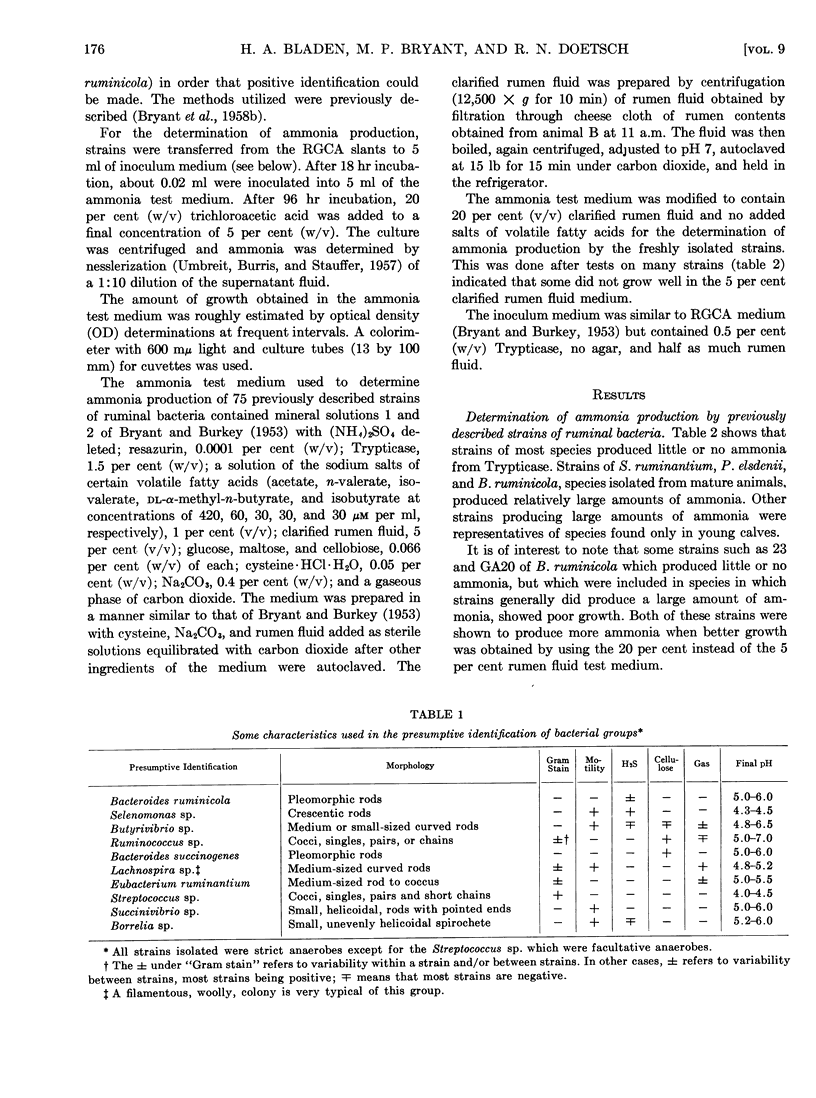
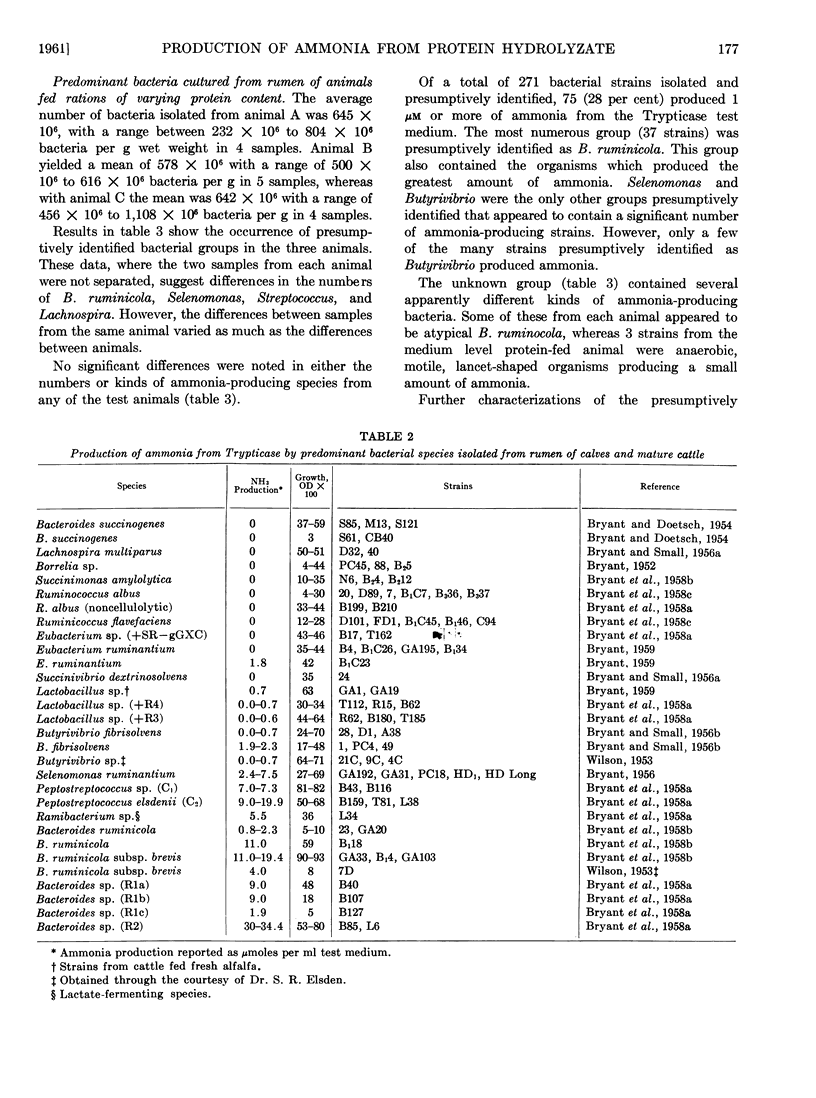
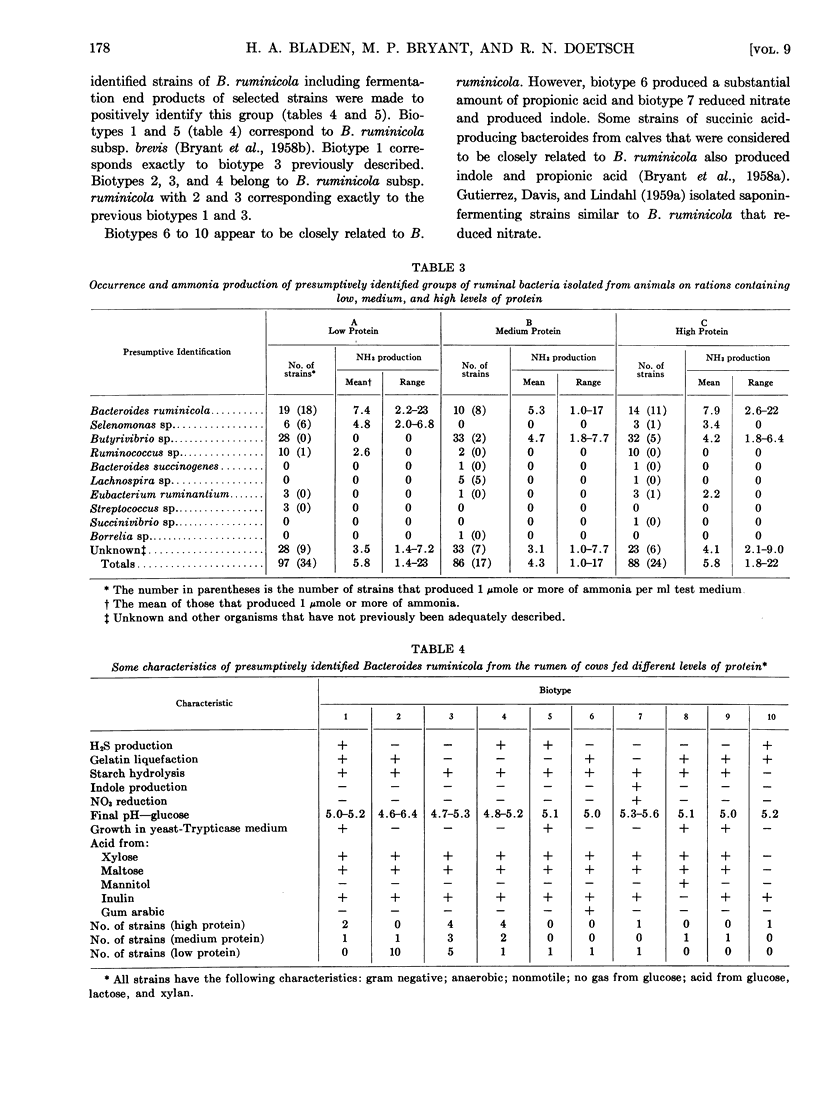
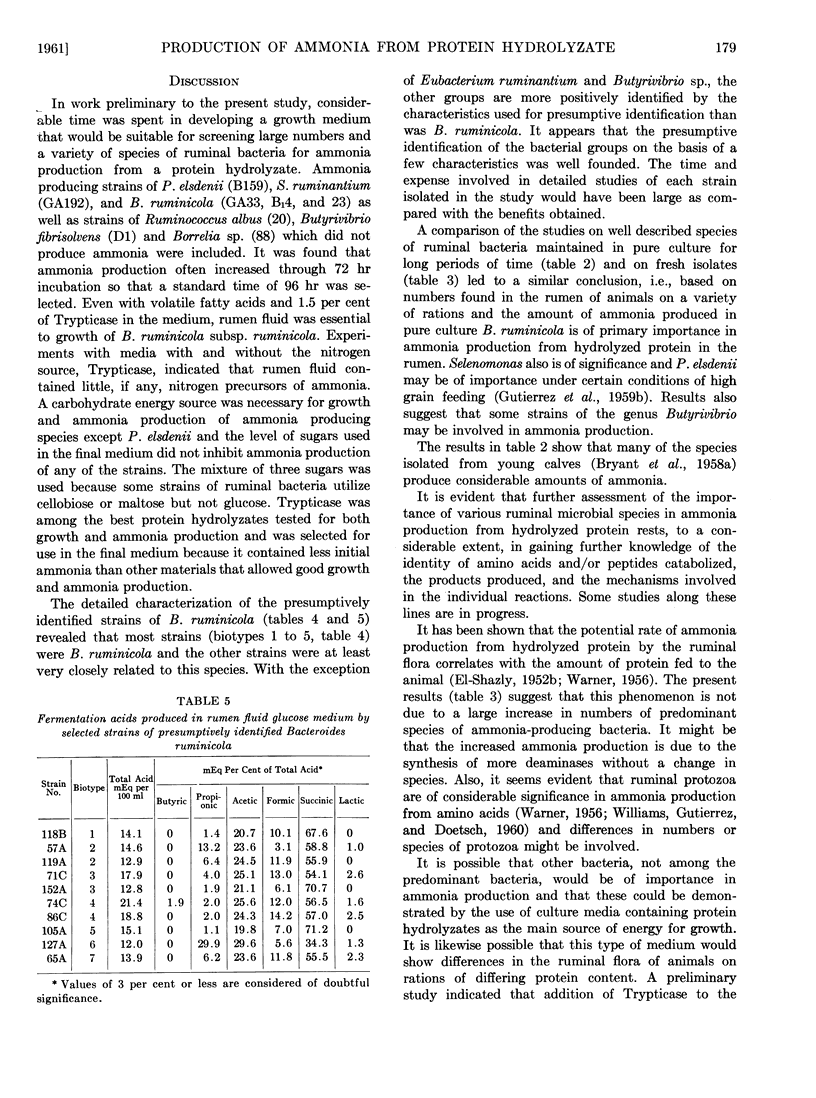
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., CHU H. Bacteroides ruminicola n. sp. and Succinimonas amylolytica; the new genus and species; species of succinic acid-producing anaerobic bacteria of the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.15-23.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., ROBINSON I. M. Characteristics of ruminal anaerobic celluloytic cocci and Cillobacterium cellulosolvens n. sp. J Bacteriol. 1958 Nov;76(5):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.529-537.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. Characteristics of two new genera of anaerobic curved rods isolated from the rumen of cattle. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.22-26.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.16-21.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. The characteristics of strains of Selenomonas isolated from bovine rumen contents. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):162–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.162-167.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. The isolation and characteristics of a spirochete from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1952 Sep;64(3):325–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.3.325-335.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-SHAZLY K. Degradation of protein in the rumen of the sheep. I. Some volatile fatty acids, including branched-chain isomers, found in vivo. Biochem J. 1952 Aug;51(5):640–647. doi: 10.1042/bj0510640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-SHAZLY K. Degradation of protein in the rumen of the sheep. II. The action of rumen micro-organisms on amino acids. Biochem J. 1952 Aug;51(5):647–653. doi: 10.1042/bj0510647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTIERREZ J., DAVIS R. E., LINDAHL I. L. Characteristics of saponin-utilizing bacteria from the rumen of cattle. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Sep;7:304–308. doi: 10.1128/am.7.5.304-308.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTIERREZ J., DAVIS R. E., LINDAHL I. L., WARWICK E. J. Bacterial changes in the rumen during the onset of feed-lot bloat of cattle and characteristics of Peptostreptococcus elsdenii n. sp. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Jan;7(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/am.7.1.16-22.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS D. Amino-acid metabolism in the rumen of the sheep. Br J Nutr. 1955;9(3):215–230. doi: 10.1079/bjn19550035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS D., ELSDEN S. R. The fermentation of L-threonine, L-serine, L-cysteine and acrylic acid by a gram-negative coccus. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):683–692. doi: 10.1042/bj0600683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER A. C. Proteolysis by rumen micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):749–762. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


