Abstract
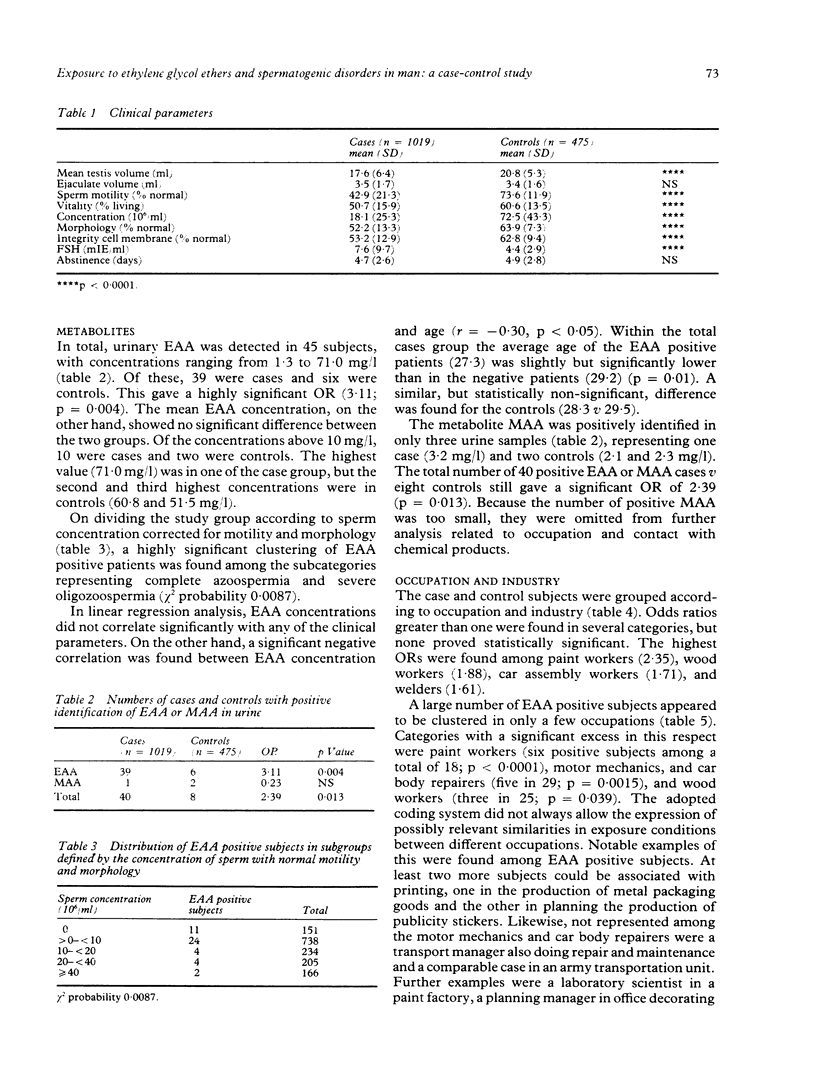
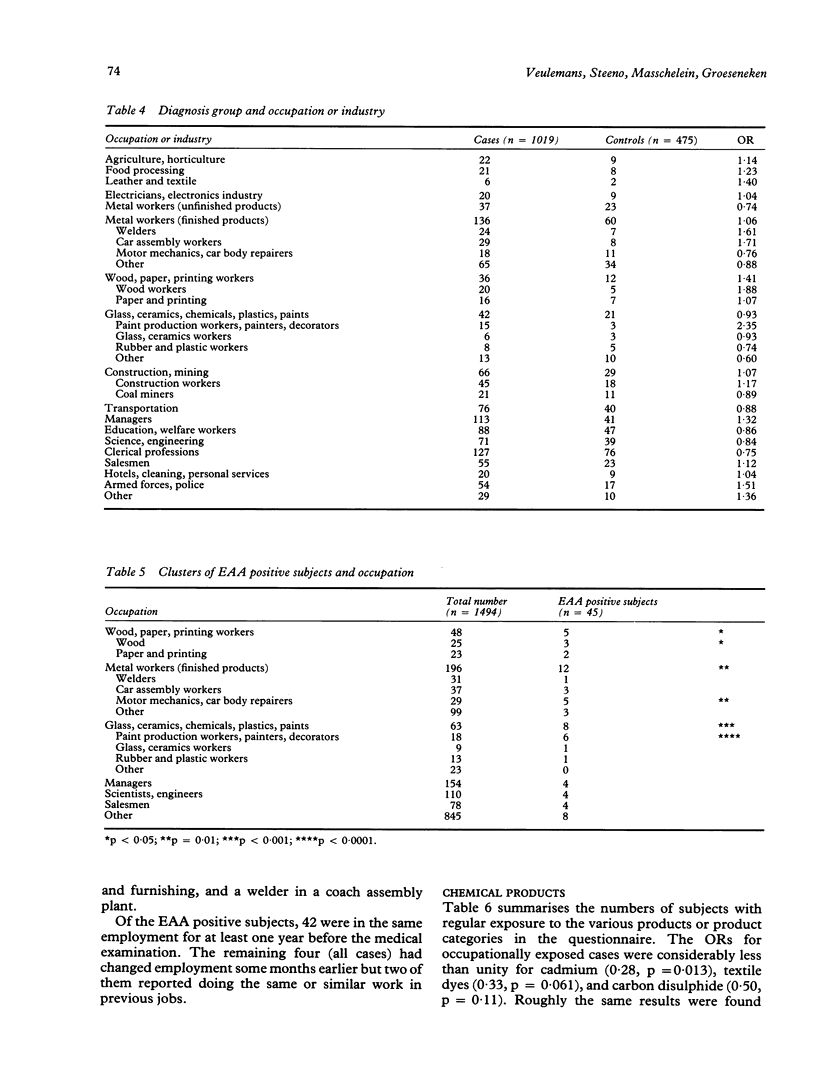
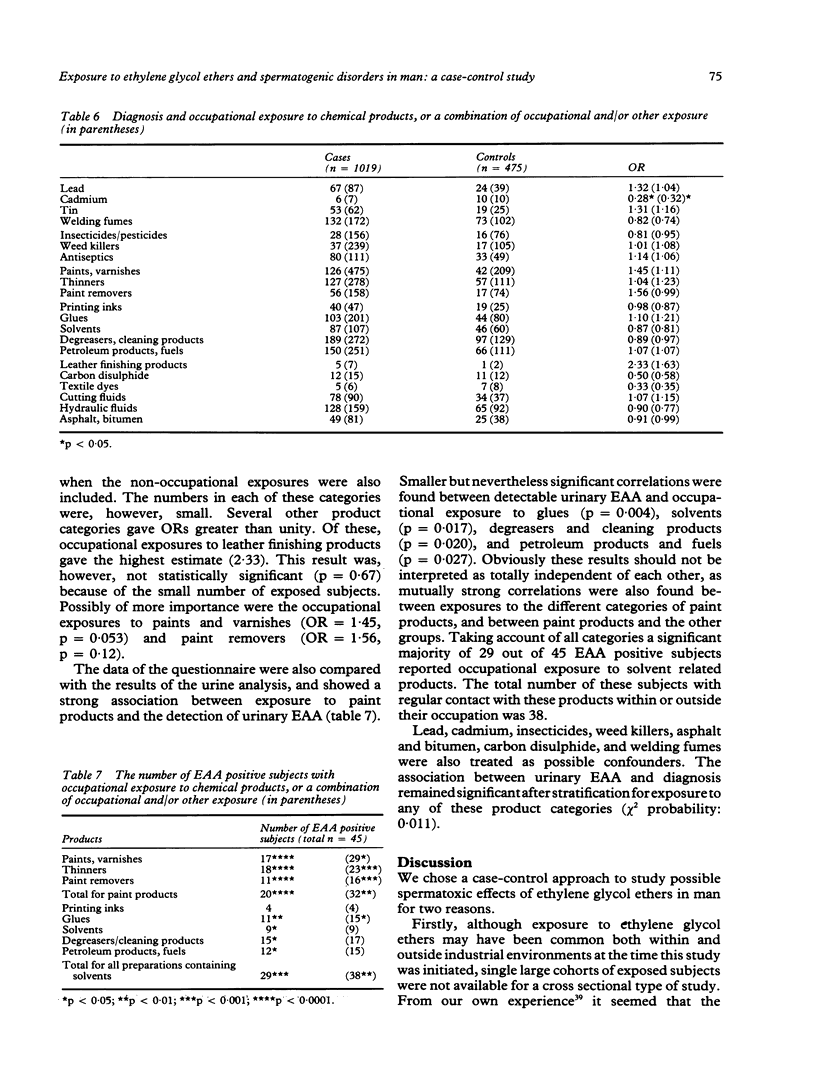
A case-control study was conducted among first time patients at a clinic for reproductive disorders. The study group consisted of 1019 cases, defined as patients diagnosed infertile or subfertile on the basis of a spermiogram and 475 controls who were diagnosed as normally fertile by the same procedure. Possible exposure to ethylene glycol ethers was assessed by the presence of the urinary metabolites methoxyacetic acid (MAA) and ethoxyacetic acid (EAA) respectively for 2-methoxyethanol and 2-ethoxyethanol or their acetates. In total, EAA was detected in 39 cases and six controls, with a highly significant odds ratio of 3.11 (p = 0.004). On the other hand, MAA was only found in one case and two controls. The presence of EAA in urine proved to be strongly associated with exposure to preparations containing solvents, especially paint products, and with some groups of occupations, the most important of which were also directly or possibly connected with paint products. The absence of a significant correlation between the concentration of urinary EAA and the various measures of sperm quality could be explained by the expected latent period between exposure and observed effects. Other temporal aspects of the relation between exposure as judged from the presence of urinary EAA and diagnosis are also discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Brinkworth M. H., Jenkinson P. C., Clode S. A., Creasy D. M., Gangolli S. D. Effect of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether on spermatogenesis, dominant lethality, and F1 abnormalities in the rat and the mouse after treatment of F0 males. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 1987;7(2):141–158. doi: 10.1002/tcm.1770070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angerer J., Lichterbeck E., Begerow J., Jekel S., Lehnert G. Occupational chronic exposure to organic solvents. XIII. Glycolether exposure during the production of varnishes. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1990;62(2):123–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00383588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbee S. J., Terrill J. B., DeSousa D. J., Conaway C. C. Subchronic inhalation toxicology of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether in the rat and rabbit. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:157–163. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8457157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin R. E., Dutton S. L., Ross M. D., Lamb J. C., 4th Effects of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether (EGME) on mating performance and epididymal sperm parameters in F344 rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Feb;5(1):182–189. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin R. E., Lamb J. C., 4th Effects of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether on various parameters of testicular function in the F344 rat. