Abstract
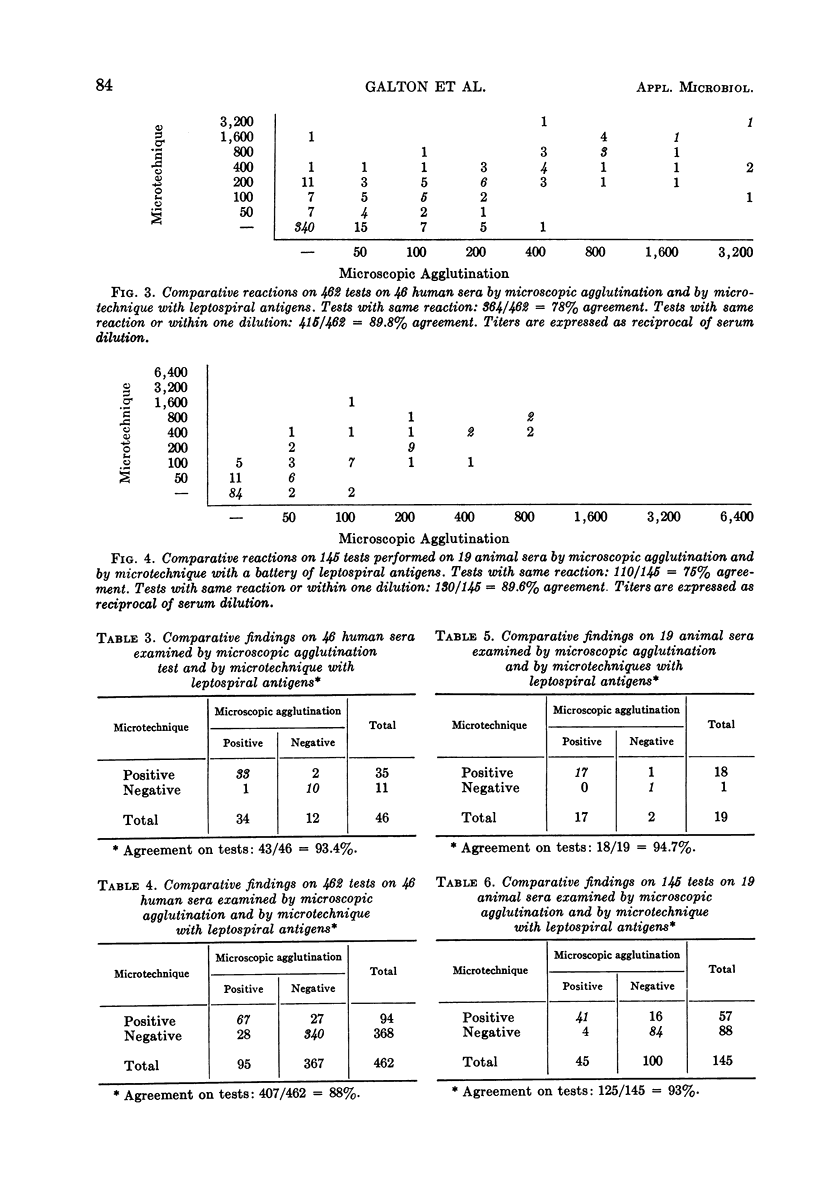
A microtechnique has been developed and adapted successfully to the microscopic agglutination test with live antigens for detection of leptospiral antibodies. Simultaneous titrations were performed by the conventional microscopic agglutination test and the microtechnique. When the microtechnique was used to screen 50 unknown leptospiral strains with a battery of hyperimmune sera, 98% agreement was obtained with the conventional procedure. Comparative data on 635 tests on these 50 cultures established the reliability of the microtechnique. Results with the two tests on 46 human sera revealed 93% agreement in the detection of leptospiral antibodies. The validity and reliability of the microtechnique obtained in these comparative studies suggests that it can be used as a valuable screening procedure for the microscopic agglutination test for preliminary cross agglutination studies on unknown strains and for the detection of leptospiral antibodies in human and animal sera.
Full text
PDF
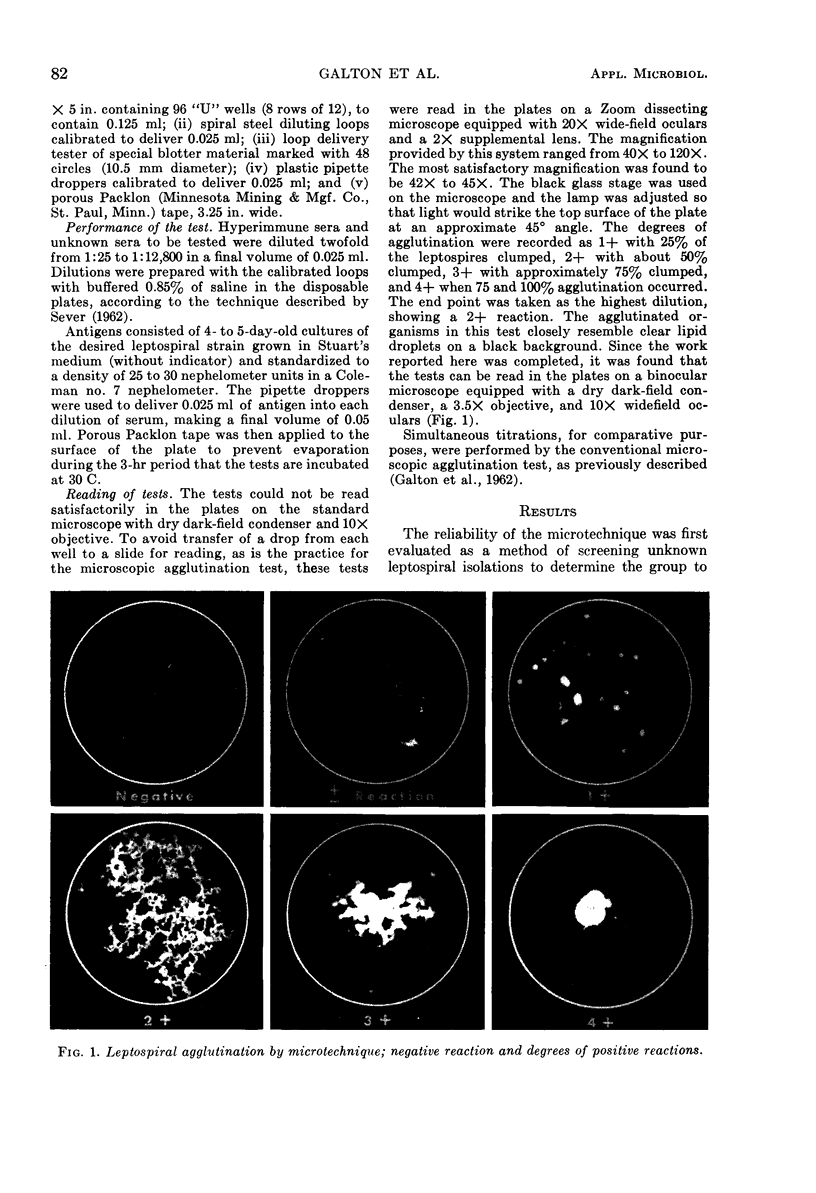


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GALTON M. M., GORMAN G. W., SHOTTS E. B., Jr A new leptospiral subserotype in the hebdomadis group. Public Health Rep. 1960 Oct;75:917–921. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKATSY G. The use of spiral loops in serological and virological micro-methods. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]