Abstract
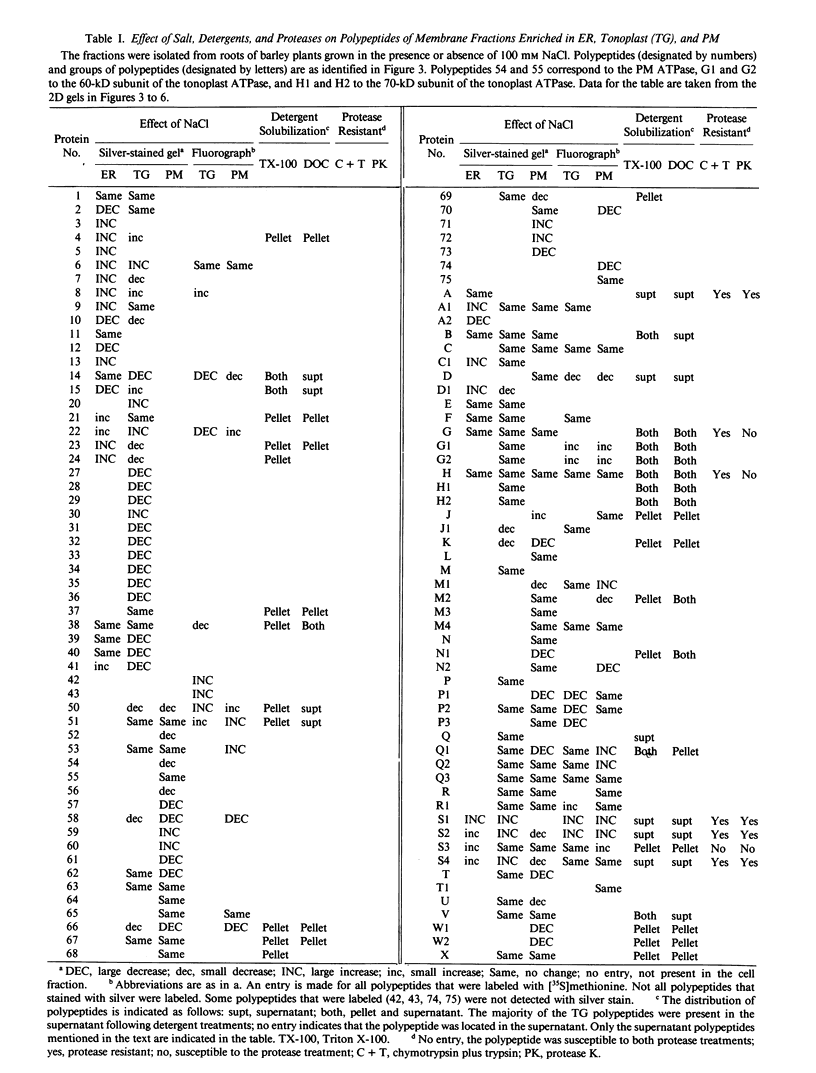
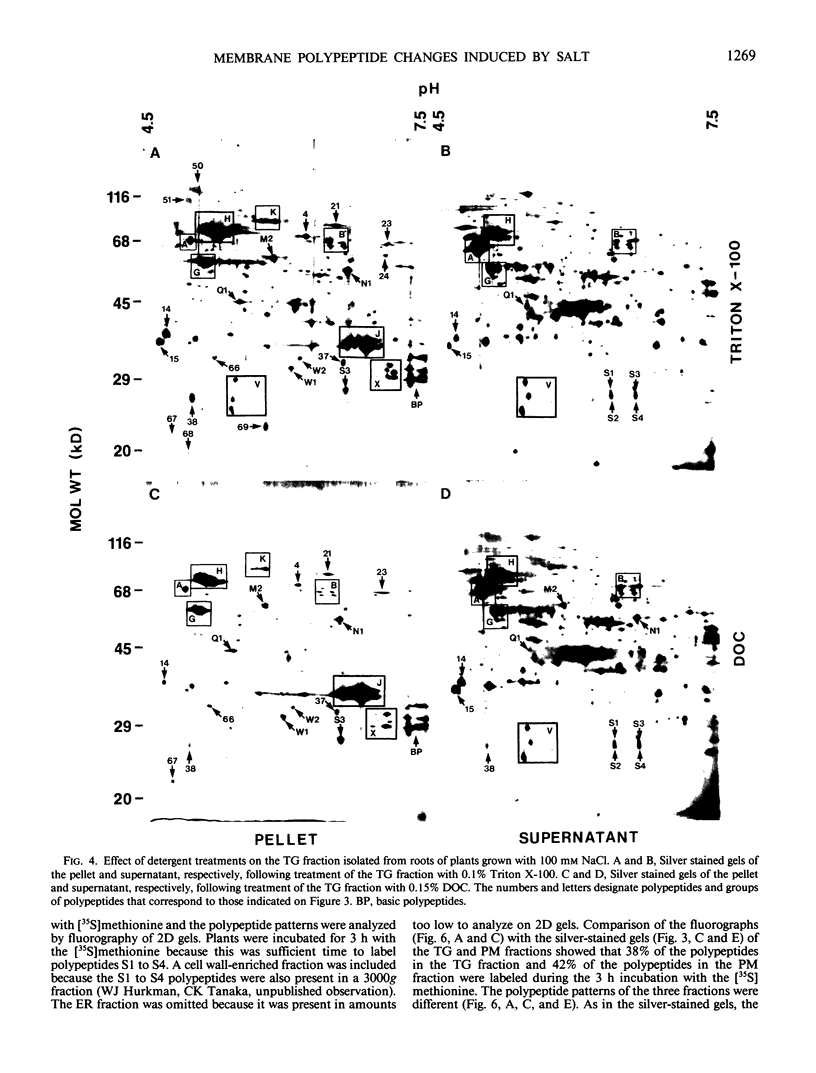
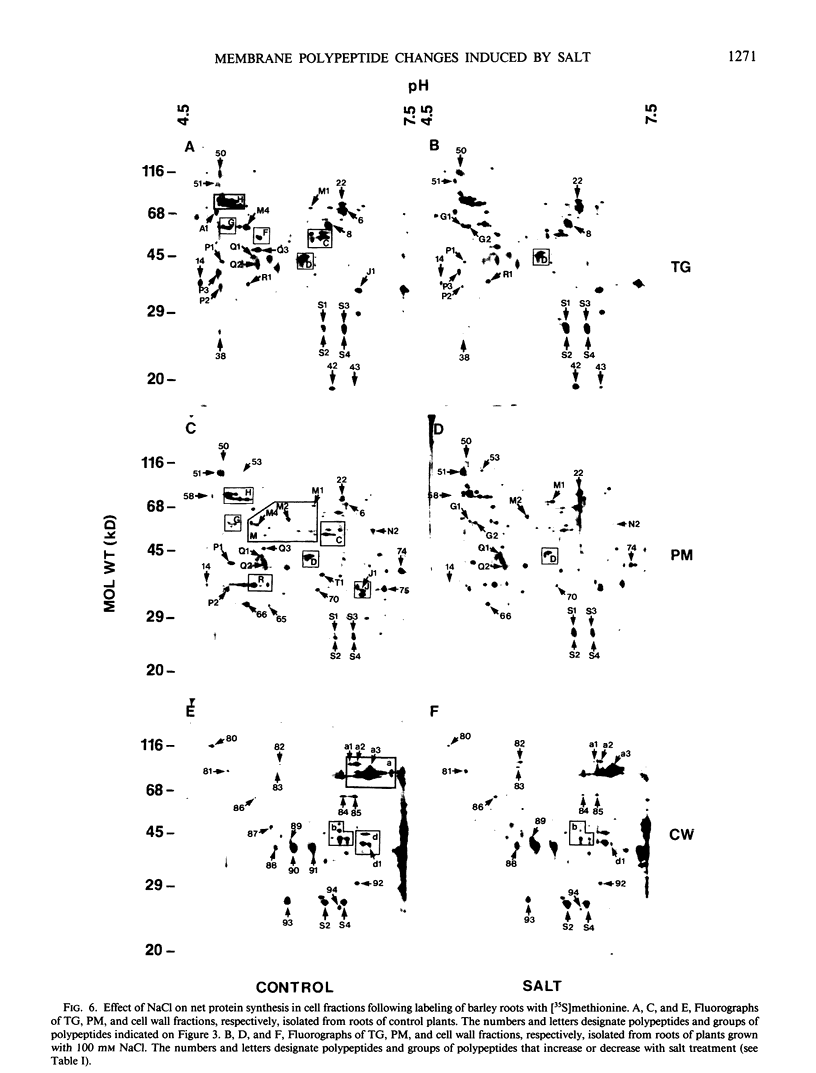
Cell fractions enriched in endoplasmic reticulum, tonoplast, plasma membrane, and cell walls were isolated from roots of barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv CM 72) and the effect of NaCl on polypeptide levels was examined by two-dimensional (2D) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The distribution of membranes on continuous sucrose gradients was not significantly affected by growing seedlings in the presence of NaCl; step gradients were used to isolate comparable membrane fractions from roots of control and salt-grown plants. The membrane and cell wall fractions each had distinctive polypeptide patterns on 2D gels. Silver-stained gels showed that salt stress caused increases or decreases in a number of polypeptides, but no unique polypeptides were induced by salt. The most striking change was an increase in protease resistant polypeptides with isoelectric points of 6.3 and 6.5 and molecular mass of 26 and 27 kilodaltons in the endoplasmic reticulum and tonoplast fractions. Fluorographs of 2D gels of the tonoplast, plasma membrane, and cell wall fractions isolated from roots of intact plants labeled with [35S]methionine in vivo also showed that salt induced changes in the synthesis of a number of polypeptides. There was no obvious candidate for an integral membrane polypeptide that might correspond to a salt-induced sodium-proton anti-porter in the tonoplast membrane.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthon G. E., Spanswick R. M. Purification and properties of the h-translocating ATPase from the plasma membrane of tomato roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1080–1085. