Abstract
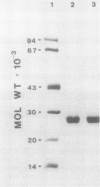
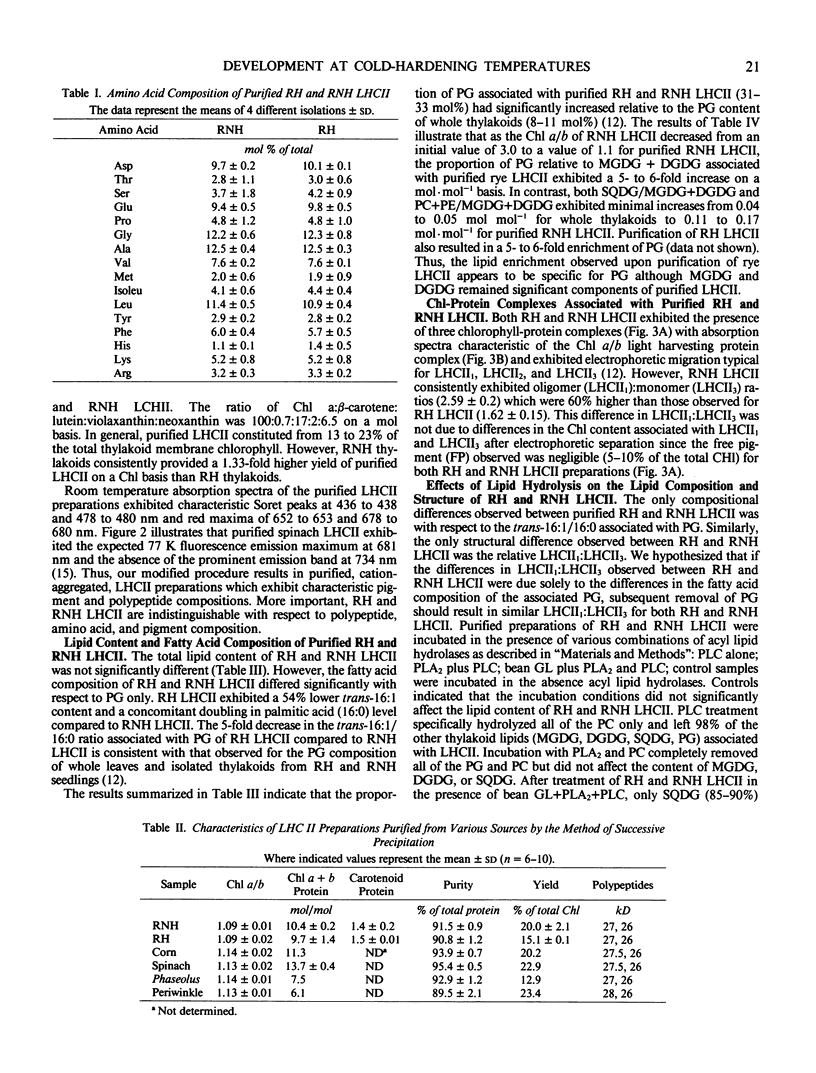
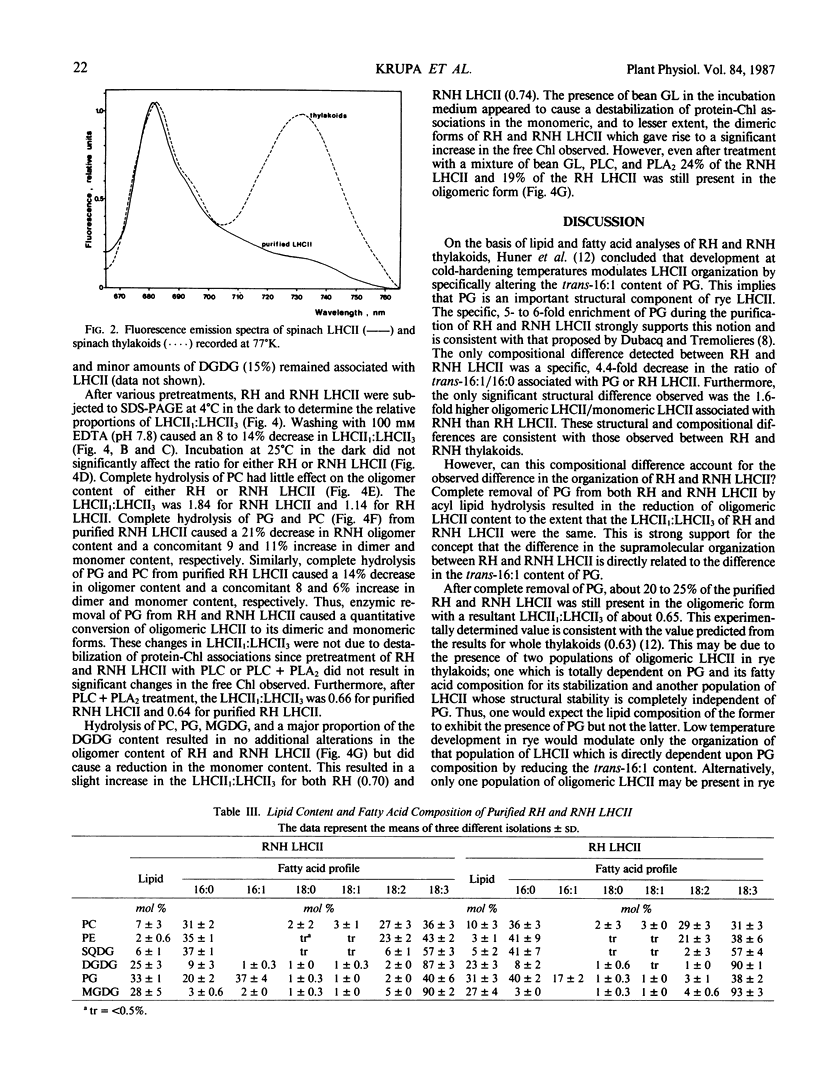
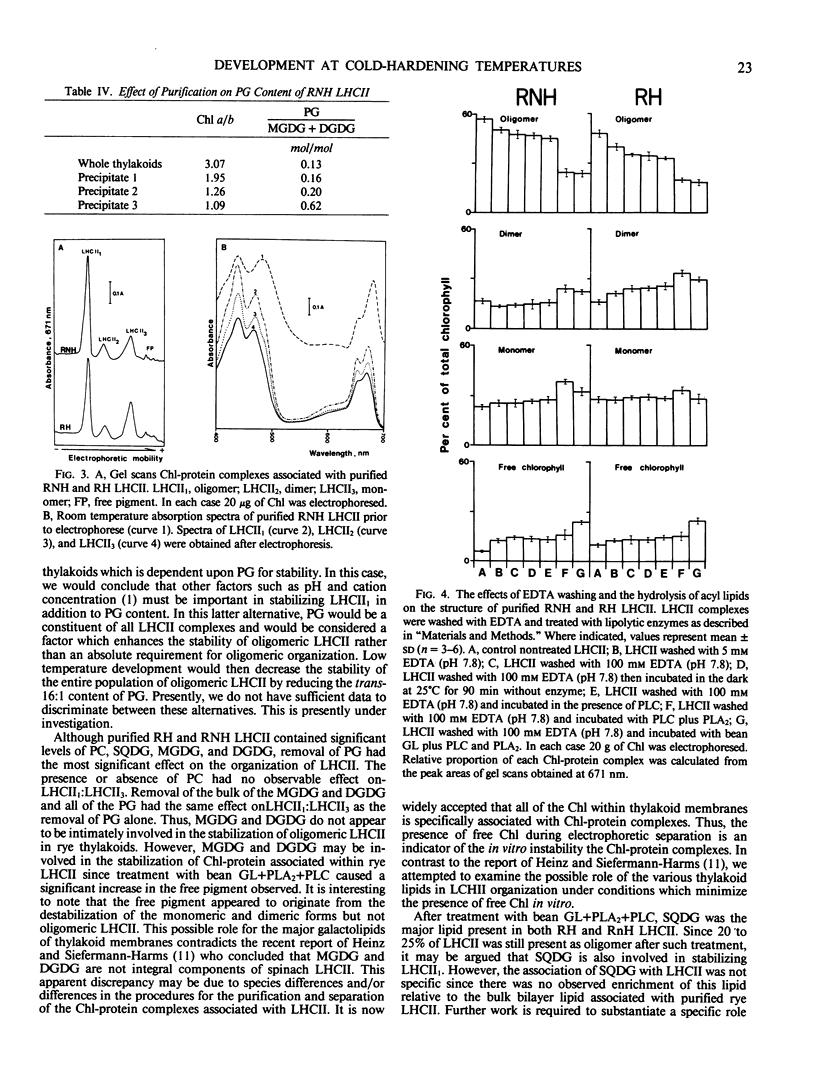
Light harvesting complex II (LHCII) was purified from cold-hardened (RH) and nonhardened winter rye (RNH) (Secale cereale L. cv Puma) employing a modified procedure of JJ Burke, CL Ditto, CJ Arntzen (Arch Biochem Biophys 187: 252-263). Triton X-100 solubilization of thylakoid membranes followed by three successive precipitations with 100 mm KCl and 10 mm MgCl2 resulted in yields of up to 25% on a chlorophyll (Chl) basis and a purity of 90 to 95%, based on polypeptide analysis within 4 hours. Polypeptide and pigment analyses, 77 K fluorescence emission and room temperature absorption spectra indicate the LHCII obtained by this modified method is comparable to LHCII obtained by other published methods. Comparison of purified RH and RNH LHCII indicated no significant differences with respect to polypeptide, amino acid, Chl, and carotenoid compositions as well as no differences in lipid content. However, RH LHCII differed from RNH LHCII