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:219–224. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8457219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. R., Bodner K. M., Kolesar R. C., Uhlmann C. S., VanPeenen P. F., Dickson G. S., Flanagan K. A cross-sectional study of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether process employees. Arch Environ Health. 1982 Nov-Dec;37(6):346–351. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1982.10667589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasy D. M., Flynn J. C., Gray T. J., Butler W. H. A quantitative study of stage-specific spermatocyte damage following administration of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in the rat. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Dec;43(3):321–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuston M. H., Bodnar K. R., Kerstetter S. L., Grink C. P., Belcak M. J., Singer E. J. Reproductive toxicity of 2-methoxyethanol applied dermally to occluded and nonoccluded sites in male rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;100(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. M., Blackburn D. M., Moore R. B., Lloyd S. C. Testicular toxicity of 2-methoxyacetaldehyde, a possible metabolite of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, in the rat. Toxicol Lett. 1986 Jul-Aug;32(1-2):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(86)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. M., Creasy D. M., Foster J. R., Gray T. J. Testicular toxicity produced by ethylene glycol monomethyl and monoethyl ethers in the rat. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:207–217. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8457207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. M., Creasy D. M., Foster J. R., Thomas L. V., Cook M. W., Gangolli S. D. Testicular toxicity of ethylene glycol monomethyl and monoethyl ethers in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;69(3):385–399. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(83)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeseneken D., Veulemans H., Masschelein R. Urinary excretion of ethoxyacetic acid after experimental human exposure to ethylene glycol monoethyl ether. Br J Ind Med. 1986 Sep;43(9):615–619. doi: 10.1136/oem.43.9.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeseneken D., Veulemans H., Masschelein R., Van Vlem E. An improved method for the determination in urine of alkoxyacetic acids. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1989;61(4):249–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00381422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeseneken D., Veulemans H., Masschelein R., Van Vlem E. Comparative urinary excretion of ethoxyacetic acid in man and rat after single low doses of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether. Toxicol Lett. 1988 Apr;41(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(88)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeseneken D., Veulemans H., Masschelein R., Van Vlem E. Ethoxyacetic acid: a metabolite of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate in man. Br J Ind Med. 1987 Jul;44(7):488–493. doi: 10.1136/oem.44.7.