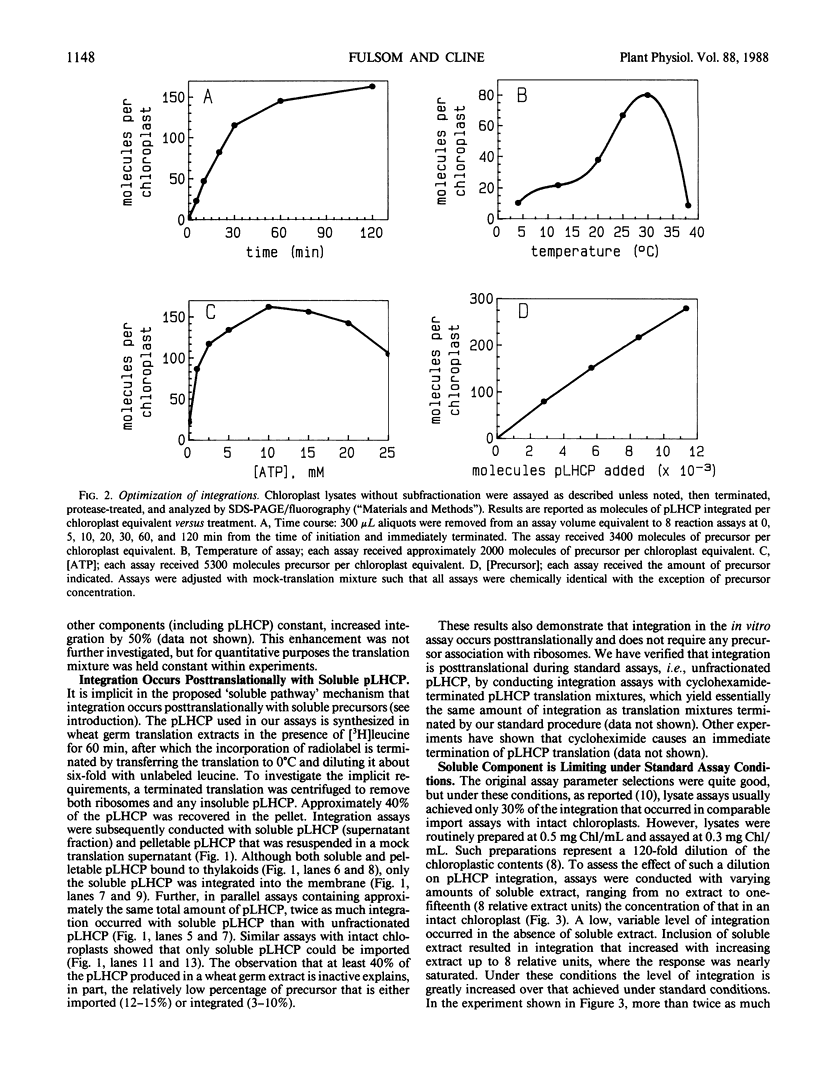
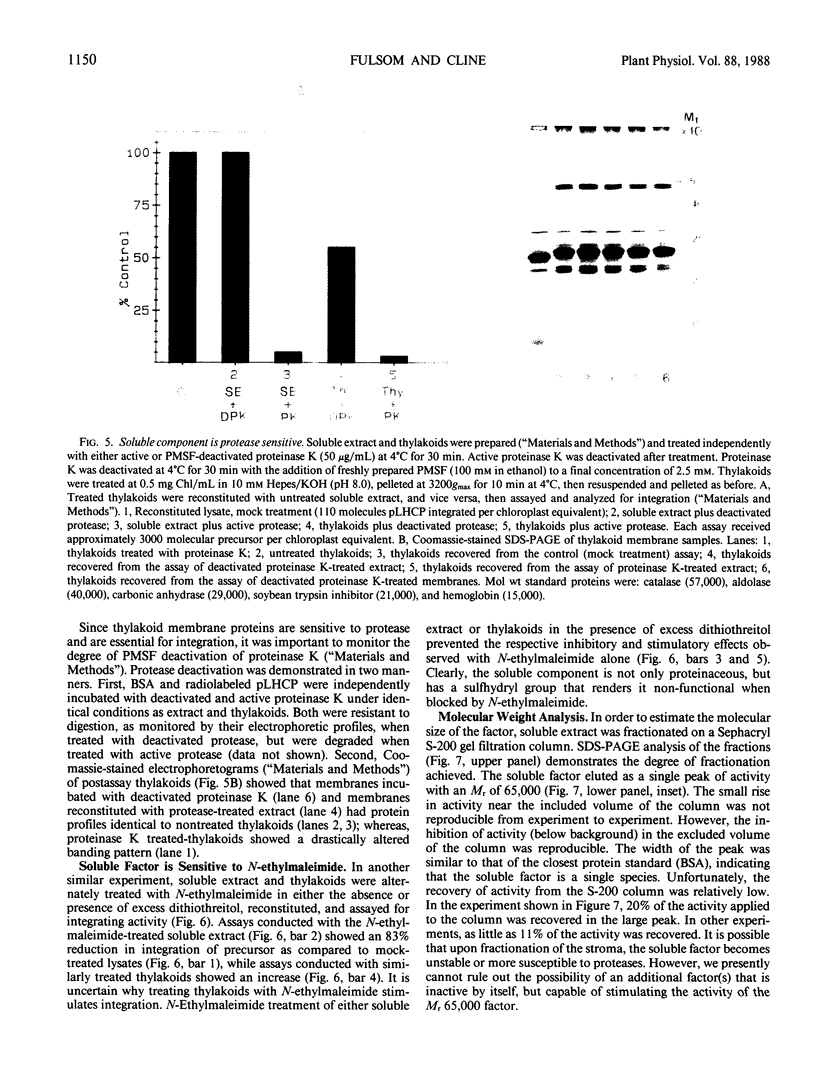
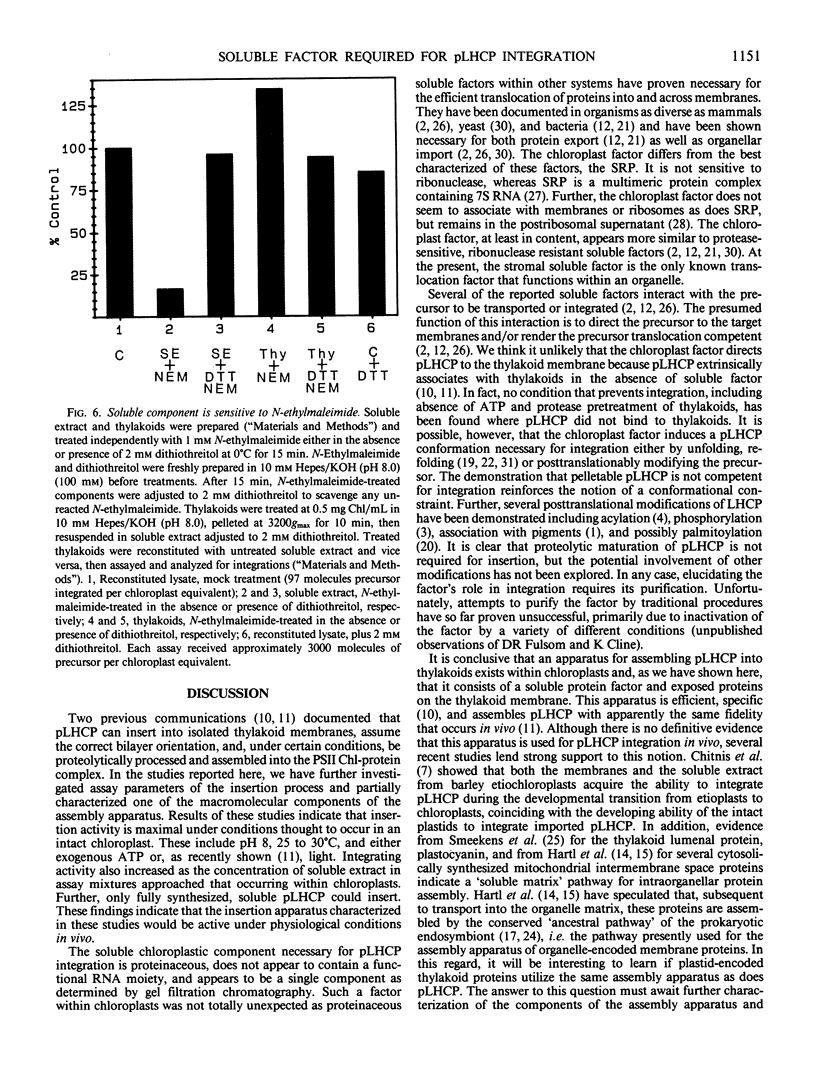
Abstract
The precursor to the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of photosystem II can insert into isolated thylakoid membranes if reaction mixtures also contain ATP and a soluble extract of chloroplasts. Optimization of this insertion process and the initial characterization of the soluble chloroplastic component are presented. With a fixed amount of precursor, maximum integration rates occurred during the first 30 minutes at pH 8.0 and 30°C when the soluble chloroplast extract was increased eight-fold over the stoichiometric amount. Under these conditions, insertion was routinely about 60% of that which occurred during import into intact chloroplasts. Integration also increased virtually linearly with increasing amounts of precursor. However, assays revealed that at least 40% of the in vitro-synthesized pLHCP was pelletable and inactive. The soluble chloroplastic component exhibited characteristics expected of a protein. It was inactivated by heat, protease, and N-ethylmaleimide, but was insensitive to ribonuclease. The soluble component migrated on a Sephacryl S-200 gel filtration column as a single peak with an Mr of approximately 65,000. The proteinaceous nature of this factor suggests a similarity to soluble factors required for protein transport/integration in other membrane systems.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Anderson J. M., Ryrie I. J. Transbilayer organization of the chlorophyll-proteins of spinach thylakoids. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argan C., Shore G. C. The precursor to ornithine carbamyl transferase is transported to mitochondria as a 5S complex containing an import factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91801-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D., Lewin A. Inhibition of the import of mitochondrial proteins by RNase. