Abstract
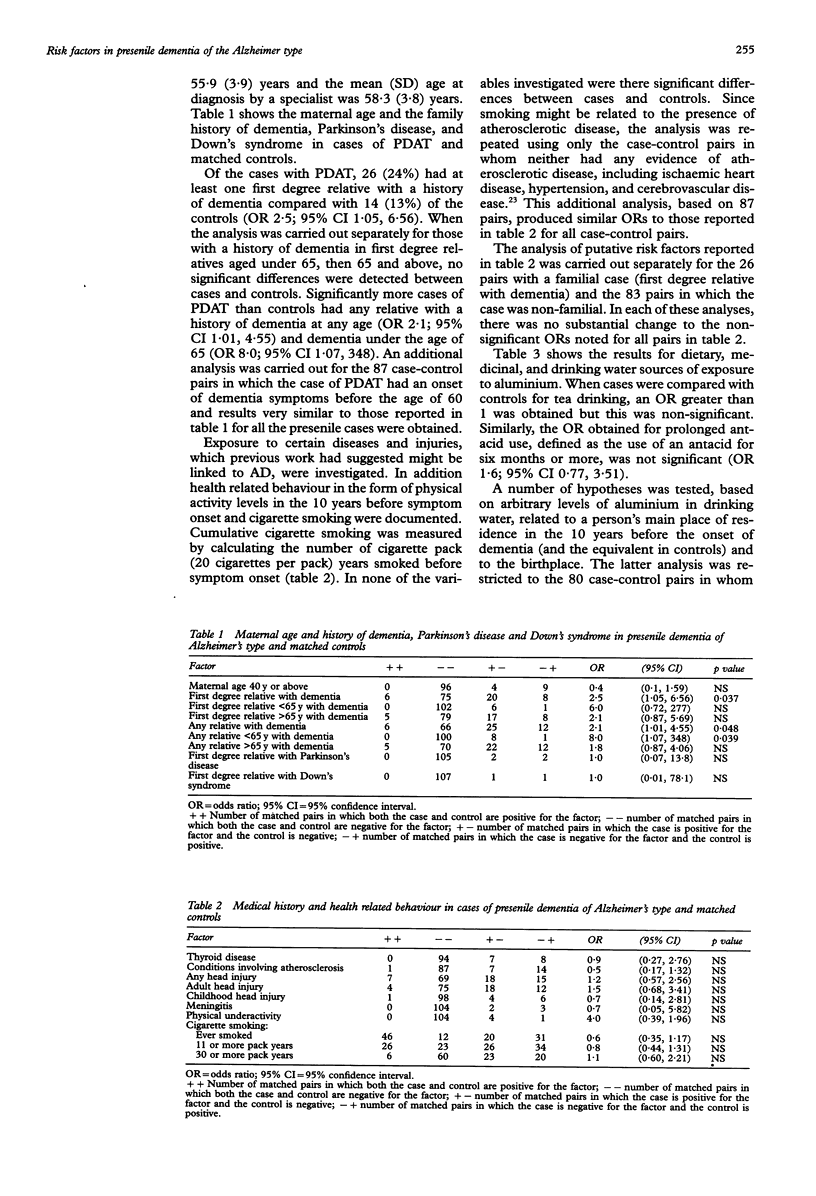
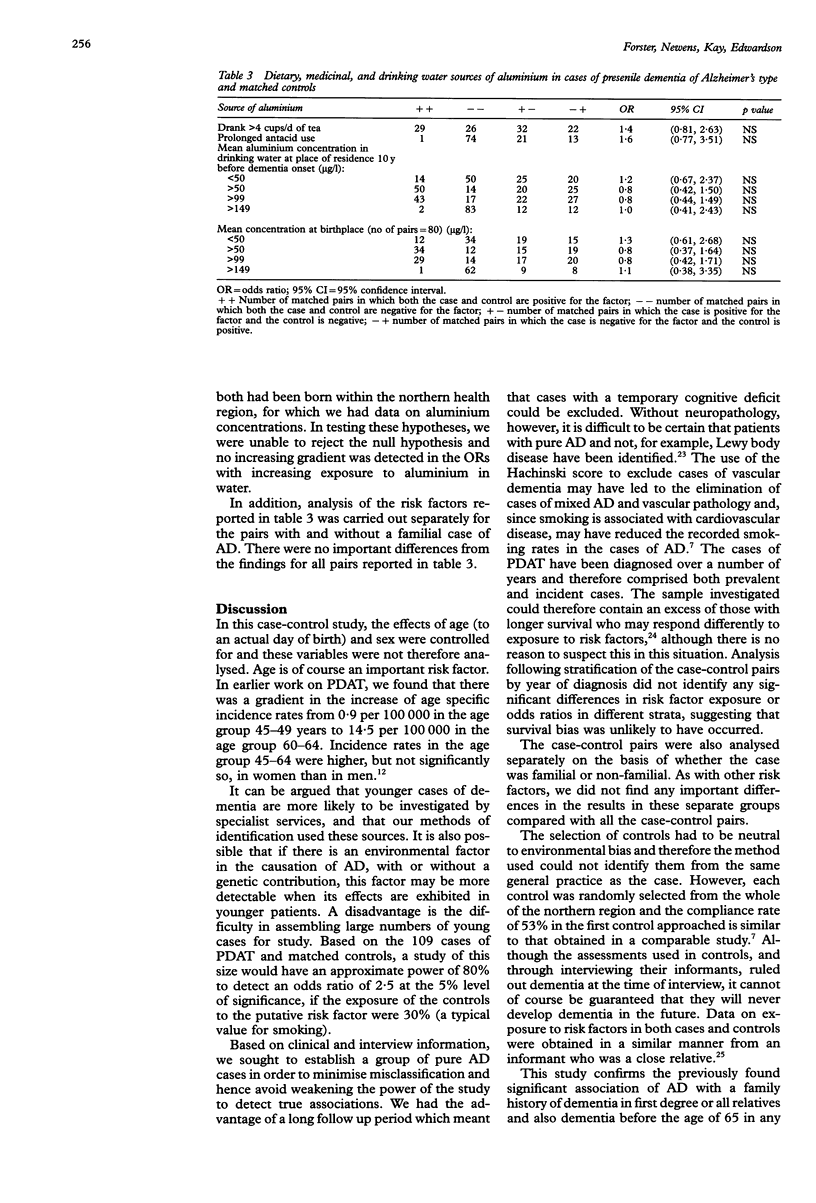
STUDY OBJECTIVE--To investigate the relationship between presenile dementia of the Alzheimer type (PDAT) and family history, medical history, cigarette smoking, and exposure to aluminum. DESIGN--A case-control study in which 109 cases of clinically diagnosed PDAT and 109 controls matched for age and sex were compared for exposure to the risk factors. Odds ratios (ORs) were calculated using McNemar's test. SETTING--The northern health region of England. PATIENTS--Cases comprised those under 65 years diagnosed as having dementia by specialist services, who met clinical algorithm criteria for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Cases were confirmed at interview. MAIN RESULTS--Comparing cases with controls, (ORs) significantly greater than unity were obtained when there was a first degree relative with dementia (OR 2.5, 95% confidence interval 1.05, 6.56), any relative with dementia (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.01, 4.55), and any relative aged less than 65 with dementia (OR 8.0, 95% CI 1.07, 348). Exposure to moderate levels of cigarette smoking (cumulative) was not significant; nor was exposure to aluminum in drinking water, diet, and medicinal sources. CONCLUSION--In this study of modest statistical power, a family history of dementia was confirmed as a risk factor in PDAT. No significant relationship between exposure to aluminium in water supplies, tea, and antacids was found. What is important, however, is the bioavailability of all dietary aluminium, determined by the concentrations of dissolved silicon in water: this requires further investigation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birchall J. D., Chappell J. S. Aluminium, water chemistry, and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1989 Apr 29;1(8644):953–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessed G., Tomlinson B. E., Roth M. The association between quantitative measures of dementia and of senile change in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Jul;114(512):797–811. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.512.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. E., Kukull W. A., van Belle G., Bowen J. D., McCormick W. C., Teri L., Larson E. B. Relationship between cigarette smoking and Alzheimer's disease in a population-based case-control study. Neurology. 