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeseneken D., Veulemans H., Masschelein R., Van Vlem E. Experimental human exposure to ethylene glycol monomethyl ether. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1989;61(4):243–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00381421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeseneken D., van Vlem E., Veulemans H., Masschelein R. Gas chromatographic determination of methoxyacetic and ethoxyacetic acid in urine. Br J Ind Med. 1986 Jan;43(1):62–65. doi: 10.1136/oem.43.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin B. D. Reproductive toxicity of the glycol ethers. Toxicology. 1983 Jun;27(2):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(83)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. C., 4th, Gulati D. K., Russell V. S., Hommel L., Sabharwal P. S. Reproductive toxicity of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether tested by continuous breeding of CD-1 mice. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:85–90. doi: 10.1289/ehp.845785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. P., Kinney L. A. The ultrastructure and reversibility of testicular atrophy induced by ethylene glycol monomethyl ether (EGME) in the rat. Toxicol Pathol. 1989;17(4 Pt 2):759–773. doi: 10.1177/0192623389017004204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. P., Kinney L. A., Valentine R. Comparative testicular toxicity of bis(2-methoxyethyl) ether and 2-methoxyethanol in rats. Toxicology. 1989 Dec 15;59(3):239–258. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(89)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. R., Ayres J. A., Young J. T., McKenna M. J. Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether. I. Subchronic vapor inhalation study with rats and rabbits. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/s0272-0590(83)80172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. R., Hermann E. A., Young J. T., Landry T. D., Calhoun L. L. Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and propylene glycol monomethyl ether: metabolism, disposition, and subchronic inhalation toxicity studies. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:233–239. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8457233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss E. J., Thomas L. V., Cook M. W., Walters D. G., Foster P. M., Creasy D. M., Gray T. J. The role of metabolism in 2-methoxyethanol-induced testicular toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;79(3):480–489. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano K., Nakayama E., Koyano M., Oobayashi H., Adachi H., Yamada T. [Testicular atrophy of mice induced by ethylene glycol mono alkyl ethers (author's transl)]. Sangyo Igaku. 