Abstract
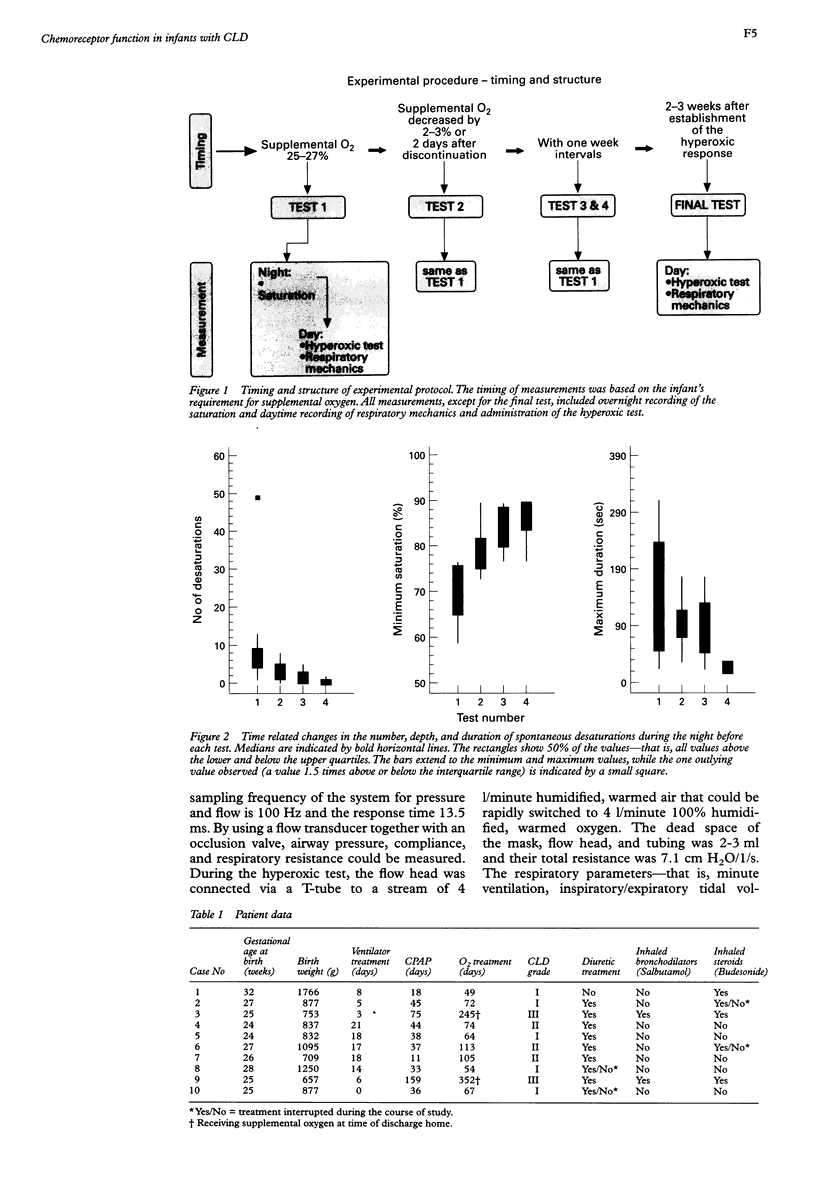
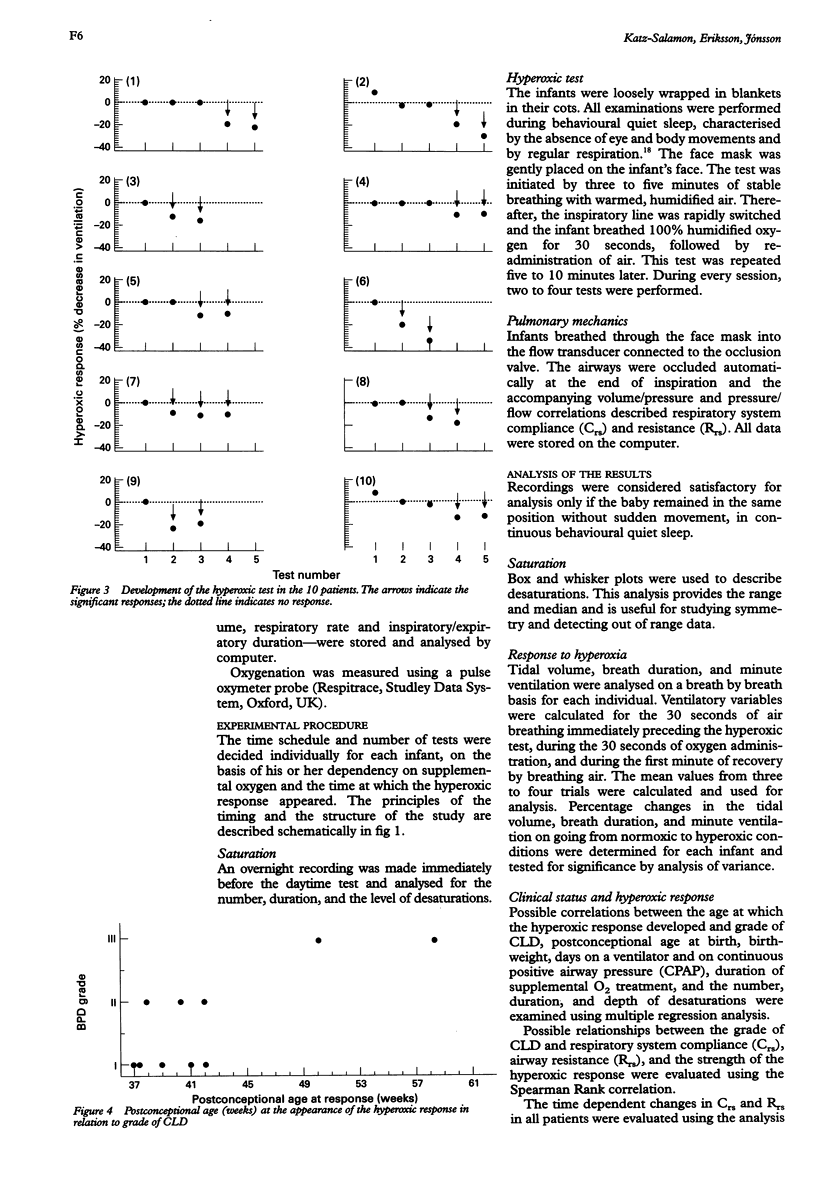
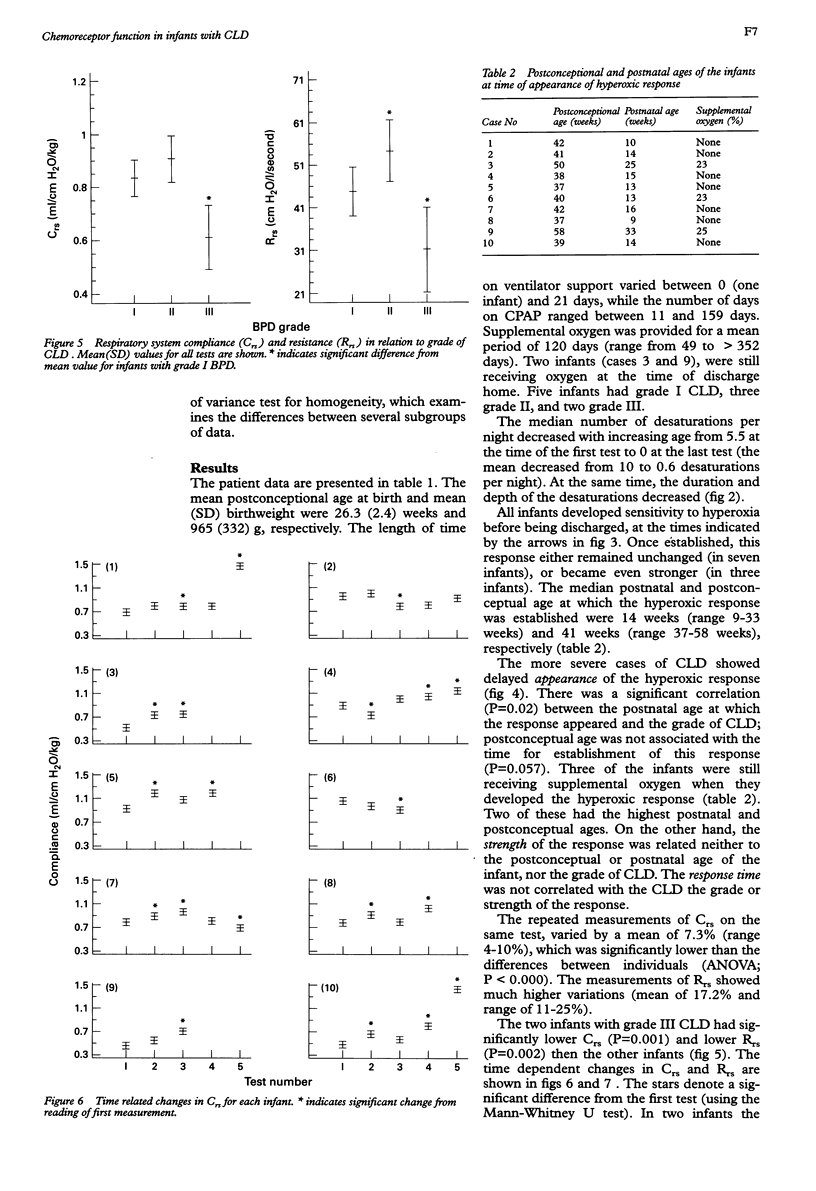
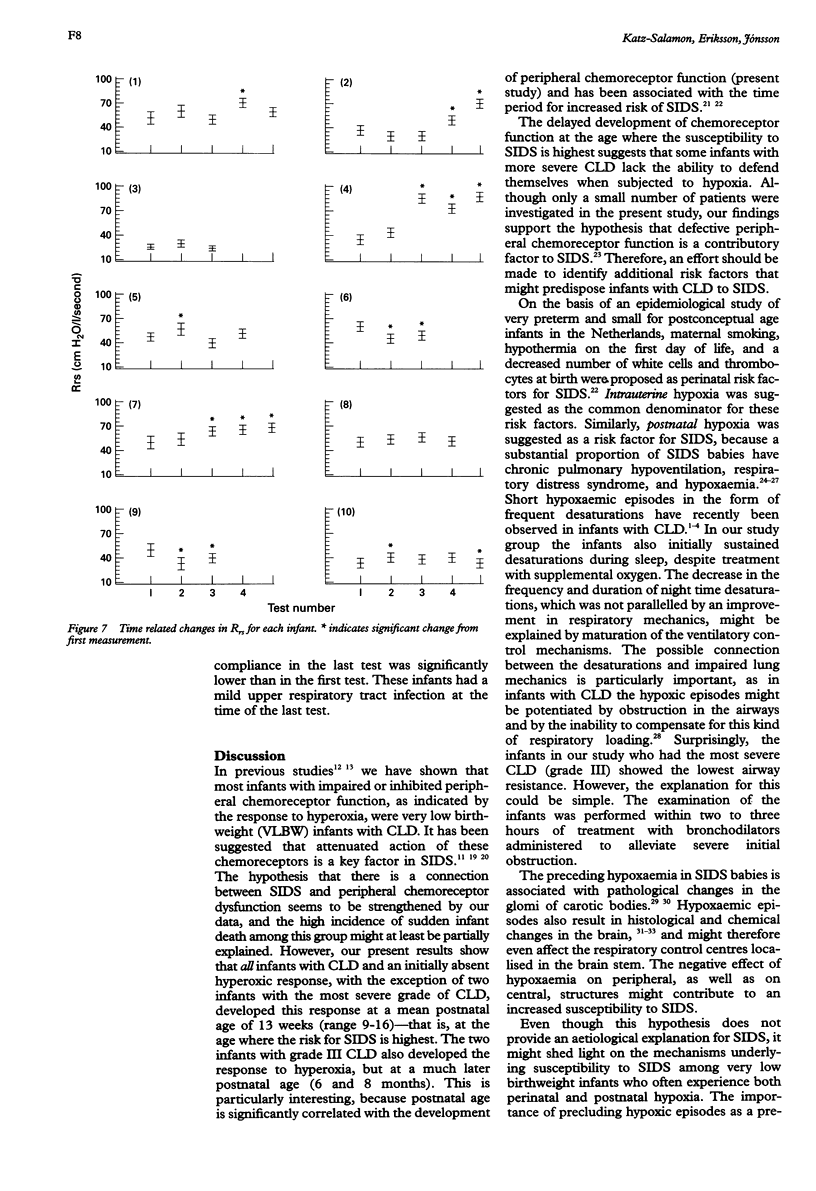
Ten preterm infants with chronic lung disease (CLD) and undeveloped peripheral chemoreceptor function, described as ventilatory response to hyperoxia, were investigated, according to an individual protocol. Each infant was followed up until the response to hyperoxic inhalation had been observed on two occasions. Each examination consisted of overnight recording of saturation, testing of lung compliance and airway resistance, and the hyperoxic test. The hyperoxic response appeared at a mean postnatal age of 14 weeks (range 9-33 weeks). This response, which was independent of the infant's lung mechanics, appeared much later in infants with the severe form of CLD. As undeveloped peripheral chemoreceptor function has been suggested to be a key factor in sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), the delayed development of their chemosensitivity leaves some infants with CLD unprotected against hypoxia at the age at which the risk for SIDS is highest.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancalari E., Abdenour G. E., Feller R., Gannon J. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical presentation. J Pediatr. 1979 Nov;95(5 Pt 2):819–823. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80442-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. P., Ariagno R. L., Watts J. L., Goldman S. L., Dumpit F. M. Apnea, hypoxemia, and aborted sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatrics. 1978 Nov;62(5):686–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS K. W., OPPE T. E. The effect of inhalation of high and low concentrations of oxygen on the respiration of the premature infant. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):38–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder N. A., Williams B. A., Smyth J., Boon A. W., Kumar P., Hanson M. A. Absence of ventilatory responses to alternating breaths of mild hypoxia and air in infants who have had bronchopulmonary dysplasia: implications for the risk of sudden infant death. Pediatr Res. 1994 Jun;35(6):677–681. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199406000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand M., McEvoy C., MacDonald K. Spontaneous desaturations in intubated very low birth weight infants with acute and chronic lung disease. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1992 Jul;13(3):136–142. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950130303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewell J. E., Kondo C. S., Dascalu V., Filyk S. C. Influence of carotid denervation on the arousal and cardiopulmonary response to rapidly developing hypoxemia in lambs. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):473–477. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg M., Kurzner S. I., Bautista D., Keens T. G. Hypoxic arousal responses in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 1988 Jul;82(1):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. H., Rogers Y. Are infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia at risk for sudden infant death syndrome? Pediatrics. 1994 May;93(5):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Abbasi S., Bhutani V. K. Sequential changes in pulmonary mechanics in the very low birth weight (less than or equal to 1000 grams) infant. J Pediatr. 1988 Oct;113(4):732–737. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Wolfson M. R., Locke R. G., Allen J. L., Shaffer T. H. Increased respiratory drive and limited adaptation to loaded breathing in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res. 1992 Sep;32(3):356–359. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199209000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D., Khan Q., Smith P. Histopathology of the carotid bodies in neonates and infants. Histopathology. 