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett H. S., Wyrick A. D., Lee S. W., McNeil J. H. Science and art in preparing tissues embedded in plastic for light microscopy, with special reference to glycol methacrylate, glass knives and simple stains. Stain Technol. 1976 Mar;51(2):71–97. doi: 10.3109/10520297609116677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booz M. L., Travis R. L. Electrophoretic comparison of polypeptides from enriched plasma membrane fractions from developing soybean roots. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1037–1043. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Intracellular localization of heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1197–1203. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Hurkman W. J. Separation of the Mg-ATPases from the Ca-Phosphatase Activity of Microsomal Membranes Prepared from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):857–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Tanaka C. K., Hurkman W. J. separation and Immunological Characterization of Membrane Fractions from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):717–724. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M. Variable Effects of Nitrate on ATP-Dependent Proton Transport by Barley Root Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):526–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Norlyn J. D. Seawater-based crop production: a feasibility study. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):249–251. doi: 10.1126/science.197.4300.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. NaCl Induces a Na/H Antiport in Tonoplast Vesicles from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):231–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. L., Niemi K. J., Brambl R. Altered gene expression during cold acclimation of spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):802–806. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. The effects of salt on the pattern of protein synthesis in barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):517–524. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S., Taiz L. Partial purification of a tonoplast ATPase from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jun;78(2):327–333. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleski N. A., Bennett A. B. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: IV. N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide Binding and Inhibition of the Plasma Membrane H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):569–572. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A. M., Davies E. Ribonucleic Acid and Protein Metabolism in Pea Epicotyls : II. Response to Wounding in Aged Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):817–821. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A. M., Davies E. Ribonucleic Acid and protein metabolism in pea epicotyls : I. The aging process. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):809–816. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Bracker C. A., Hasegawa P. M., Handa A. K., Buckel S., Hermodson M. A., Pfankoch E., Regnier F. E., Bressan R. A. Characterization of osmotin : a thaumatin-like protein associated with osmotic adaptation in plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1987 Oct;85(2):529–536. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura M., Yoshida S. Involvement of Plasma Membrane Alterations in Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):818–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]