Abstract
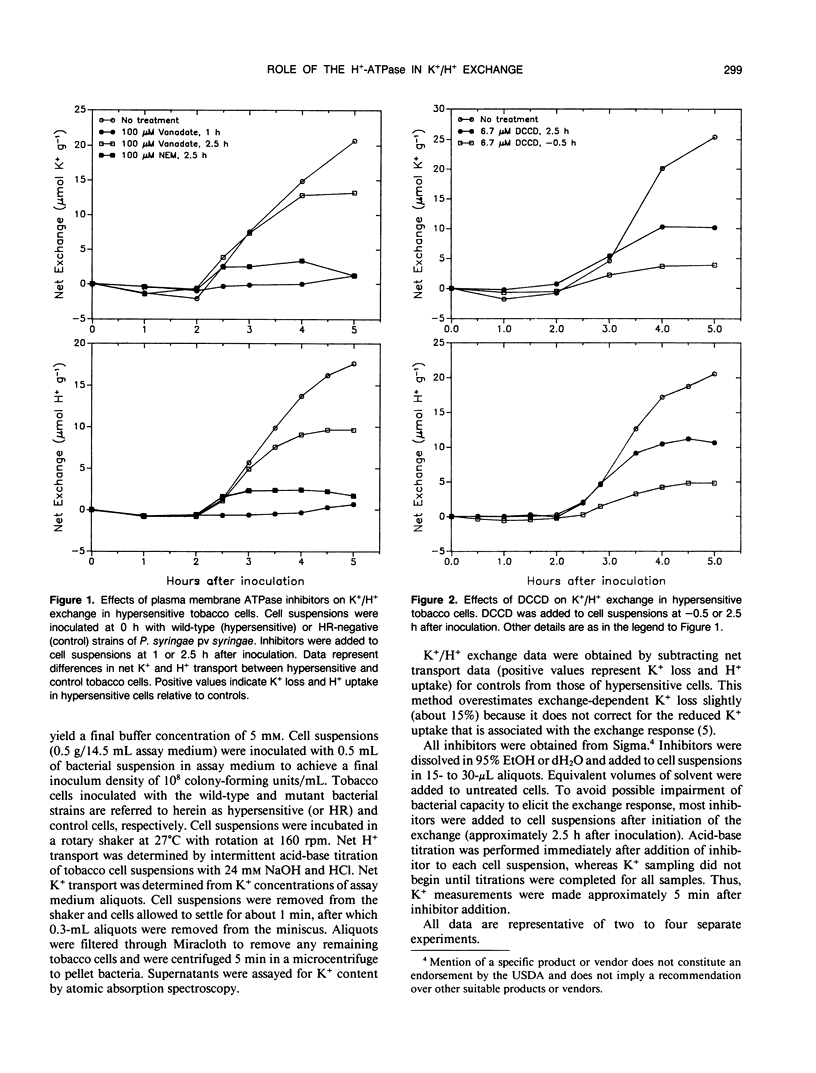
