Abstract
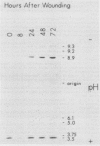
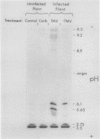
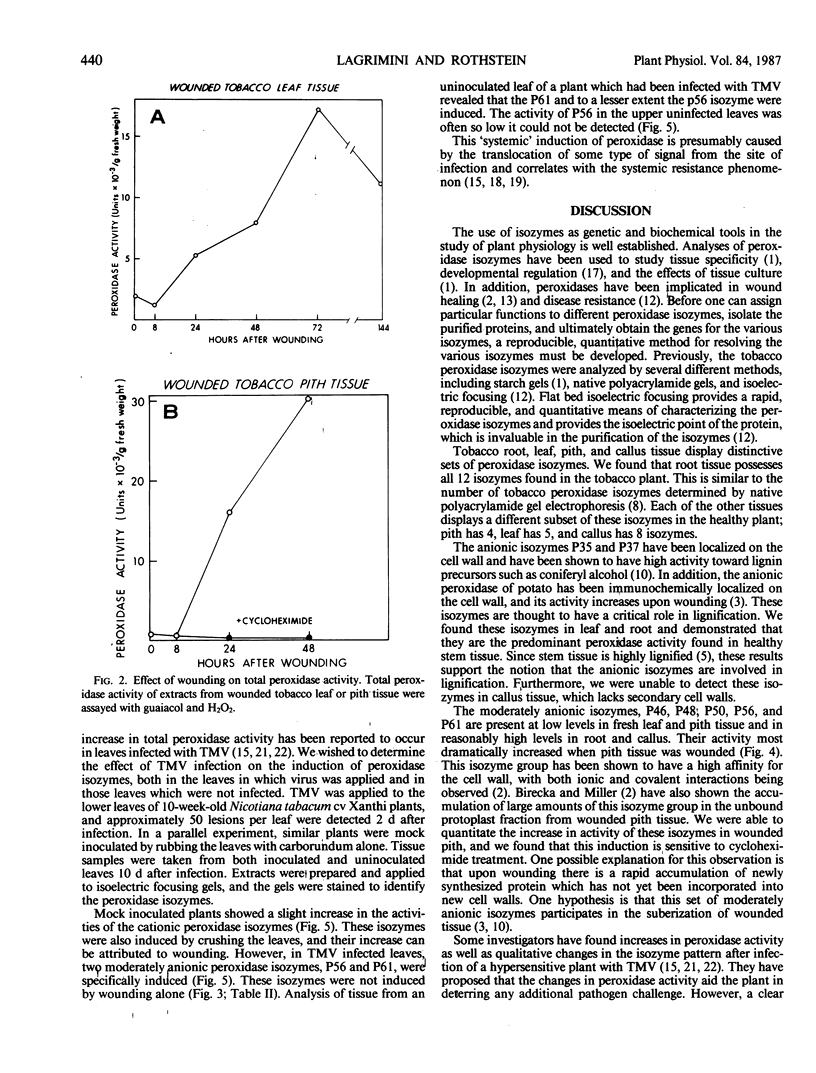
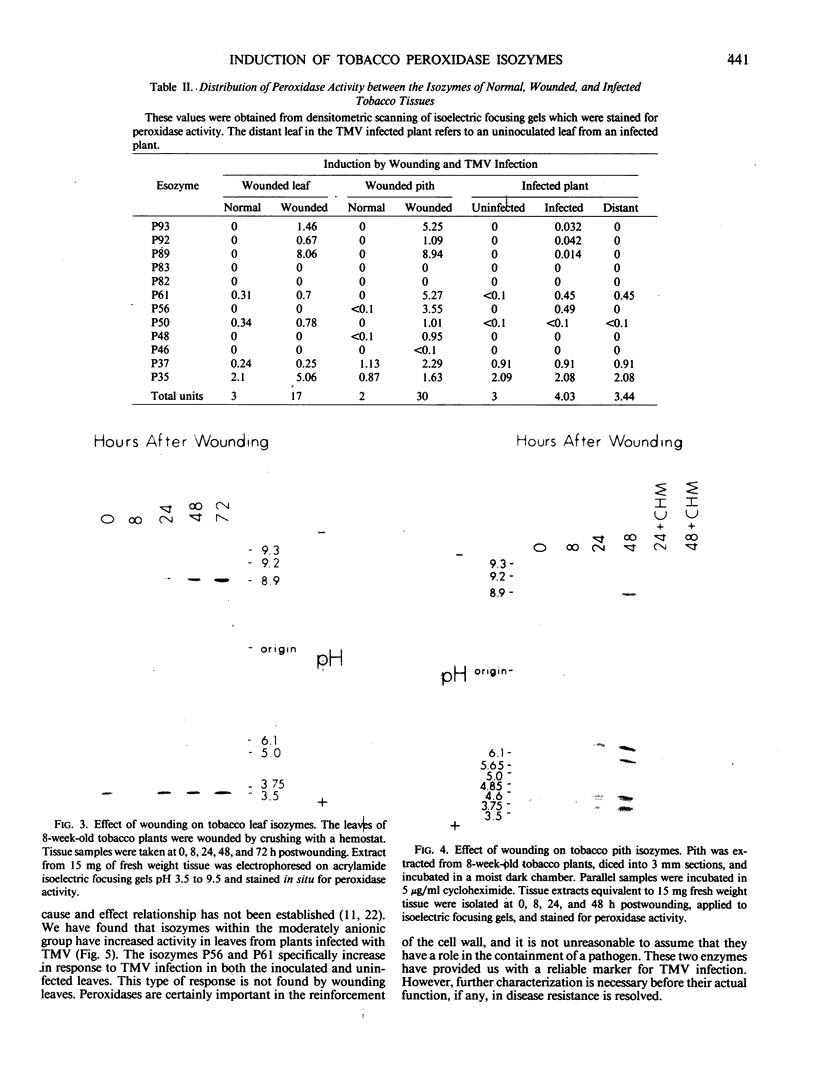
Peroxidases (EC 1.11.1.7) have been implicated in the responses of plants to physical stress and to pathogens, as well as in a variety of cellular processes including cell wall biosynthesis. Tissue samples from leaf, root, pith, and callus of Nicotiana tabacum were assayed for specific peroxidase isozymes by analytical isoelectric focusing. Each tissue type was found to exhibit a unique isozyme fingerprint. Root tissue expressed all of the detectable peroxidase isozymes in the tobacco plant, whereas each of the other tissues examined expressed a different subset of these isozymes. In an effort to determine which peroxidase isozymes from Nicotiana tabacum are involved in cell wall biosynthesis or other normal cellular functions and which respond to stress, plants were subjected to either wounding or infection with tobacco mosaic virus. Wounding the plant triggered the expression of several cationic isozymes in the leaf and both cationic and anionic isozymes in pith tissue. Maximum enzyme activity was detected at 72 hours after wounding, and cycloheximide treatment prevented this induction. Infection of tobacco with tobacco mosaic virus induced two moderately anionic isozymes in the leaves in which virus was applied and also systemically induced in leaves which were not inoculated with virus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birecka H., Miller A. Cell wall and protoplast isoperoxidases in relation to injury, indoleacetic Acid, and ethylene effects. Plant Physiol. 1974 Apr;53(4):569–574. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.4.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espelie K. E., Franceschi V. R., Kolattukudy P. E. Immunocytochemical localization and time course of appearance of an anionic peroxidase associated with suberization in wound-healing potato tuber tissue. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):487–492. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira L. Mechanisms of induced resistance in plants. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:51–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon L. C. Induction by 2-chloroethylophosphonic acid of viral-like lesions, associated proteins, and systemic resistance in tobacco. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):417–420. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]