1993 Feb;43(2):293–300. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broe G. A., Henderson A. S., Creasey H., McCusker E., Korten A. E., Jorm A. F., Longley W., Anthony J. C. A case-control study of Alzheimer's disease in Australia. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1698–1707. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Eisdorfer C., Leverenz J. Alzheimer's disease and maternal age. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1982 Oct;30(10):656–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1982.tb05065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R. Review: Alzheimer's disease and environmental aluminium. Age Ageing. 1993 Mar;22(2):138–153. doi: 10.1093/ageing/22.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardson J. A., Moore P. B., Ferrier I. N., Lilley J. S., Newton G. W., Barker J., Templar J., Day J. P. Effect of silicon on gastrointestinal absorption of aluminium. Lancet. 1993 Jul 24;342(8865):211–212. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R. J., Doll M. A., Baumstark B. R., Hein D. W. Polymorphic arylamine N-acetyltransferase encoding gene (NAT2) from homozygous rapid and slow acetylator congenic Syrian hamsters. Gene. 1994 Mar 25;140(2):247–249. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90552-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves A. B., White E., Koepsell T. D., Reifler B. V., van Belle G., Larson E. B. The association between aluminum-containing products and Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(90)90053-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):632–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510088009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Jorm A. F., Korten A. E., Creasey H., McCusker E., Broe G. A., Longley W., Anthony J. C. Environmental risk factors for Alzheimer's disease: their relationship to age of onset and to familial or sporadic types. Psychol Med. 1992 May;22(2):429–436. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700030373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman A., Wilkinson W. E., Stafford J. A., Helms M. J., Sigmon A. H., Weinberg T. Alzheimer's disease: a study of epidemiological aspects. Ann Neurol. 1984 Apr;15(4):335–341. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorm A. F., Korten A. E. Assessment of cognitive decline in the elderly by informant interview. Br J Psychiatry. 1988 Feb;152:209–213. doi: 10.1192/bjp.152.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korten A. E., Jorm A. F., Henderson A. S., McCusker E., Creasey H. Control-informant agreement on exposure history in case-control studies of Alzheimer's disease. Int J Epidemiol. 1992 Dec;21(6):1121–1131. doi: 10.1093/ije/21.6.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn C. N., Barker D. J., Osmond C., Harris E. C., Edwardson J. A., Lacey R. F. Geographical relation between Alzheimer's disease and aluminum in drinking water. Lancet. 1989 Jan 14;1(8629):59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeith I., Fairbairn A., Perry R., Thompson P., Perry E. Neuroleptic sensitivity in patients with senile dementia of Lewy body type. BMJ. 1992 Sep 19;305(6855):673–678. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6855.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri L. C., Hewitt D. Aluminium, Alzheimer's disease, and drinking water. Lancet. 1991 Aug 10;338(8763):390–390. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90531-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newens A. J., Forster D. P., Kay D. W., Kirkup W., Bates D., Edwardson J. Clinically diagnosed presenile dementia of the Alzheimer type in the Northern Health Region: ascertainment, prevalence, incidence and survival. Psychol Med. 1993 Aug;23(3):631–644. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700025411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs J. E. Smoking and Alzheimer's disease: protective effect or differential survival bias? Lancet. 1993 Sep 25;342(8874):793–794. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91547-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L. Bias in analytic research. J Chronic Dis. 1979;32(1-2):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(79)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Bonnycastle L., Weber J. L., Alonso M. E. Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., Hofman A. Relation between nicotine intake and Alzheimer's disease. BMJ. 1991 Jun 22;302(6791):1491–1494. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6791.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


