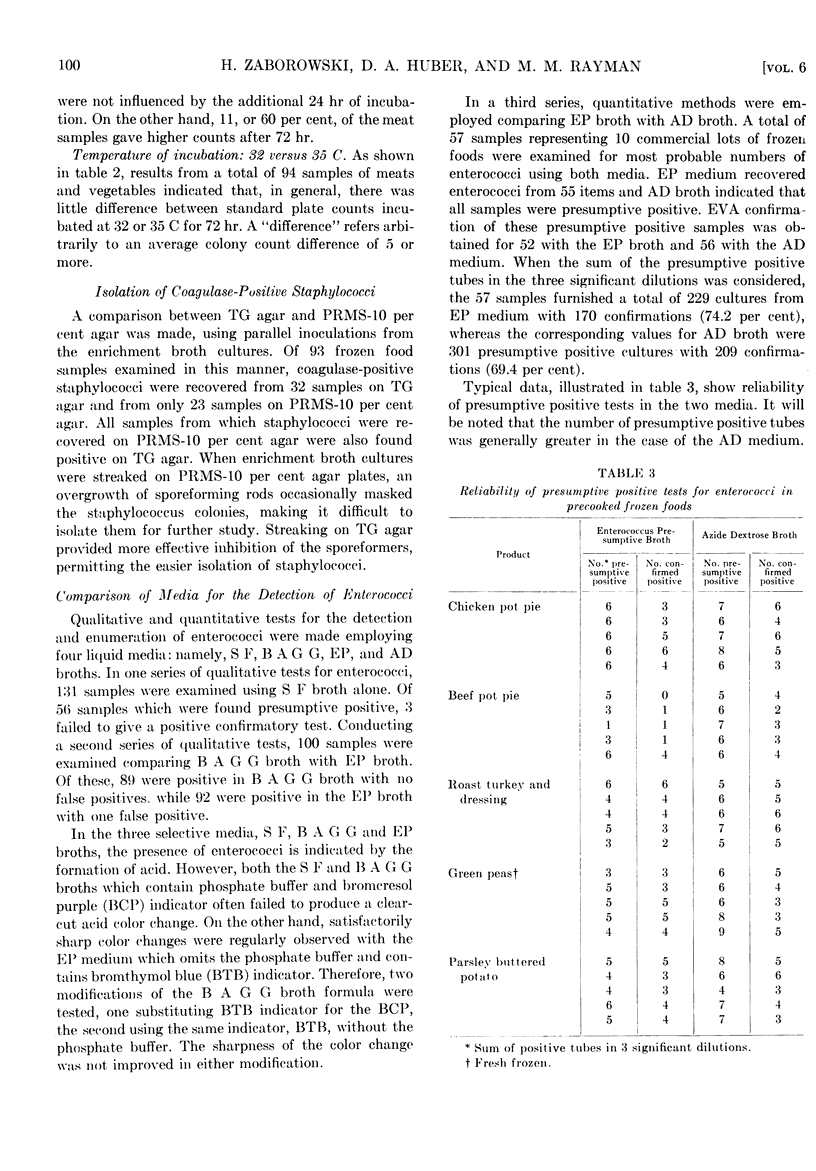
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON M. O. Comparison of coliform and enterococcus organisms as indices of pollution in frozen foods. Food Res. 1949 Sep-Oct;14(5):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1949.tb16253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYRNE A. F., RAYMAN M. M., SCHNEIDER M. D. Methods for the detection and estimation of numbers of Salmonella in dried eggs and other food products. Appl Microbiol. 1955 Nov;3(6):368–372. doi: 10.1128/am.3.6.368-372.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman G. H. The Significance of Sodium Chloride in Studies of Staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1945 Aug;50(2):201–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. B., BUETTNER L. G., NIVEN C. F., Jr Evaluation of the coagulase test in the study of staphylococci associated with food poisoning. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):481–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.481-484.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajna A. A., Perry C. A. Comparative Study of Presumptive and Confirmative Media for Bacteria of the Coliform Group and for Fecal Streptococci. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1943 May;33(5):550–556. doi: 10.2105/ajph.33.5.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. H., White E. C. SODIUM CHLORIDE MEDIA FOR THE SEPARATION OF CERTAIN GRAM-POSITIVE COCCI FROM GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. J Bacteriol. 1929 Jul;18(1):43–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.18.1.43-57.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES A. H., FERGUSON W. E. A study of methods of preparing food products for microbiological analyses. Food Res. 1951 Mar-Apr;16(2):126–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1951.tb17359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARKIN E. P., LITSKY W., FULLER J. E. Fecal streptococci in frozen foods. II. Effect of freezing storage on Escherichia coli and some fecal streptococci inoculated onto green beans. Appl Microbiol. 1955 Mar;3(2):102–104. doi: 10.1128/am.3.2.102-104.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITSKY W., MALLMANN W. L., FIFIELD C. W. Comparison of the most probable numbers of Escherichia coli and enterococci in river waters. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1955 Aug;45(8):1049–1053. doi: 10.2105/ajph.45.8.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALLMANN W. L., SELIGMANN E. B., Jr A comparative study of media for the detection of streptococci in water and sewage. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Mar;40(3):286–289. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.3.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M., Mauer J. C., Stark P. Streptococcus fecalis. J Bacteriol. 1937 Mar;33(3):275–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.33.3.275-282.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEBOVITZ E., EVANS J. B., NIVEN C. F., Jr Tellurite-glycine agar: a selective plating medium for the quantitative detection of coagulase-positive staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):686–690. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.686-690.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


