare professionals and parents."
In conclusion, the approach to diagnosing low-level parental mosaicism should start at the genetic clinic. Attention should be given to cautious observation of any mild symptom in parents, an increased paternal age at conception or a previously affected child with PAE/candidate PAE or X-linked dominant disorders. Although paternal mosaicism is known to be common, possibility of maternal gonadal mosaicism cannot be excluded. Technically, the detection of parental mosaicism relies on using appropriate sample types, such as buccal and/or semen samples, in conjunction with sensitive methods that exceed those routinely applied in clinical diagnostics. The robust detection of parental mosaicism is crucial as it permits accurate assessment of recurrence risk during genetic counseling. This information allows families to make early, informed decisions about future pregnancies. Additionally, it enables prenatal medical teams to formulate appropriate plans for pregnancy, prenatal testing, and delivery.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Apparent de novo variants for all families in this study.
Additional file 2. Primer and probe sequences for the BDA experiments.
Additional file 3. Primer and probe sequences for the ddPCR experiments.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the medical staff for the referrals and the healthcare professionals who managed the patients, and families for their participation in this study. We would like to acknowledge the support from Bioresearch Support Core of CPOS at the University of Hong Kong for providing instruments and services.
Author contributions
BHYC, ASYK and RHWL made substantial contributions to the supervision, coordination and design of the study. ML, JCKC and PHLD helped with patient recruitment. ML conducted molecular laboratory work, data analysis and drafted the manuscript. ACYL performed initial database screening. CCYM and AKYK critically revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the overall interpretation of the data and have reviewed and approved the final draft for submission.
Funding
This project is supported by the Seed Funding for Basic Research (201910159064) from the University of Hong Kong, the Society for the Relief of Disabled Children in Hong Kong, and the Edward and Yolanda Wong Fund.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from parents of the patients to participate in the study. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong/Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster. (UW 12–211).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Thorpe J, Osei-Owusu IA, Avigdor BE, Tupler R, Pevsner J. Mosaicism in human health and disease. Annu Rev Genet. 2020;54:487–510. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-041720-093403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Biesecker LG, Spinner NB. A genomic view of mosaicism and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14(5):307–320. doi: 10.1038/nrg3424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wright CF, Prigmore E, Rajan D, et al. Clinically-relevant postzygotic mosaicism in parents and children with developmental disorders in trio exome sequencing data. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2985. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11059-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cao Y, Tokita MJ, Chen ES, et al. A clinical survey of mosaic single nucleotide variants in disease-causing genes detected by exome sequencing. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13073-019-0658-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rohlin A, Wernersson J, Engwall Y, Wiklund L, Bjork J, Nordling M. Parallel sequencing used in detection of mosaic mutations: comparison with four diagnostic DNA screening techniques. Hum Mutat. 2009;30(6):1012–1020. doi: 10.1002/humu.20980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goldmann JM, Veltman JA, Gilissen C. De novo mutations reflect development and aging of the human germline. Trends Genet. 2019;35(11):828–839. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Acuna-Hidalgo R, Veltman JA, Hoischen A. New insights into the generation and role of de novo mutations in health and disease. Genome Biol. 2016;17(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1110-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goriely A. Decoding germline de novo point mutations. Nat Genet. 2016;48(8):823–824. doi: 10.1038/ng.3629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Goldmann JM, Seplyarskiy VB, Wong WSW, et al. Germline de novo mutation clusters arise during oocyte aging in genomic regions with high double-strand-break incidence. Nat Genet. 2018;50(4):487–492. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goriely A, Wilkie AO. Missing heritability: paternal age effect mutations and selfish spermatogonia. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(8):589. doi: 10.1038/nrg2809-c1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Goriely A, Wilkie AO. Paternal age effect mutations and selfish spermatogonial selection: causes and consequences for human disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90(2):175–200. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.12.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hancarova M, Havlovicova M, Putzova M, et al. Parental gonadal but not somatic mosaicism leading to de novo NFIX variants shared by two brothers with Malan syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2019;179(10):2119–2123. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zemet R, Van den Veyver IB, Stankiewicz P. Parental mosaicism for apparent de novo genetic variants: scope, detection, and counseling challenges. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42(7):811–821. doi: 10.1002/pd.6144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Breuss MW, Antaki D, George RD, et al. Autism risk in offspring can be assessed through quantification of male sperm mosaicism. Nat Med. 2020;26(1):143–150. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0711-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Frisk S, Wachtmeister A, Laurell T, et al. Detection of germline mosaicism in fathers of children with intellectual disability syndromes caused by de novo variants. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022;10(4):e1880. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17(5):405–424. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Karolak JA, Liu Q, Xie NG, et al. Highly sensitive blocker displacement amplification and droplet digital PCR reveal low-level parental FOXF1 somatic mosaicism in families with alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins. J Mol Diagn. 2020;22(4):447–456. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu LR, Chen SX, Wu Y, Patel AA, Zhang DY. Multiplexed enrichment of rare DNA variants via sequence-selective and temperature-robust amplification. Nat Biomed Eng. 2017;1:714–723. doi: 10.1038/s41551-017-0126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hindson CM, Chevillet JR, Briggs HA, et al. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat Methods. 2013;10(10):1003–1005. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee M, Lui ACY, Mak CCY, et al. Clinical implications of mosaicism: a 10-year retrospective review of 83 families in a university-affiliated genetics clinic. Clin Dysmorphol. 