Abstract
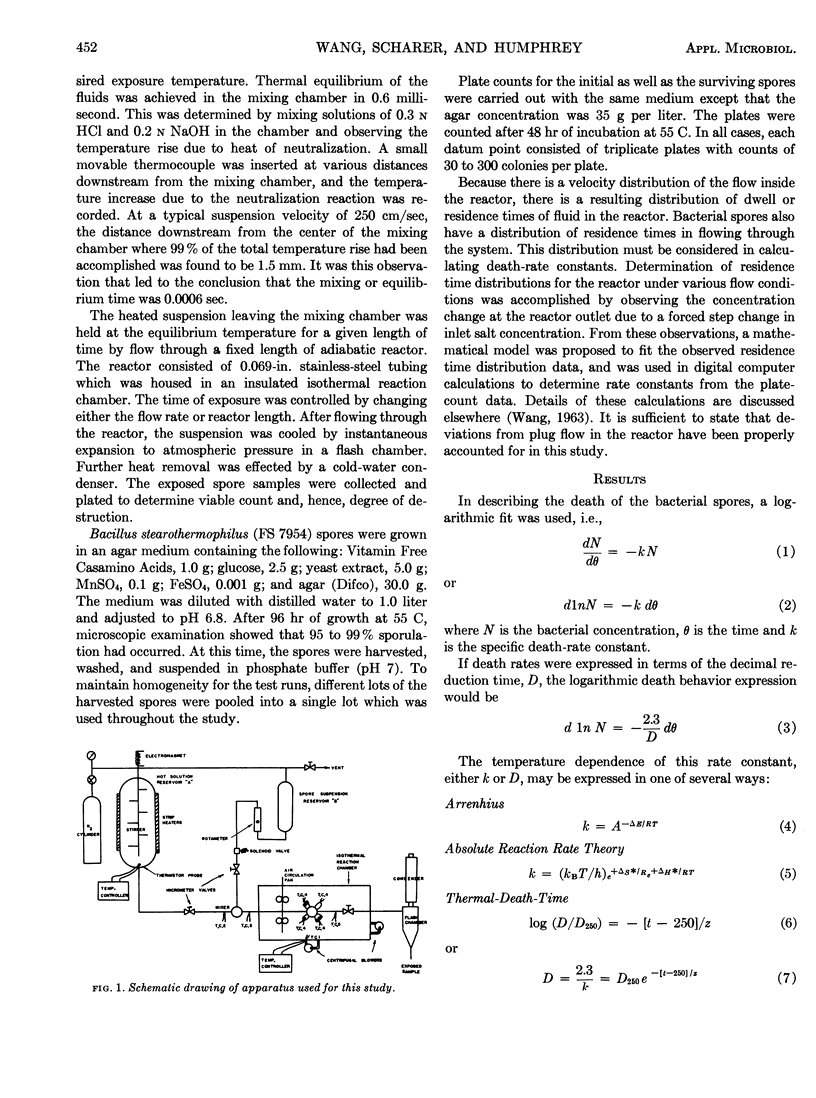
The kinetics of death of Bacillus stearothermophilus spores (FS 7954) suspended in phosphate buffer (pH 7) were studied over a temperature range of 127.2 to 143.8 C and exposure times of 0.203 to 4.150 sec. These short exposure were achieved by use of a tubular flow reactor in which a suspension of spores was injected into a hot flowing stream at the entrance of the reactor. Thermal equilibria of the suspension with the hot stream was achieved within 0.0006 sec. After flow through a fixed length of reactor, the stream containing the spores was cooled by flash vaporization and then assayed for viable count. The death rate data were fitted by a logarithmic expression. However, logarithmic death rate was only approximated in the tail or high-kill regions of exposure. Death rate constants obtained from this portion of the data were found to correlate by Arrhenius as well as Absolute Reaction Rate Theory relationships. Thermal-death time curves were found to correlate the data rather poorly. The activation energy and frequency constant for an Arrhenius relationship fit of the data were found to be 83.6 kcal/gmole and 1047.2 min-1, respectively. The standard enthalpy and entropy changes for an Absolute Reaction Rate Theory relationship fit of the data were found to be 84.4 kcal/gmole and 157 cal/gmole-K, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON E. E., ESSELEN W. B., Jr, FELLERS C. R. Effect of acids, salt, sugar and other food ingredients on thermal resistance of Bacillus thermoacidurans. Food Res. 1949 Nov-Dec;14(6):499–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1949.tb16261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS E. B., DUNKLEY W. L., PERRY R. L., EDMONDSON L. F. Thermal destruction of Micrococcus freudenreichii and Streptococcus thermophilus with particular reference to pasteurization without holding. Appl Microbiol. 1956 May;4(3):133–140. doi: 10.1128/am.4.3.133-140.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn O. PHYSICAL METHODS OF STERILIZATION OF MICROORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1945 Mar;9(1):1–47. doi: 10.1128/br.9.1.1-47.1945_1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


