Abstract
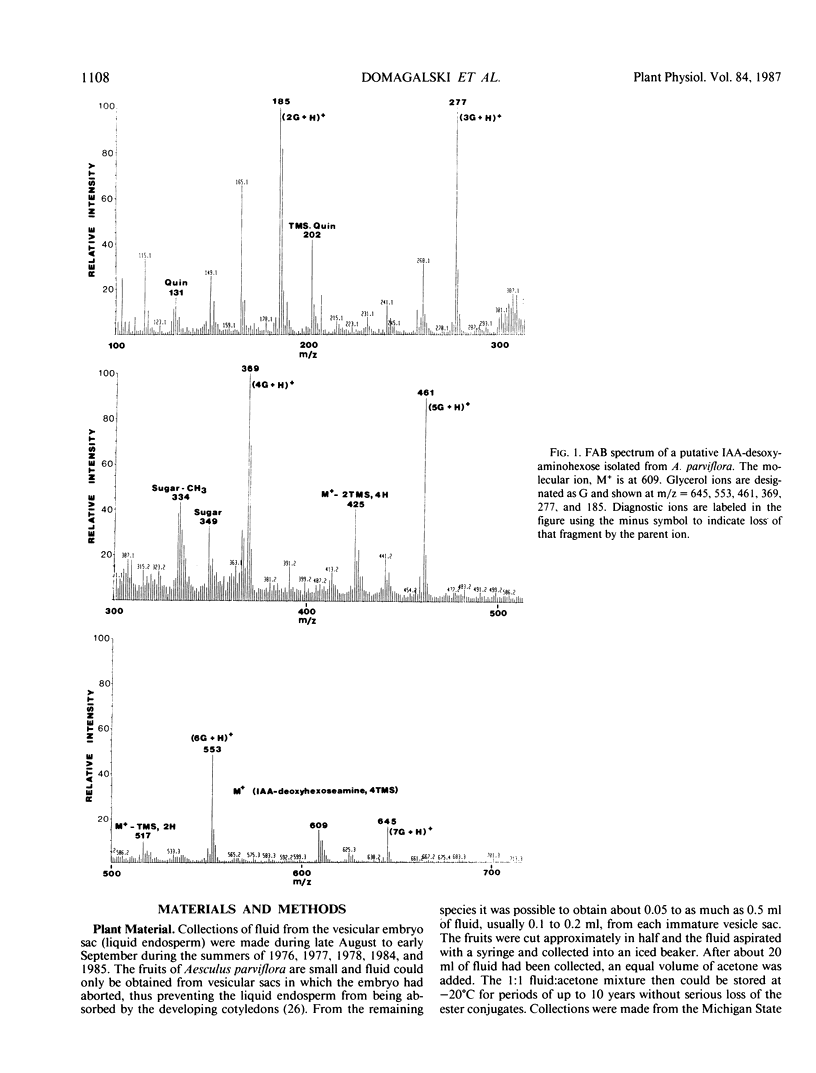
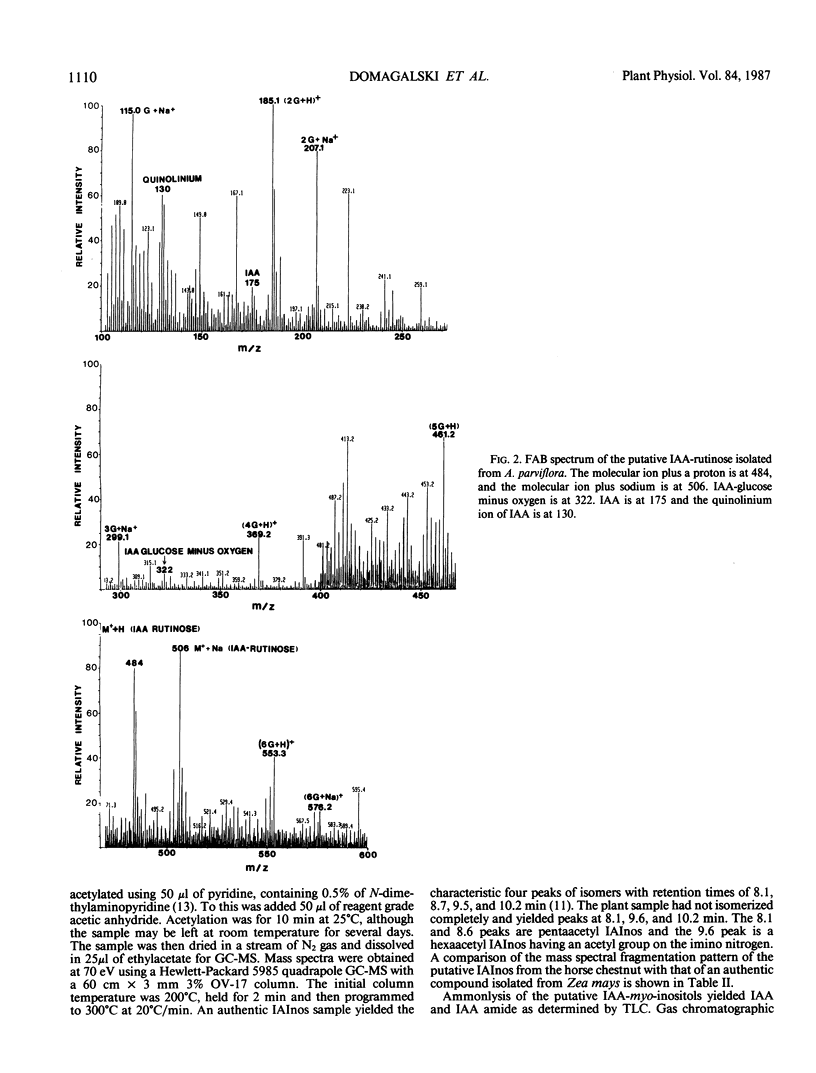
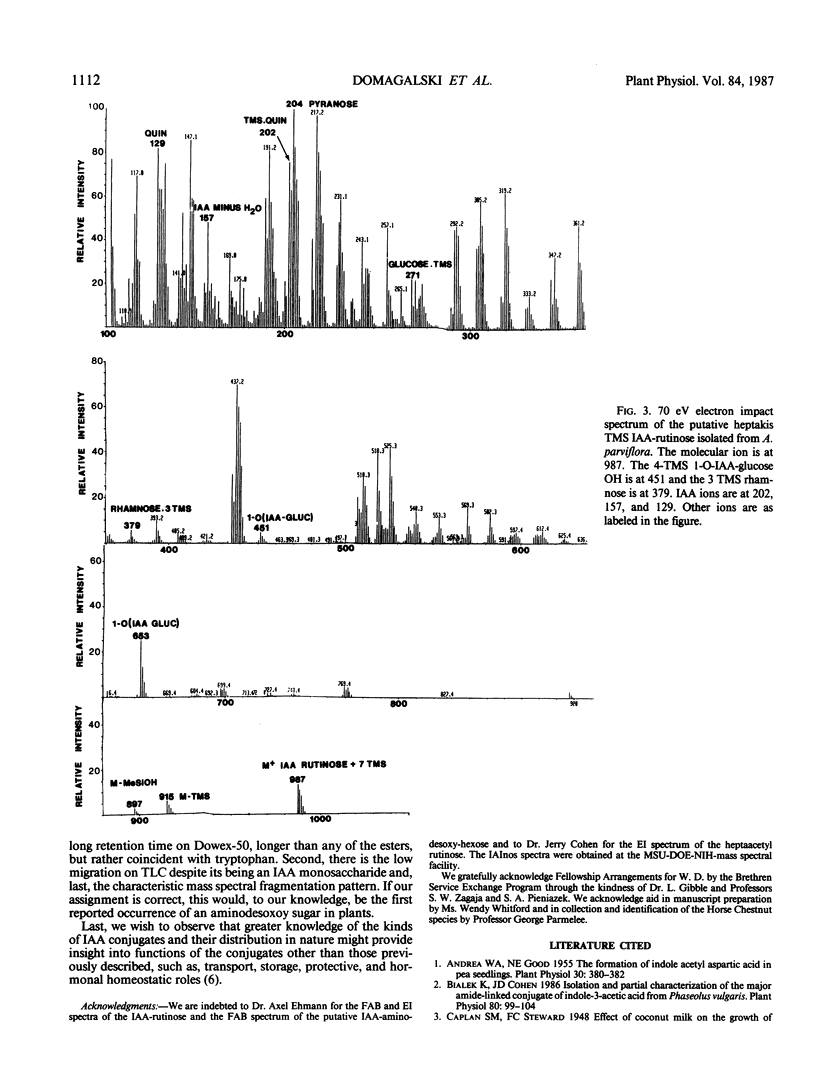
Esters of indole-3-acetic acid were extracted and purified from the liquid endosperm of immature fruits of various species of the horse chestnut (Aesculus parviflora, A. baumanni, A.pavia rubra, and A. pavia humulis). The liquid endosperm contained, at least 12 chromatographically distinct esters. One of these compounds was purified and characterized as an ester of indole-3-acetic acid and myo-inositol. A second compound was found to be an ester of indole-3-acetic acid and the disaccharide rutinose (glucosyl-rhamnose). A third compound was partially characterized as an ester of indole-3-acetic acid and a desoxyaminohexose.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreae W. A., Good N. E. The Formation of Indoleacetylaspartic Acid in Pea Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):380–382. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialek K., Cohen J. D. Isolation and Partial Characterization of the Major Amide-Linked Conjugate of Indole-3-Acetic Acid from Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):99–104. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisnell J. R. Myo-inositol esters of indole-3-acetic acid are endogenous components of Zea mays L. shoot tissue. Plant Physiol. 1984;74:278–283. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. D. Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Indole-3-Acetyl-l-Aspartate from Seeds of Glycine max L. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):749–753. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann A. Identification of 2-O (indole-3-acetyl)-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-(indole-3-acetyl)-D-glucopyranose and 6-O-(indole-3-acetyl)-D-glucopyranose from kernels of Zea mays by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Carbohydr Res. 1974 May;34(1):99–114. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)80374-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann A. The van urk-Salkowski reagent--a sensitive and specific chromogenic reagent for silica gel thin-layer chromatographic detection and identification of indole derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1977 Feb 11;132(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Baldi B. G., Cohen J. D. Identification of Indole-3-Acetylglutamate from Seeds of Glycine max L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):256–258. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hangarter R. P., Good N. E. Evidence That IAA Conjugates Are Slow-Release Sources of Free IAA in Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1424–1427. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutzinger O., Kosuge T. Microbial synthesis and degradation of indole-3-acetic acid. 3. The isolation and characterization of indole-3-acetyl-epsilon-L-lysine. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):601–605. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoszynski M., Bandurski R. S. Transport and metabolism of indole-3-acetyl-myo-inositol-galactoside in seedlings of Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1986;80:961–964. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Nicholls P. B., Bandurski R. S. A partial characterization of indoleacetylinositols from ZEA mays. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 8;20(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalczuk L., Bandurski R. S. Enzymic synthesis of 1-O-indol-3-ylacetyl-beta-D-glucose and indol-3-ylacetyl-myo-inositol. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):273–281. doi: 10.1042/bj2070273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival F. W., Bandurski R. S. Esters of indole-3-acetic Acid from Avena seeds. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jul;58(1):60–67. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival F. W. Isolation of Indole-3-Acetyl Amino Acids using Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):259–263. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piskornik Z., Bandurski R. S. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Glucan Containing Indole-3-acetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jul;50(1):176–182. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda M., Ehmann A., Bandurski R. S. Gas-Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Indole-3-acetic Acid Myoinositol Esters in Maize Kernels. Plant Physiol. 1970 Nov;46(5):715–719. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZENK M. H. I-(Indole-3-acetyl)-beta-D-glucose, a new compound in the metabolism of indole-3-acetic acid in plants. Nature. 1961 Jul 29;191:493–494. doi: 10.1038/191493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinbo M., Sherman W. R. Gas chromatography and mass spectrometry of trimethylsilyl sugar phosphates. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Apr 8;92(7):2105–2114. doi: 10.1021/ja00710a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