1979 Jan;21(1):29–35. doi: 10.1539/joh1959.21.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano K., Nakayama E., Oobayashi H., Nishizawa T., Okuda H., Yamazaki K. Experimental studies on toxicity of ethylene glycol alkyl ethers in Japan. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:75–84. doi: 10.1289/ehp.845775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudiz D. J., Zenick H., Niewenhuis R. J., McGinnis P. M. Male reproductive toxicity and recovery associated with acute ethoxyethanol exposure in rats. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1984;13(4-6):763–775. doi: 10.1080/15287398409530538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudiz D., Zenick H. In vivo and in vitro evaluations of spermatotoxicity induced by 2-ethoxyethanol treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;84(3):576–583. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe J. M., Schrader S. M., Clapp D. E., Halperin W. E., Turner T. W., Hornung R. W. Semen quality in workers exposed to 2-ethoxyethanol. Br J Ind Med. 1989 Jun;46(6):399–406. doi: 10.1136/oem.46.6.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels D. M., Doe J. E., Tinston D. J. The effects on the rat testis of single inhalation exposures to ethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, in particular ethylene glycol monomethyl ether. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1984;7:167–170. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69132-4_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeno O. P., Pangkahila A. Occupational influences on male fertility and sexuality. I. Andrologia. 1984 Jan-Feb;16(1):5–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.1984.tb00227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veulemans H., Groeseneken D., Masschelein R., Van Vlem E. Field study of the urinary excretion of ethoxyacetic acid during repeated daily exposure to the ethyl ether of ethylene glycol and the ethyl ether of ethylene glycol acetate. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1987 Jun;13(3):239–242. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veulemans H., Groeseneken D., Masschelein R., van Vlem E. Survey of ethylene glycol ether exposures in Belgian industries and workshops. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1987 Aug;48(8):671–676. doi: 10.1080/15298668791385390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch L. S., Schrader S. M., Turner T. W., Cullen M. R. Effects of exposure to ethylene glycol ethers on shipyard painters: II. Male reproduction. Am J Ind Med. 1988;14(5):509–526. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenick H., Oudiz D., Niewenhuis R. J. Spermatotoxicity associated with acute and subchronic ethoxyethanol treatment. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Aug;57:225–231. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8457225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


