Abstract
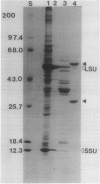
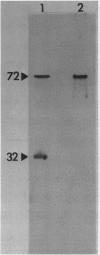
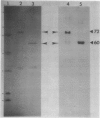
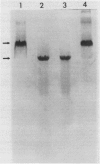
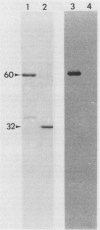
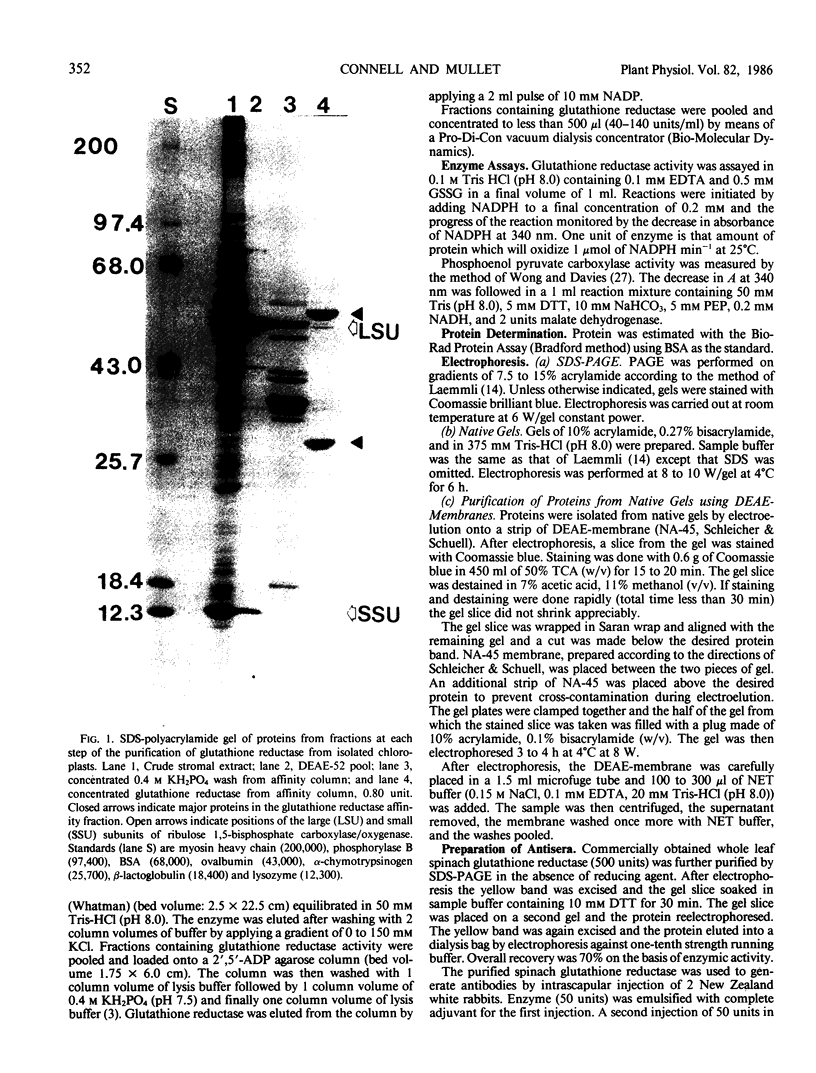
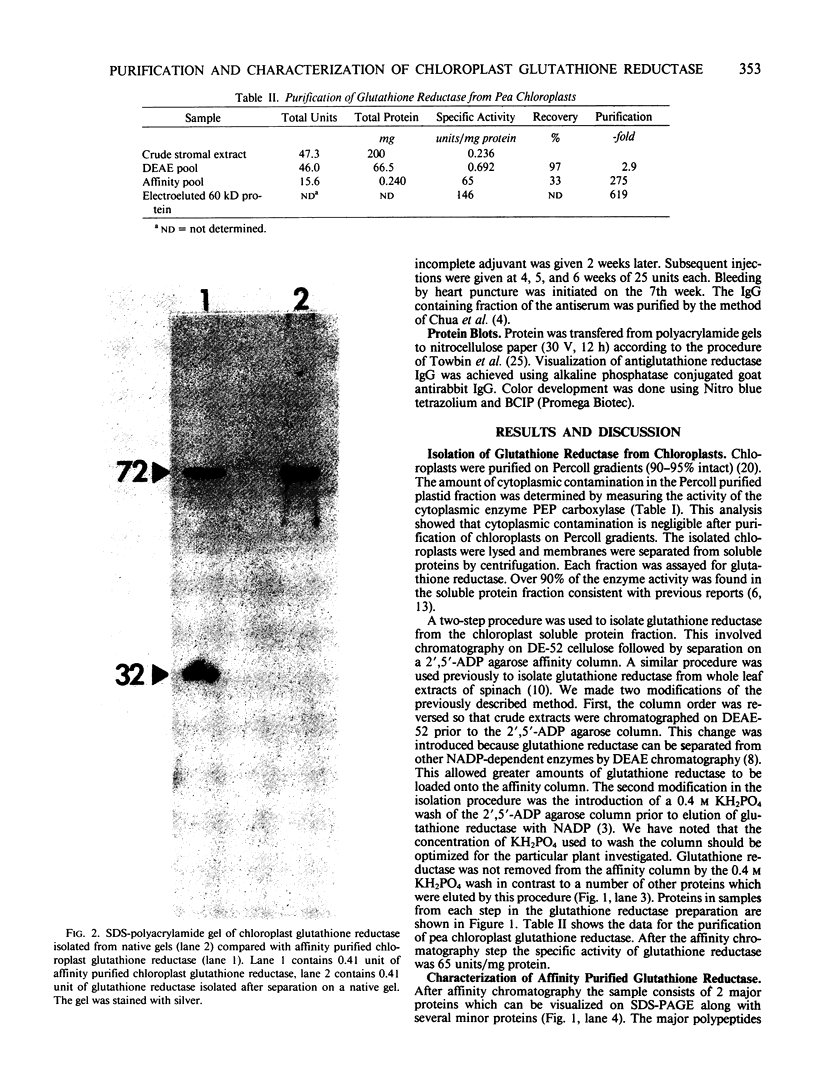
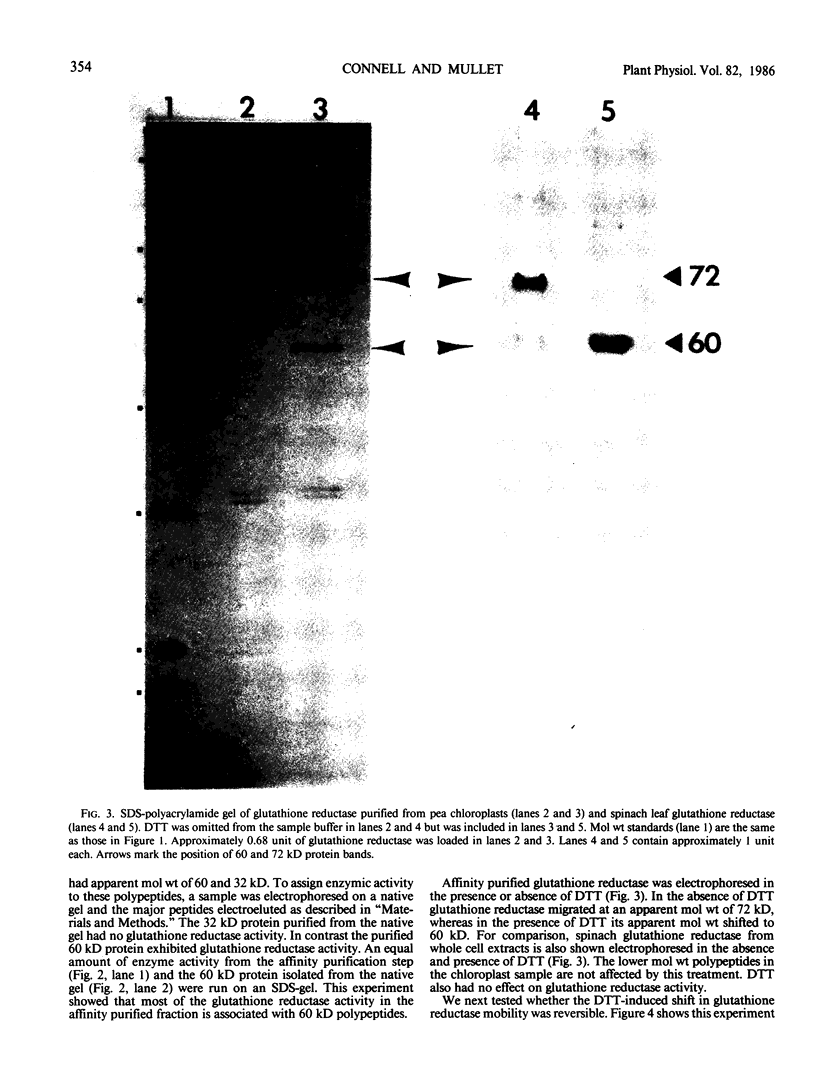
Glutathione reductase (EC 1.6.4.2) was purified from intact pea (Pisum sativum) chloroplasts by a method which includes affinity chromatography on ADP-agarose. Fractions from the affinity column which had glutathione reductase activity consisted of polypeptides of 60 and 32 kilodaltons. Separation of the proteins by electrophoresis on native gels showed that glutathione reductase activity was associated with 60 kilodalton polypeptides and not with the 32 kilodalton polypeptides. Antibodies to spinach whole leaf glutathione reductase (60 kilodaltons) cross-react with the chloroplast 60 kilodalton glutathione reductase but not the 32 kilodalton polypeptides. In the absence of dithiothreitol the 60 kilodalton polypeptides showed a shift in apparent molecular weight on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels to 72 kilodaltons. Dithiothreitol did not alter the activity of the chloroplast enzyme. Chloroplast glutathione reductase is relatively insensitive to NADPH.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg I., Mannervik B. Purification by affinity chromatography of yeast glutathione reductase, the enzyme responsible for the NADPH-dependent reduction of the mixed disulfide of coenzyme A and glutathione. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 13;484(2):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egneus H., Heber U., Matthiesen U., Kirk M. Reduction of oxygen by the electron transport chain of chloroplasts during assimilation of carbon dioxide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 11;408(3):252–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble P. E., Burke J. J. Effect of water stress on the chloroplast antioxidant system: I. Alterations in glutathione reductase activity. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):615–621. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barea J., Lee C. Y. Mouse-liver glutathione reductase. Purification, kinetics, and regulation. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):487–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata A. M., Pinto M. C., López-Barea J. Redox interconversion of Escherichia coli glutathione reductase. A study with permeabilized and intact cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 Oct;68(2):121–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00219376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata A. M., Pinto M. C., López-Barea J. Redox interconversion of glutathione reductase from Escherichia coli. A study with pure enzyme and cell-free extracts. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 May;67(1):65–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00220987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenthaler J. J., Marsden M. P., Price C. A. Factors affecting the separation of photosynthetically competent chloroplasts in gradients of silica sols. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 May;168(1):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto M. C., Mata A. M., López-Barea J. The redox interconversion mechanism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae glutathione reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaedle M. Chloroplast glutathione reductase. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):1011–1012. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano A., Rivas J., Losada M. Purification and properties of glutathione reductase from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain 7119. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):317–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.317-324.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieme R., Pai E. F., Schirmer R. H., Schulz G. E. Three-dimensional structure of glutathione reductase at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):763–782. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. F., Davies D. D. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of Zea mays by metabolites. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):451–458. doi: 10.1042/bj1310451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. C., Conn E. E. The Reduction and Oxidation of Glutathione by Plant Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1956 May;31(3):205–211. doi: 10.1104/pp.31.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]