1990 Dec;17(6):511–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb00790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. E., McCulloch K., Brouillette R. T. Diminished hypoxic ventilatory responses in near-miss sudden infant death syndrome. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jun;50(6):1313–1317. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.6.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz-Salamon M., Jonsson B., Lagercrantz H. Blunted peripheral chemoreceptor response to hyperoxia in a group of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1995 Aug;20(2):101–106. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950200209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendeel S. R., Ferris J. A. Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy. J Clin Pathol. 1977 May;30(5):481–485. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.5.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L., Fisher R., Ryser M., Whalen P. Carotid body in the sudden infant death syndrome. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):567–569. doi: 10.1126/science.1251191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L. Hypoxemia and the sudden infant death syndrome. Science. 1974 Nov 29;186(4166):837–838. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4166.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L. Pulmonary arterial abnormalities in the sudden-infant-death syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 29;289(22):1167–1170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311292892204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H. M., Mellins R. B. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Unresolved neonatal acute lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):694–709. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusz G. S., Hóbor M., Tulassay T., Sallay P., Miltényi M. 24 hour blood pressure monitoring in healthy and hypertensive children. Arch Dis Child. 1994 Feb;70(2):90–94. doi: 10.1136/adc.70.2.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein F., Johnston M. V. Effects of hypoxia-ischemia on monoamine metabolism in the immature brain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Apr;15(4):342–347. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer L., Martin R. J., Hawkins S. W., Benson-Szekely L. J., Yamashita T. S., Carlo W. A. Oxygen desaturation complicates feeding in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia after discharge. Pediatrics. 1992 Sep;90(3):380–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinschneider A. Prolonged apnea and the sudden infant death syndrome: clinical and laboratory observations. Pediatrics. 1972 Oct;50(4):646–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toce S. S., Farrell P. M., Leavitt L. A., Samuels D. P., Edwards D. K. Clinical and roentgenographic scoring systems for assessing bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Jun;138(6):581–585. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140440065017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Samson-Dollfus D., Menard J. Sudden unexpected infant death in a French county. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Nov;59(11):1082–1087. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.11.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werthammer J., Brown E. R., Neff R. K., Taeusch H. W., Jr Sudden infant death syndrome in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga H., Brand R., Geudeke T., van Geijn H. P., van der Harten H., Verloove-Vanhorick S. P. Prenatal risk factors for cot death in very preterm and small for gestational age infants. Early Hum Dev. 1990 Jun;23(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(90)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinman R., Blanchard P. W., Vachon F. Oxygen saturation during sleep in patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Biol Neonate. 1992;61(2):69–75. doi: 10.1159/000243533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


