Abstract
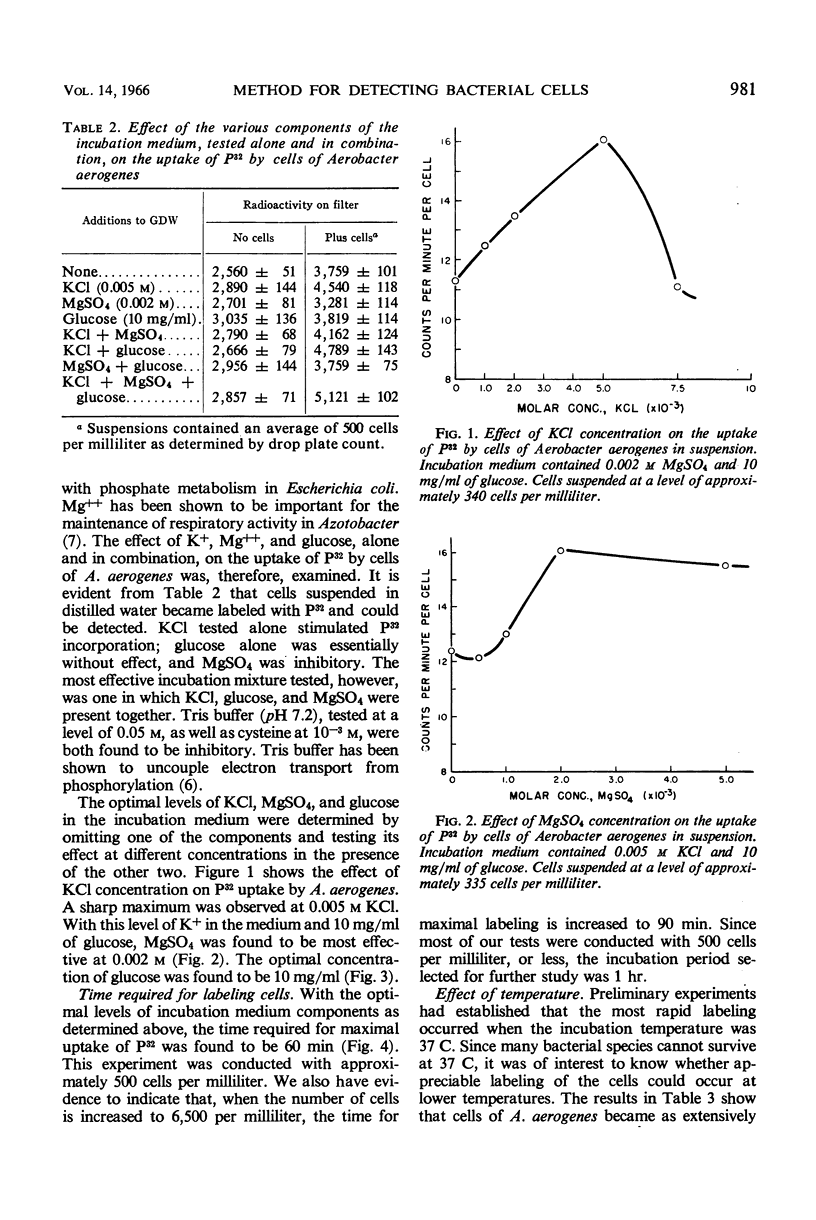
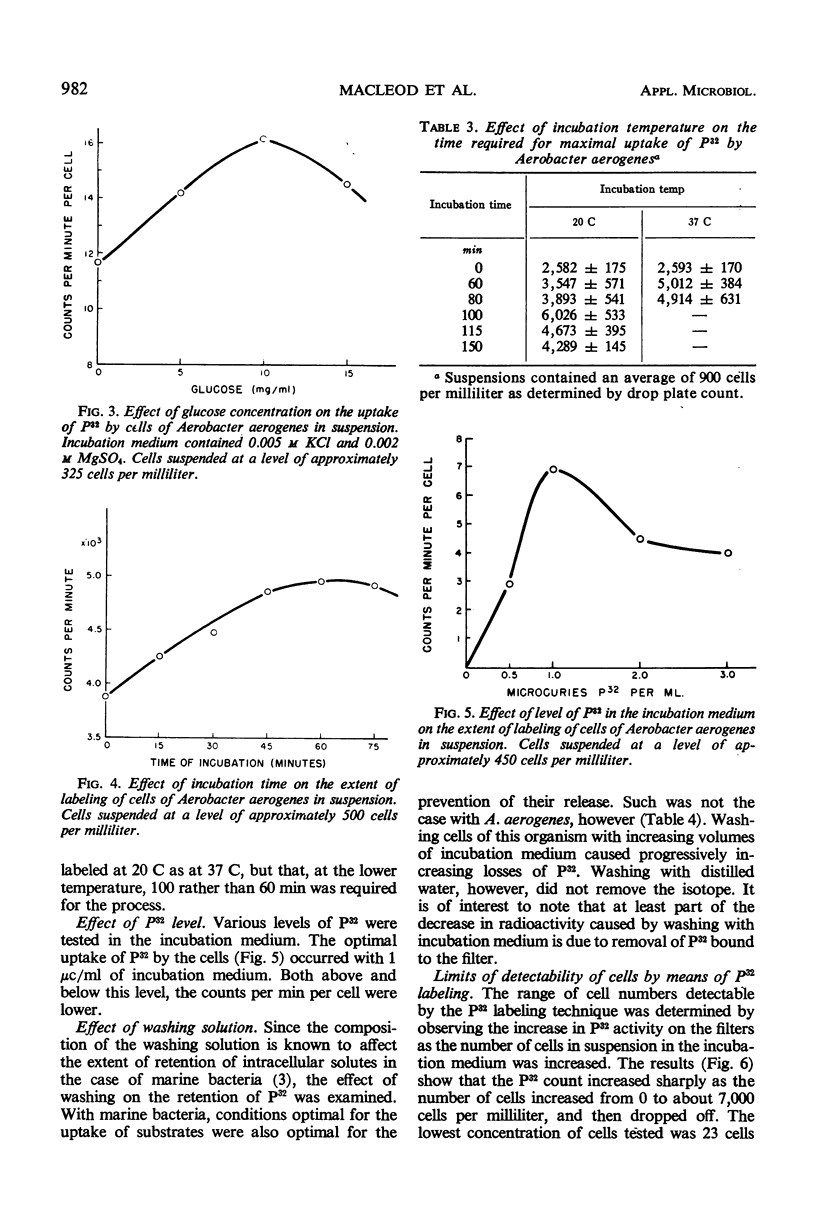
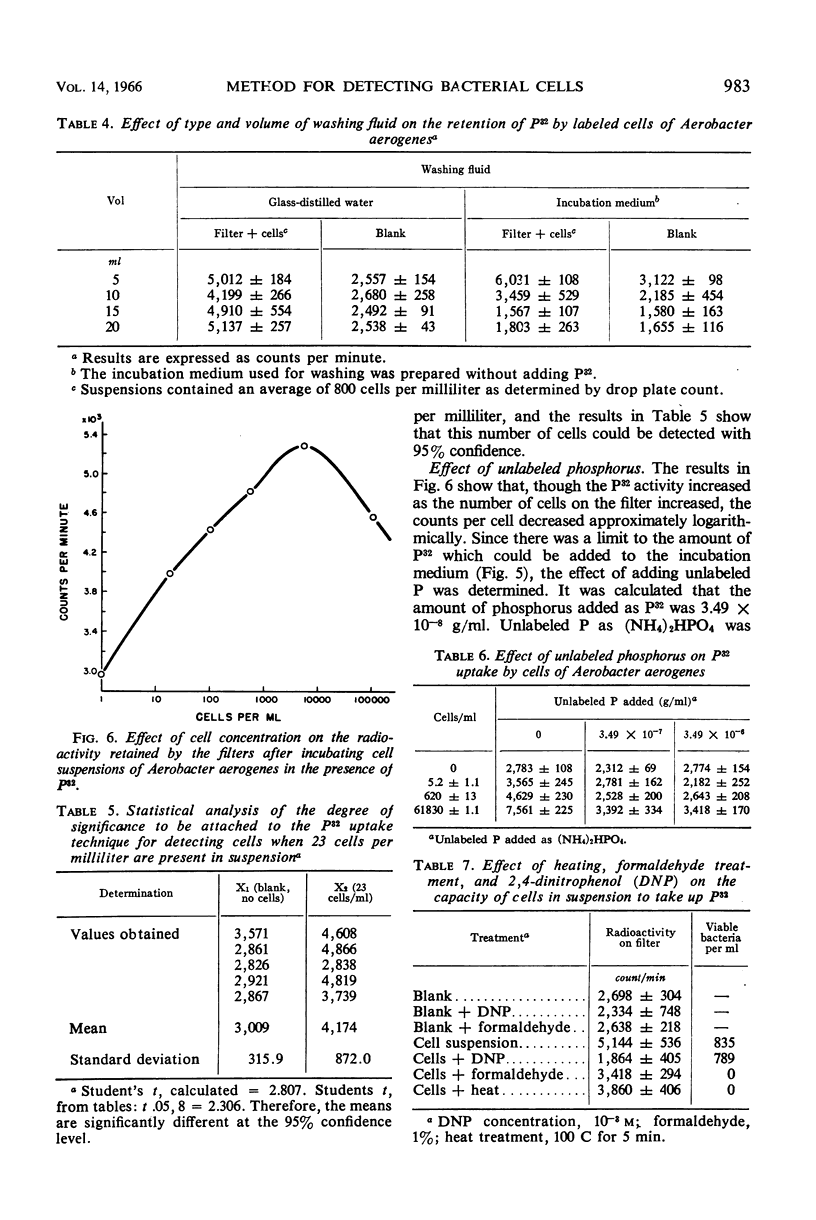
A rapid sensitive method for the detection of viable bacterial cells is described in which P32 as inorganic orthophosphate is used to label the cells. Factors affecting the uptake of P32 by cells as well as the sensitivity of the method have been explored with suspensions of Aerobacter aerogenes. The uptake of P32O4 is dependent on several factors. Of various incubation media tested, one composed of 0.005 m KCl, 0.002 m MgSO4 and 10 mg/ml of glucose was found to best stimulate the uptake of the tracer. Incubation time and temperature and level of isotope and of unlabeled P also affected uptake. Labeled cells were collected on a membrane filter for measurement of radioactivity. Under optimal conditions, as few as 23 viable cells per milliliter were detected in 1 hr with 95% confidence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON D. E., MCFADDEN B. A. Use of membrane filters in the measurement of biological incorporation of radioactive isotopes. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):123–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.1.123-124.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKLAND F. E., HARPER G. J., MORTON J. D. Use of spores labelled with radiophosphorus in the study of the respiratory retention of aerosols. Nature. 1950 Aug 26;166(4217):354–355. doi: 10.1038/166354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., MacLeod R. A. A role for inorganic ions in the maintenance of intracellular solute concentrations in a marine pseudomonad. Nature. 1965 May 1;206(983):531–531. doi: 10.1038/206531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD N. E. Uncoupling of the Hill reaction from photophosphorylation by anions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Mar;96:653–661. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUCHER C. R., SARACHEK A., KOCHOLATY W. A time-course respiratory inactivation associated with Azobacter cells deprived of Mg++. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jul;70(1):120–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.1.120-124.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korgaonkar K. S., Ranade S. S. Evaluation of acridine orange fluorescence test in viability studies on Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):185–190. doi: 10.1139/m66-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN G. V. RAPID MICROBIOLOGICAL DETERMINATIONS WITH RADIOISOTOPES. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1963;5:95–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALLIN M. L., KAPLAN N. O. Uptake of P32 in resting cells of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1959 Feb;77(2):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.2.125-130.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONIER T. Labeling crown gall bacteria with P32 for radioautography. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):259–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.259-268.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