specifically with respect to the fatty acid composition of phosphatidyldiacylglycerol only. RH LHCII exhibited a 54% lower trans-Δ3-hexadecenoic acid level associated with PG and a 60% lower oligomeric LHCII:monomeric LHCII (LHCII1:LHCII3) than RNH LHCII. Both RH and RNH LHCII exhibited a 5-fold enrichment in PG specifically. Complete removal of PG by enzymic hydrolysis resulted in a significant reduction in the oligomeric content of both RH and RNH LHCII such that LHCII1:LHCII3 of RH and RNH LHCII preparations were the same. This confirms that this specific compositional change accounts for the structural differences between RH and RNH LCHII observed in situ and in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Dorne A. J., Joyard J., Douce R. Preparation and characterization of membrane fractions enriched in outer and inner envelope membranes from spinach chloroplasts. II. Biochemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13281–13286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. J., Ditto C. L., Arntzen C. J. Involvement of the light-harvesting complex in cation regulation of excitation energy distribution in chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 15;187(1):252–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foyer C. H., Hall D. O. A rapid procedure for the preparation of light harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex. An assessment of its manganese content. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 15;101(2):324–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huner N. P., Krol M., Williams J. P., Maissan E., Low P. S., Roberts D., Thompson J. E. Low Temperature Development Induces a Specific Decrease in trans-Delta-Hexadecenoic Acid Content which Influences LHCII Organization. Plant Physiol. 1987 May;84(1):12–18. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. U., Williams J. P. Improved thin-layer chromatographic method for the separation of major phospholipids and glycolipids from plant lipid extracts and phosphatidyl glycerol and bis(monoacylglyceryl) phosphate from animal lipid extracts. J Chromatogr. 1977 Oct 11;140(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)88412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]