Abstract
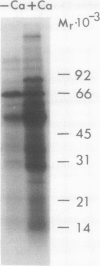
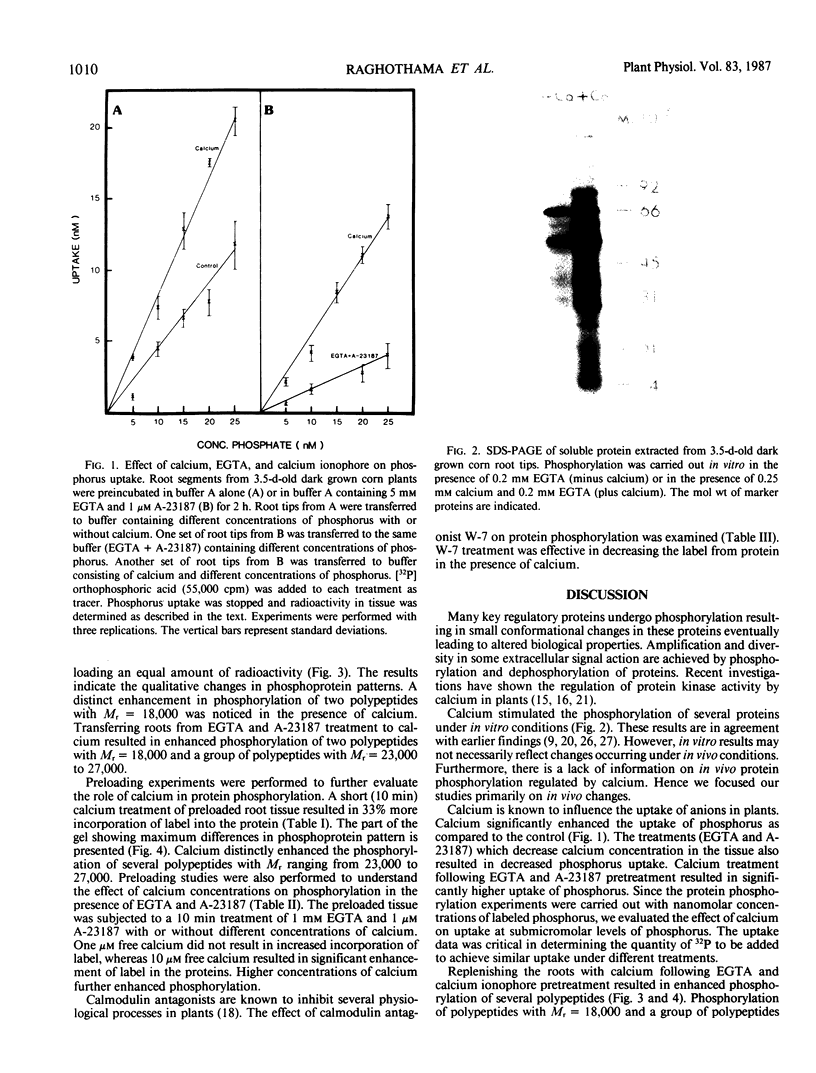
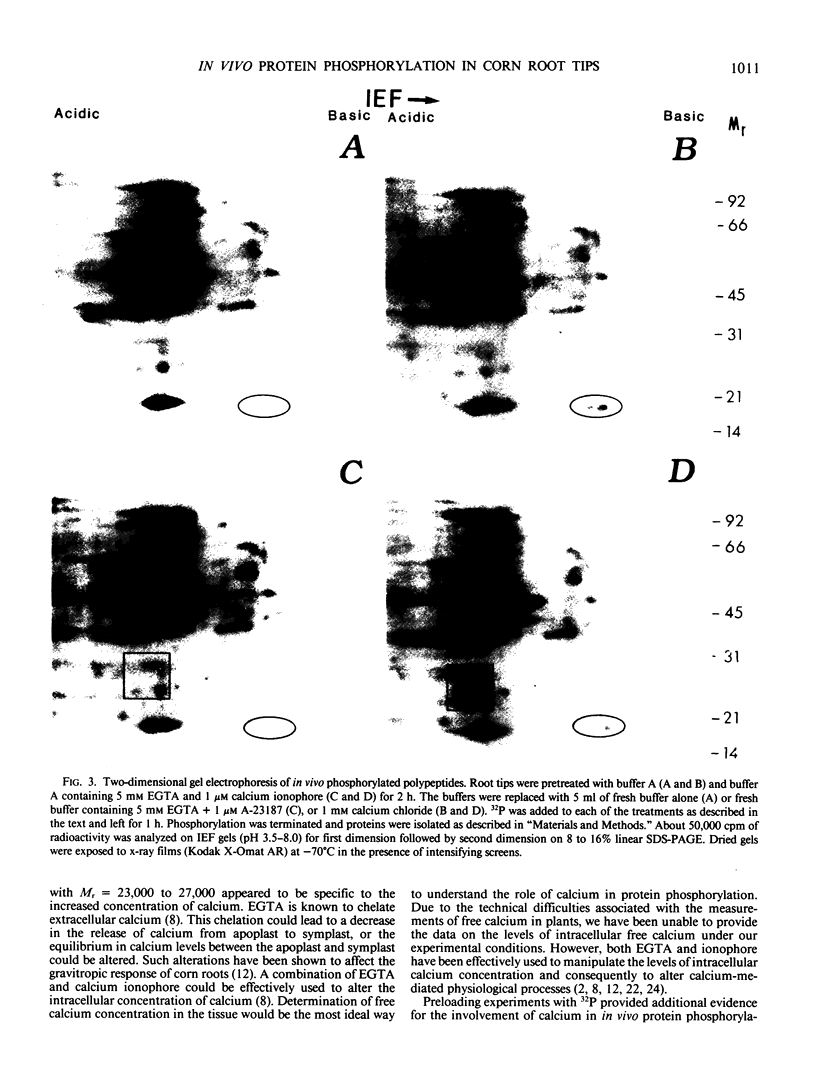
Calcium dependent protein phosphorylation was studied in corn (Zea mays L.) root tips. Prior to in vivo protein phosphorylation experiments, the effect of calcium, ethyleneglycol-bis-(β-aminoethyl ether)-N-N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) and calcium ionophore (A-23187) on phosphorus uptake was studied. Calcium increased phosphorus uptake, whereas EGTA and A-23187 decreased it. Consequently, phosphorus concentration in the media was adjusted so as to attain similar uptake in different treatments. Phosphoproteins were analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Distinct changes in phosphorylation were observed following altered calcium levels. Calcium depletion in root tips with EGTA and A-23187 decreased protein phosphorylation. However, replenishment of calcium following EGTA and ionophore pretreatment enhanced phosphorylation of proteins. Preloading of the root tips with 32P in the presence of EGTA and A-23187 followed by a ten minute calcium treatment, resulted in increased phosphorylation indicating the involvement of calcium, calcium and calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Calmodulin antagonist W-7 was effective in inhibiting calcium-promoted phosphorylation. These studies suggest a physiological role for calcium-dependent phosphorylation in calcium-mediated processes in plants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Cormier M. J. Calcium-dependent regulation of NAD kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90747-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balamani V., Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. Effect of Calcium on Tuberization in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Physiol. 1986 Apr;80(4):856–858. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Keenan C. M., Lamb S. R., Hanson W. L., Waits V. B. Leishmania donovani: oral efficacy and toxicity of formycin B in the infected hamster. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Oct;56(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Partial characterization of a phosphorylated intermediate associated with the plasma membrane ATPase of corn roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daye S., Biro R. L., Roux S. J. Inhibition of gravitropism in oat coleoptiles by the calcium chelator, ethyleneglycol-bis-(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetraacetic acid. Physiol Plant. 1984 Jul;61(3):449–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1984.tb06354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Mulkey T. J., Evans M. L. Reversible loss of gravitropic sensitivity in maize roots after tip application of calcium chelators. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1375–1376. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4604.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Leopold A. C. Deferral of leaf senescence with calcium. Plant Physiol. 1973 Sep;52(3):236–239. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghothama K. G., Mizrahi Y., Poovaiah B. W. Effect of calmodulin antagonists on auxin-induced elongation. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):28–33. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders M. J., Hepler P. K. Calcium ionophore a23187 stimulates cytokinin-like mitosis in funaria. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.217.4563.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serlin B. S., Roux S. J. Modulation of chloroplast movement in the green alga Mougeotia by the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 and by calmodulin antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6368–6372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R., Zucker R., Schatten G. Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90084-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. Calcium- and calmodulin-regulated phosphorylation of soluble and membrane proteins from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):359–365. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. Calcium-promoted protein phosphorylation in plants. Science. 1984 Jan 13;223(4632):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4632.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Poovaiah B. W. In vitro and in vivo protein phosphorylation in Avena sativa L. coleoptiles: effects of Ca2+, calmodulin antagonists, and auxin. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):836–841. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]