2022;31(3):113–124. doi: 10.1097/MCD.0000000000000418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee M, Kwong AKY, Chui MMC, et al. Diagnostic potential of the amniotic fluid cells transcriptome in deciphering mendelian disease: a proof-of-concept. NPJ Genom Med. 2022;7(1):74. doi: 10.1038/s41525-022-00347-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhytnik L, Peters M, Tilk K, et al. From late fatherhood to prenatal screening of monogenic disorders: evidence and ethical concerns. Hum Reprod Update. 2021;27(6):1056–1085. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmab023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pinheiro LB, Coleman VA, Hindson CM, et al. Evaluation of a droplet digital polymerase chain reaction format for DNA copy number quantification. Anal Chem. 2012;84(2):1003–1011. doi: 10.1021/ac202578x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dong L, Wang S, Fu B, Wang J. Evaluation of droplet digital PCR and next generation sequencing for characterizing DNA reference material for KRAS mutation detection. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9650. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27368-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Census and Statistics Department HKSAR. Women and Men in Hong Kong: Key Statistics. Accessed Aug 2 2022, https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/en/data/stat_report/product/B1130303/att/B11303032022AN22B0100.pdf
- 26.Gambin T, Liu Q, Karolak JA, et al. Low-level parental somatic mosaic SNVs in exomes from a large cohort of trios with diverse suspected Mendelian conditions. Genet Med. 2020;22(11):1768–1776. doi: 10.1038/s41436-020-0897-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shu L, Zhang Q, Tian Q, et al. Parental mosaicism in de novo neurodevelopmental diseases. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185(7):2119–2125. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pauli S, von Velsen N, Burfeind P, et al. CHD7 mutations causing CHARGE syndrome are predominantly of paternal origin. Clin Genet. 2012;81(3):234–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tellier AL, Lyonnet S, Cormier-Daire V, et al. Increased paternal age in CHARGE association. Clin Genet. 1996;50(6):548–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1996.tb02736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Blake KD, Brown D. CHARGE association looking at the future–the voice of a family support group. Child Care Health Dev Nov-Dec. 1993;19(6):395–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.1993.tb00744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Goldmann JM, Wong WS, Pinelli M, et al. Parent-of-origin-specific signatures of de novo mutations. Nat Genet. 2016;48(8):935–939. doi: 10.1038/ng.3597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kong A, Frigge ML, Masson G, et al. Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father's age to disease risk. Nature. 2012;488(7412):471–475. doi: 10.1038/nature11396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Campbell IM, Shaw CA, Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. Somatic mosaicism: implications for disease and transmission genetics. Trends Genet. 2015;31(7):382–392. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Riviere JG, Franco-Jarava C, Martinez-Gallo M, et al. Uncovering low-level maternal gonosomal mosaicism in X-linked agammaglobulinemia: implications for genetic counseling. Front Immunol. 2020;11:46. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bakker E, Van Broeckhoven C, Bonten EJ, et al. Germline mosaicism and Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. Nature. 1987;329(6139):554–556. doi: 10.1038/329554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cohn DH, Starman BJ, Blumberg B, Byers PH. Recurrence of lethal osteogenesis imperfecta due to parental mosaicism for a dominant mutation in a human type I collagen gene (COL1A1) Am J Hum Genet. 1990;46(3):591–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Myers CT, Hollingsworth G, Muir AM, et al. Parental mosaicism in "de novo" epileptic encephalopathies. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(17):1646–1648. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1714579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stosser MB, Lindy AS, Butler E, et al. High frequency of mosaic pathogenic variants in genes causing epilepsy-related neurodevelopmental disorders. Genet Med. 2018;20(4):403–410. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xu X, Yang X, Wu Q, et al. Amplicon resequencing identified parental mosaicism for approximately 10% of "de novo" SCN1A mutations in children with dravet syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2015;36(9):861–872. doi: 10.1002/humu.22819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Freed D, Pevsner J. The contribution of mosaic variants to autism spectrum disorder. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(9):e1006245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krupp DR, Barnard RA, Duffourd Y, et al. Exonic mosaic mutations contribute risk for autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2017;101(3):369–390. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fernandez-Alvarez P, Codina-Sola M, Valenzuela I, et al. A systematic study and literature review of parental somatic mosaicism of FBN1 pathogenic variants in Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet. 2022;59(6):605–612. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-107604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Elalaoui SC, Kraoua L, Liger C, Ratbi I, Cave H, Sefiani A. Germinal mosaicism in noonan syndrome: a family with two affected siblings of normal parents. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A(11):2850–2853. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tan AY, Blumenfeld J, Michaeel A, et al. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease caused by somatic and germline mosaicism. Clin Genet. 2015;87(4):373–377. doi: 10.1111/cge.12383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mensa-Vilaro A, Bravo Garcia-Morato M, de la Calle-Martin O, et al. Unexpected relevant role of gene mosaicism in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(1):359–368. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Manheimer KB, Richter F, Edelmann LJ, et al. Robust identification of mosaic variants in congenital heart disease. Hum Genet. 2018;137(2):183–193. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1871-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Campbell IM, Stewart JR, James RA, et al. Parent of origin, mosaicism, and recurrence risk: probabilistic modeling explains the broken symmetry of transmission genetics. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;95(4):345–359. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Joy RA, Thelakkattusserry SK, Vikkath N, et al. Somatic mutation detection efficiency in EGFR: a comparison between high resolution melting analysis and Sanger sequencing. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):902. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07411-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yang X, Xu X, Breuss MW, et al. Control-independent mosaic single nucleotide variant detection with DeepMosaic. Nat Biotechnol. 2023 doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01559-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Corominas J, Smeekens SP, Nelen MR, et al. Clinical exome sequencing-Mistakes and caveats. Hum Mutat. 2022 doi: 10.1002/humu.24360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Apparent de novo variants for all families in this study.
Additional file 2. Primer and probe sequences for the BDA experiments.
Additional file 3. Primer and probe sequences for the ddPCR experiments.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.