Abstract
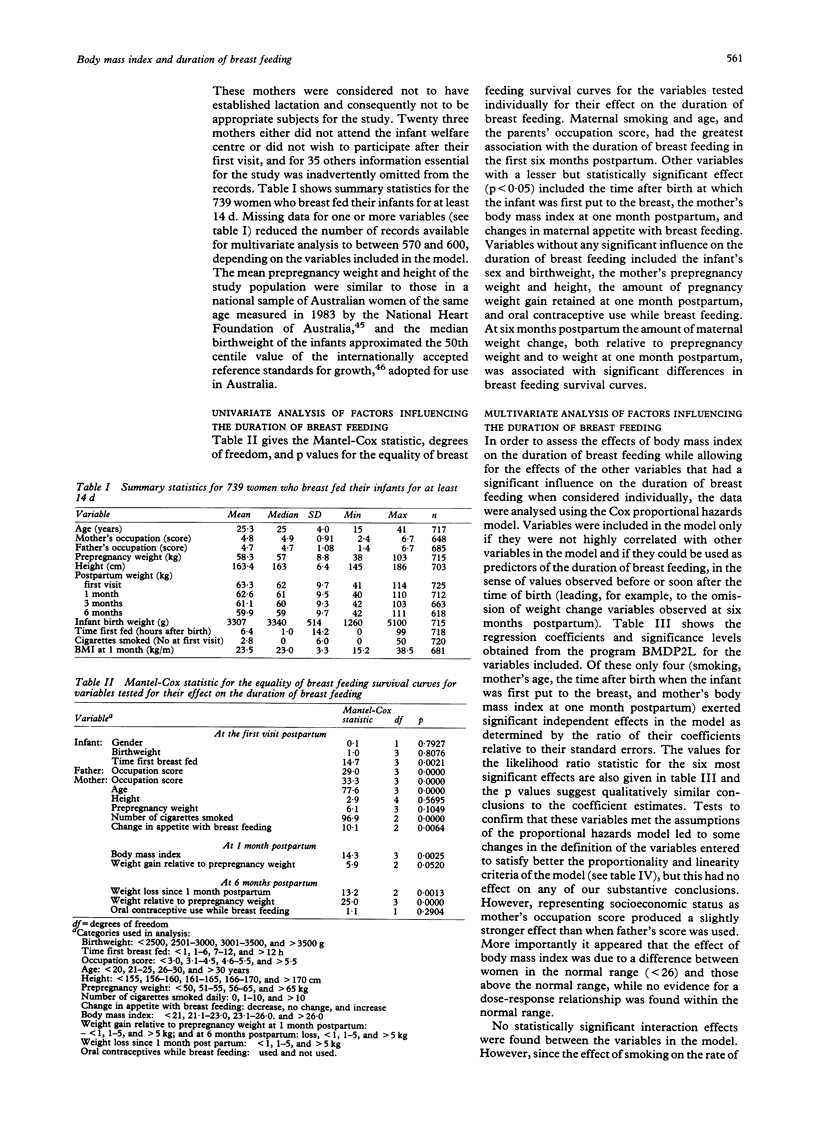
STUDY OBJECTIVE--The aim was to determine whether excess weight in lactating women is associated with earlier cessation of breastfeeding. DESIGN--The study was to prospective cohort analysis using a community sample of women. SETTING--Geelong the regional centre of the Barwon Region of Victoria, Australia, in 1984-85. SUBJECTS--All women who were breast feeding and whose first infant was born between 1 May 1984 and 30 April 1985 were asked to participate. Of these, 739 women participated, a response rate of 81%. MAIN RESULTS--Smoking, mother's age and occupation, the time the infant was first put to the breast, and mother's body mass index at one month postpartum all exerted statistically significant independent effects on the duration of breast feeding, assessed using Cox's proportional hazards regression modelling. The strongest effects were for smoking, with an adjusted relative risk for cessation of breast feeding of 2.5 (95% CI 1.9 to 3.1) for 10 cigarettes per day v no smoking, and maternal age, with relative risk of 2.2 (95% CI 1.5 to 3.1) for a 20 year old mother relative to a 30 year old. The relative risk for women with a body mass index above 26 was 1.5 (95% CI 1.1 to 2.0). CONCLUSIONS--Excess weight at one month postpartum, as determined by a body mass index above the normal range, was found to be an independent risk factor for early cessation of breast feeding and together with smoking, maternal age, occupation, and the time the infant is first put to the breast can be used to identify, early in the postpartum period, those women most likely to benefit from counselling in order to breast feed their infants successfully.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borda E. C., Feeney E. M., Morris M. M., Gupta J. M. Current patterns of breast feeding in a New South Wales maternity hospital. Med J Aust. 1978 Sep 9;2(6):250–253. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1978.tb131509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butte N. F., Garza C., Stuff J. E., Smith E. O., Nichols B. L. Effect of maternal diet and body composition on lactational performance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Feb;39(2):296–306. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/39.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. P. Breastfeeding in the Boston suburbs in relation to personal-social factors. Are pediatricians thoughtlessly influencing the outcome in their postpartum care? Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1977 Apr;16(4):352–356. doi: 10.1177/000992287701600410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugdale A. E., Eaton-Evans J. The effect of lactation and other factors on post-partum changes in body-weight and triceps skinfold thickness. Br J Nutr. 1989 Mar;61(2):149–153. doi: 10.1079/bjn19890105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekwo E. E., Dusdieker L., Booth B., Seals B. Psychosocial factors influencing the duration of breastfeeding by primigravidas. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Mar;73(2):241–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb09936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray-Donald K., Kramer M. S., Munday S., Leduc D. G. Effect of formula supplementation in the hospital on the duration of breast-feeding: a controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics. 1985 Mar;75(3):514–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn T. R. The incidence of breast feeding and reasons for weaning. N Z Med J. 1984 Jun 13;97(757):360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill P. V., Drizd T. A., Johnson C. L., Reed R. B., Roche A. F., Moore W. M. Physical growth: National Center for Health Statistics percentiles. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Mar;32(3):607–629. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.3.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurinij N., Shiono P. H., Rhoads G. G. Breast-feeding incidence and duration in black and white women. Pediatrics. 1988 Mar;81(3):365–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon A. J. Effects of smoking on breast feeding. Arch Dis Child. 1983 May;58(5):378–380. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.5.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon A. J. Factors influencing breast feeding. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Mar;73(2):268–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb09942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez G. A., Nalezienski J. P. 1980 update: the recent trend in breast-feeding. Pediatrics. 