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6153–6155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R. Structure and expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K. Import of proteins into chloroplasts. Membrane integration of a thylakoid precursor protein reconstituted in chloroplast lysates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14804–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K. Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll a/b Protein : Membrane Insertion, Proteolytic Processing, Assembly into LHC II, and Localization to Appressed Membranes Occurs in Chloroplast Lysates. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1120–1126. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Andrews J., Keegstra K. Thermolysin is a suitable protease for probing the surface of intact pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):675–678. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Lubben T. H., Keegstra K. Precursors to two nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins bind to the outer envelope membrane before being imported into chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3691–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Wickner W. Trigger factor: a soluble protein that folds pro-OmpA into a membrane-assembly-competent form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J. Chloroplast protein synthesis: principles and problems. Subcell Biochem. 1983;9:237–261. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-3533-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Ostermann J., Guiard B., Neupert W. Successive translocation into and out of the mitochondrial matrix: targeting of proteins to the intermembrane space by a bipartite signal peptide. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1027–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Schmidt B., Wachter E., Weiss H., Neupert W. Transport into mitochondria and intramitochondrial sorting of the Fe/S protein of ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):939–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90809-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Singer S. J. Disulfide bonds and the translocation of proteins across membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9001–9005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Edelman M. Intramembrane translocation and posttranslational palmitoylation of the chloroplast 32-kDa herbicide-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1497–1501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. Protein export in Escherichia coli requires a soluble activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7737–7741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Kornberg R. D. Cell biology. An unfolding story of protein translocation. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):209–210. doi: 10.1038/322209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Mishkind M. L. The transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:879–912. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. C., Lazar G., Goodman H. M. Evidence in favor of the symbiotic origin of chloroplasts: primary structure and evolution of tobacco glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90367-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S., Bauerle C., Hageman J., Keegstra K., Weisbeek P. The role of the transit peptide in the routing of precursors toward different chloroplast compartments. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Subcellular distribution of signal recognition particle and 7SL-RNA determined with polypeptide-specific antibodies and complementary DNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1693–1699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Chirico W. J., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the yeast microsomal membrane is stimulated by a soluble factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2629–2636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





