Abstract
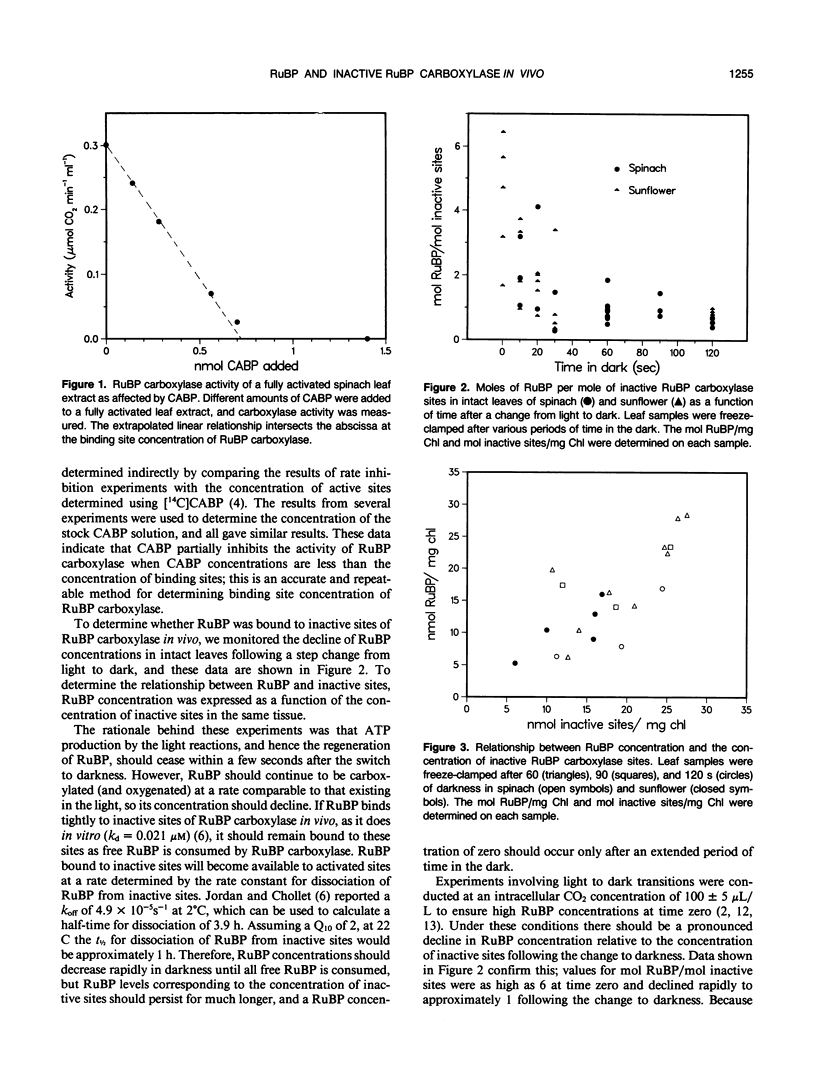
The binding of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) to inactive (noncarbamylated) sites of the enzyme RuBP carboxylase in vivo was investigated in Spinacia oleracea and Helianthus annuus. The concentrations of RuBP and inactive sites were determined in leaf tissue as a function of time after a change to darkness. RuBP concentrations fell rapidly after the change to darkness and were approximately equal to the concentration of inactive sites after 60 s. Variations in the concentration of inactive sites, which were induced by differences in the light intensity before the light-dark transition, correlated with the concentration of RuBP between 60 and 120 s after the change to darkness. These data are discussed as evidence that RuBP binds to inactive sites of RuBP carboxylase in vivo. After the concentration of RuBP fell below that of inactive sites (at times longer than 60 s of darkness), the decline in RuBP was logarithmic with time. This would be expected if the dissociation of RuBP from inactive sites controlled the decline in RuBP concentration. These data were used to estimate the rate constant for dissociation of RuBP from inactive sites in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A., Portis A. R. Protein-bound ribulose bisphosphate correlates with deactivation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in leaves. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):244–249. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Berry J. A. Effects of pH on Activity and Activation of Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase at Air Level CO(2). Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):77–82. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A. Do Stomata Respond to CO(2) Concentrations Other than Intercellular? Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):200–203. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J., Tolbert N. E., Barker R. Interaction of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase with transition-state analogues. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):934–942. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Salvucci M. E., Ogren W. L. Activation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase at Physiological CO(2) and Ribulosebisphosphate Concentrations by Rubisco Activase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):967–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Berry J. A., Freas S. M., Krump M. A. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
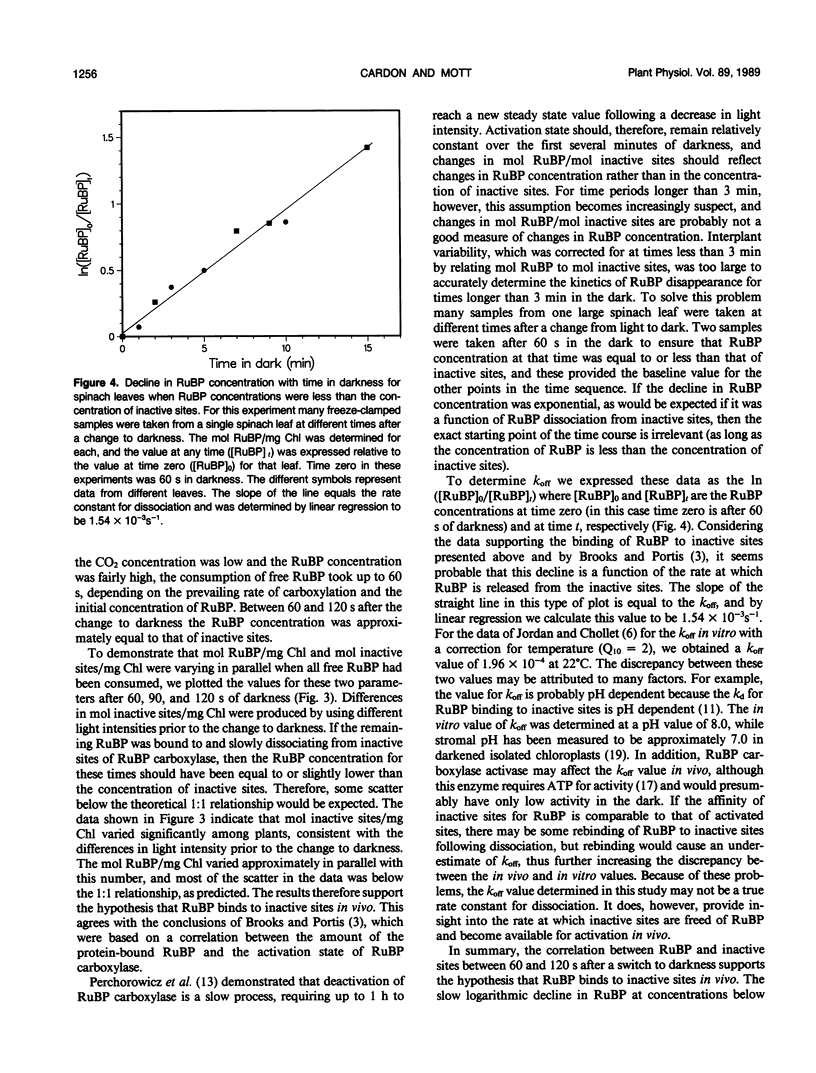
- Streusand V. J., Portis A. R. Rubisco Activase Mediates ATP-Dependent Activation of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):152–154. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W., Milovancev M. The role of pH in the regulation of carbon fixation in the chloroplast stroma. Studies on CO2 fixation in the light and dark. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 11;396(2):276–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