1981 Feb;67(2):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice A. M., Prentice A. Energy costs of lactation. Annu Rev Nutr. 1988;8:63–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.08.070188.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Cole T. J., Coward W. A. Lactational performance in relation to energy intake in the baboon. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Jun;41(6):1270–1276. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/41.6.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salariya E. M., Easton P. M., Cater J. I. Duration of breast-feeding after early initiation and frequent feeding. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1141–1143. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels S. E., Margen S., Schoen E. J. Incidence and duration of breast-feeding in a health maintenance organization population. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Sep;42(3):504–510. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.3.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölin S., Hofvander Y., Hillervik C. Factors related to early termination of breast feeding. A retrospective study in Sweden. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 Jul;66(4):505–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölin S., Hofvander Y., Hillervik C. Factors related to early termination of breast feeding. A retrospective study in Sweden. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 Jul;66(4):505–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smibert J. The return to breast feeding. Med J Aust. 1978 Nov 18;2(11):533–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling J., Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J., Taylor B. Breast feeding success and failure. Aust Paediatr J. 1979 Dec;15(4):271–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1979.tb01244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strode M. A., Dewey K. G., Lönnerdal B. Effects of short-term caloric restriction on lactational performance of well-nourished women. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Mar;75(2):222–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamminen T., Verronen P., Saarikoski S., Göransson A., Tuomiranta H. The influence of perinatal factors on breast feeding. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Jan;72(1):9–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weile B., Rubin D. H., Krasilnikoff P. A., Kuo H. S., Jekel J. F. Infant feeding patterns during the first year of life in Denmark: factors associated with the discontinuation of breast-feeding. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43(12):1305–1311. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(90)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. P. Factors influencing the duration of breast-feeding. J Biosoc Sci. 1980 Jul;12(3):325–331. doi: 10.1017/s0021932000012864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whichelow M. J. Breast feeding in Cambridge, England: factors affecting the mother's milk supply. J Adv Nurs. 1979 May;4(3):253–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.1979.tb03007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whichelow M. J., King B. E. Breast feeding and smoking. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Mar;54(3):240–241. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.3.240-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whichelow M. J. Letter: Calorie requirements for successful breast feeding. Arch Dis Child. 1975 Aug;50(8):669–669. doi: 10.1136/adc.50.8.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright H. J., Walker P. C. Prediction of duration of breast feeding in primiparas. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1983 Jun;37(2):89–94. doi: 10.1136/jech.37.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Château P., Holmberg H., Jakobsson K., Winberg J. A study of factors promoting and inhibiting lactation. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1977 Oct;19(5):575–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1977.tb07989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen W. M., Kusin J. A., de With C., Lacko E., Jansen A. A. Lactation performance of mothers with contrasting nutritional status in rural Kenya. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Nov;72(6):805–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


