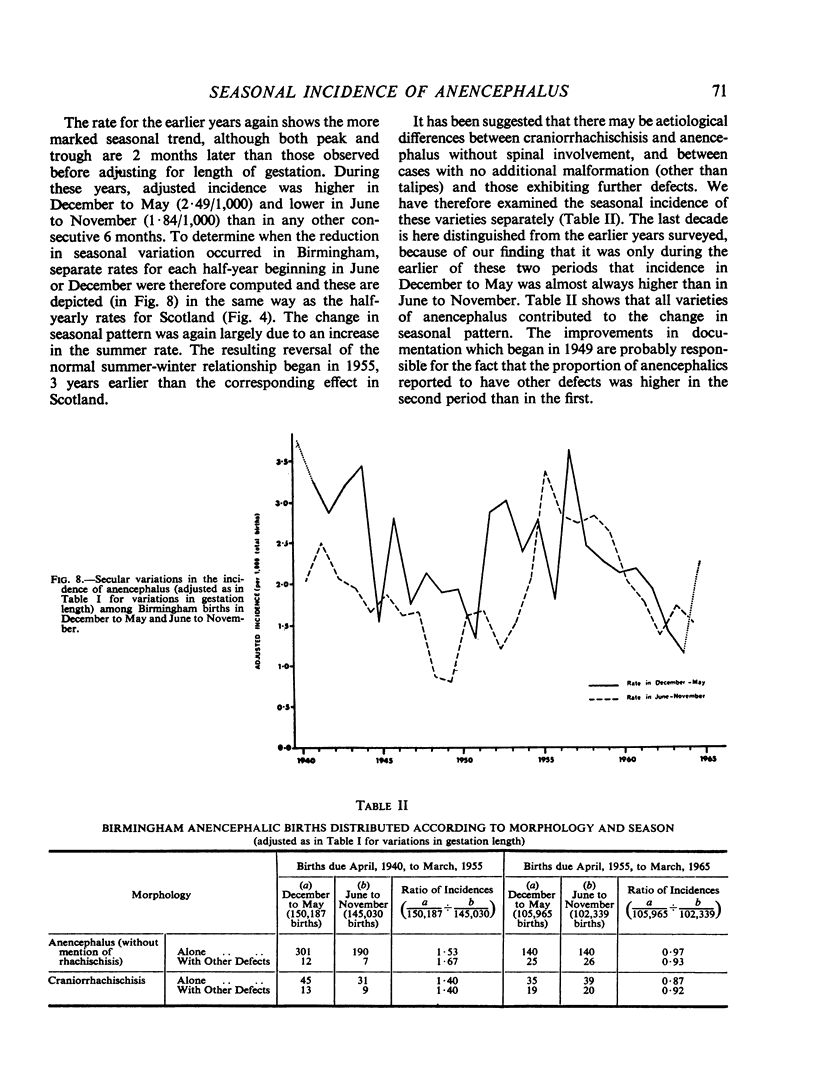
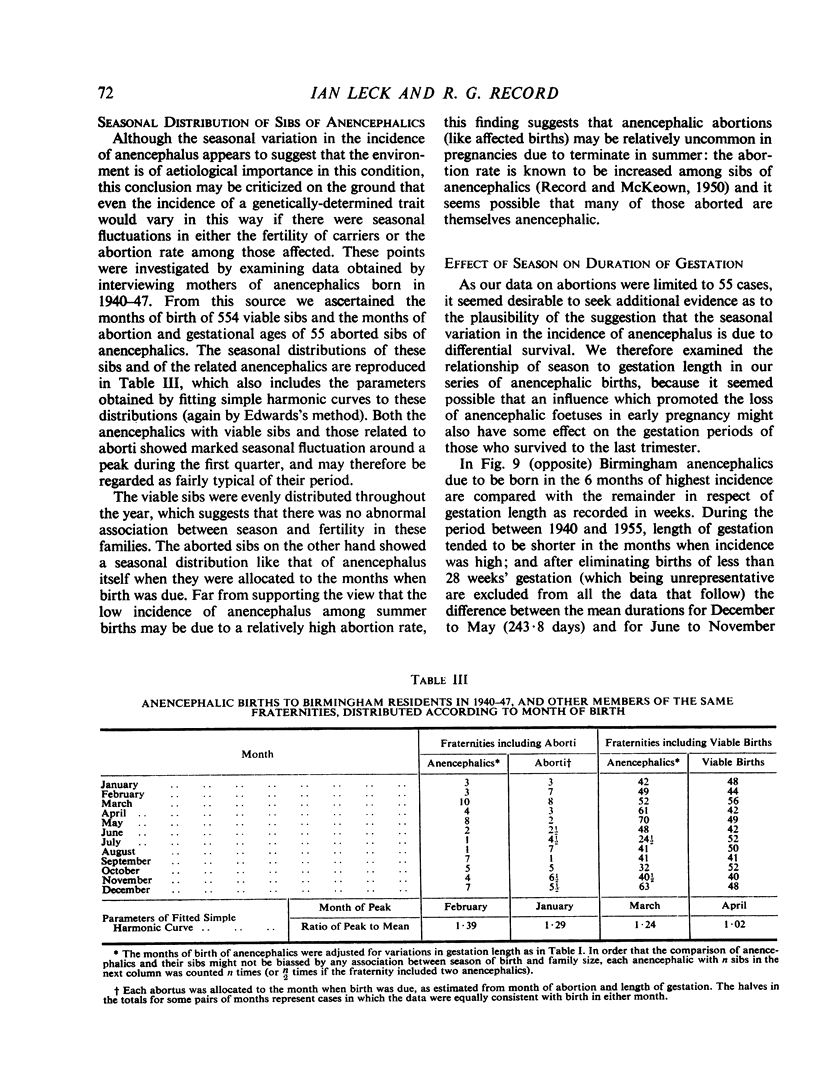
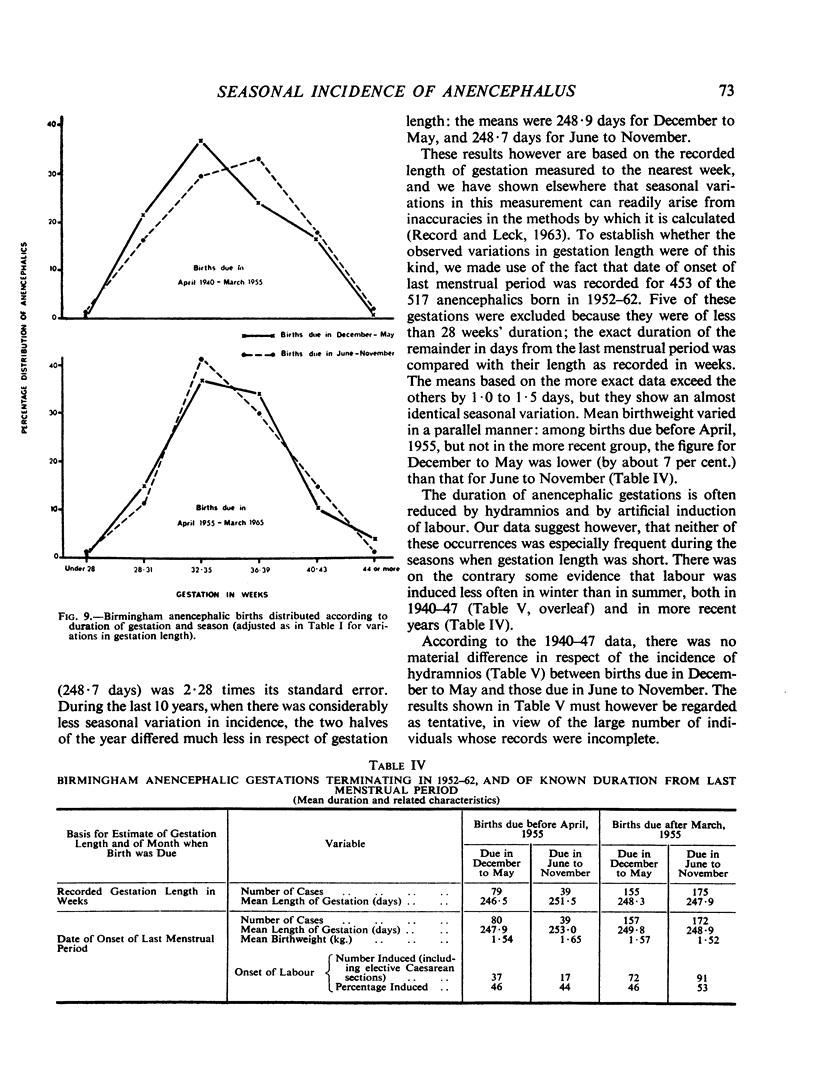
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHARLES E. Statistical utilization of maternity and child welfare records. Br J Soc Med. 1951 Jan;5(1):41–61. doi: 10.1136/jech.5.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREZAL J., KELLEY J., GUILLEMOT M. L., LAMY M. ANENECEPHALY IN FRANCE. Am J Hum Genet. 1964 Sep;16:336–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACMAHON B., MCKEOWN T. A note on the sex ratio in anencephalus. Br J Soc Med. 1952 Oct;6(4):265–266. doi: 10.1136/jech.6.4.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACMAHON B., PUGH T. F., INGALLS T. H. Anencephalus, spina bifida, and hydrocephalus incidence related to sex, race, and season of birth, and incidence in siblings. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1953 Oct;7(4):211–219. doi: 10.1136/jech.7.4.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKEOWN T., RECORD R. G. Seasonal incidence of congenital malformations of the central nervous system. Lancet. 1951 Jan 27;1(6648):192–196. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)93354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECORD R. G. Anencephalus in Scotland. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1961 Jul;15:93–105. doi: 10.1136/jech.15.3.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECORD R. G., LECK I. SOURCES OF SEASONAL VARIATION IN RECORDED LENGTH OF GESTATION. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1963 Jul;17:128–132. doi: 10.1136/jech.17.3.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHELLS R. W., CHINN E. R., FRANKLIN D. ANENCEPHALY IN LIVERPOOL. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1964 Jun;6:231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1964.tb10782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