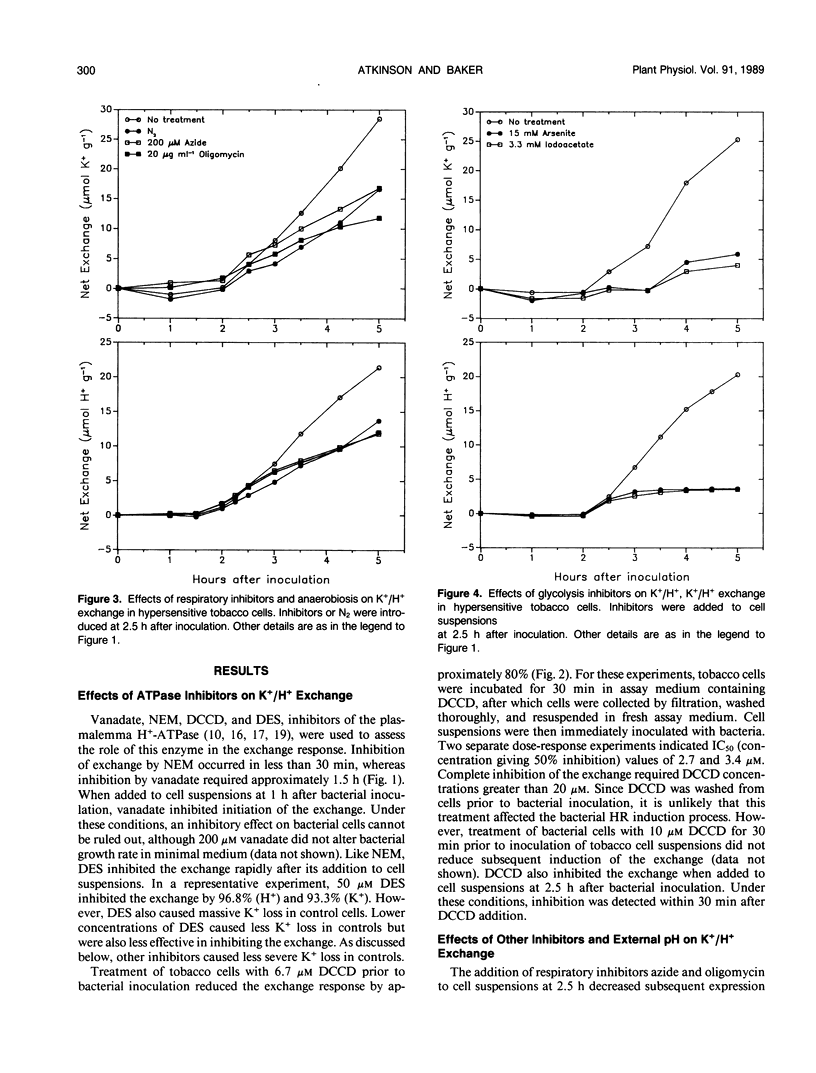
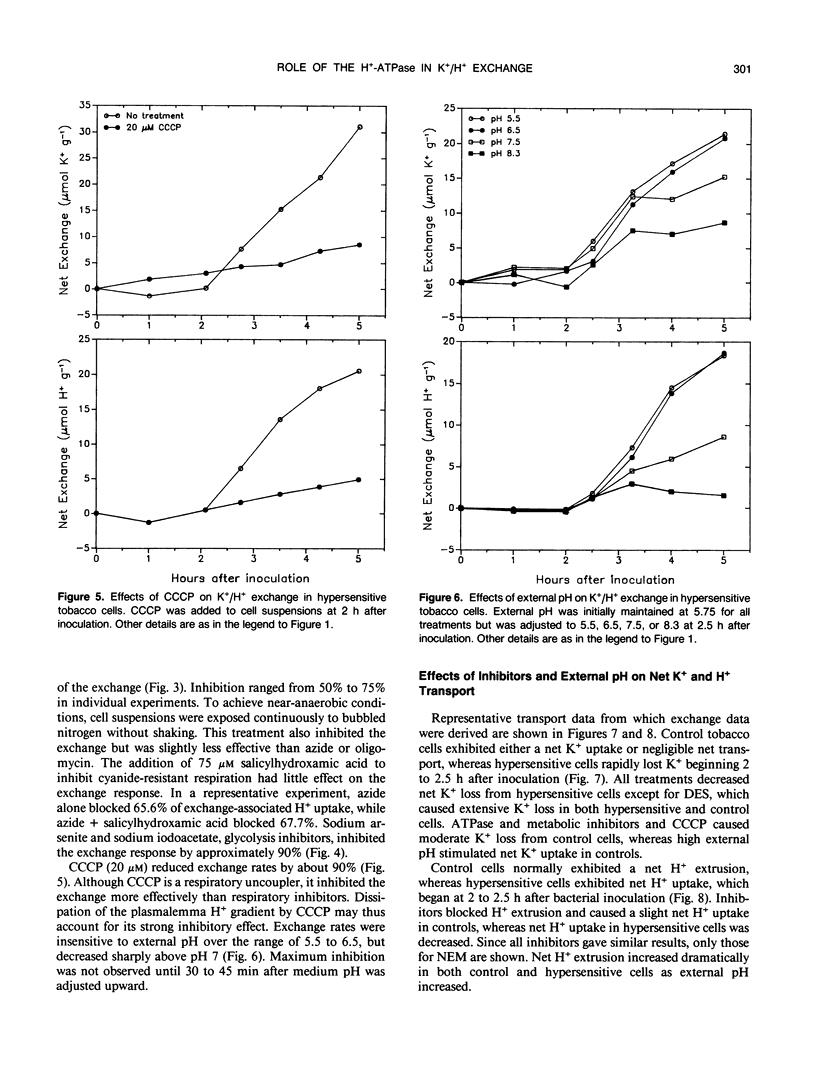
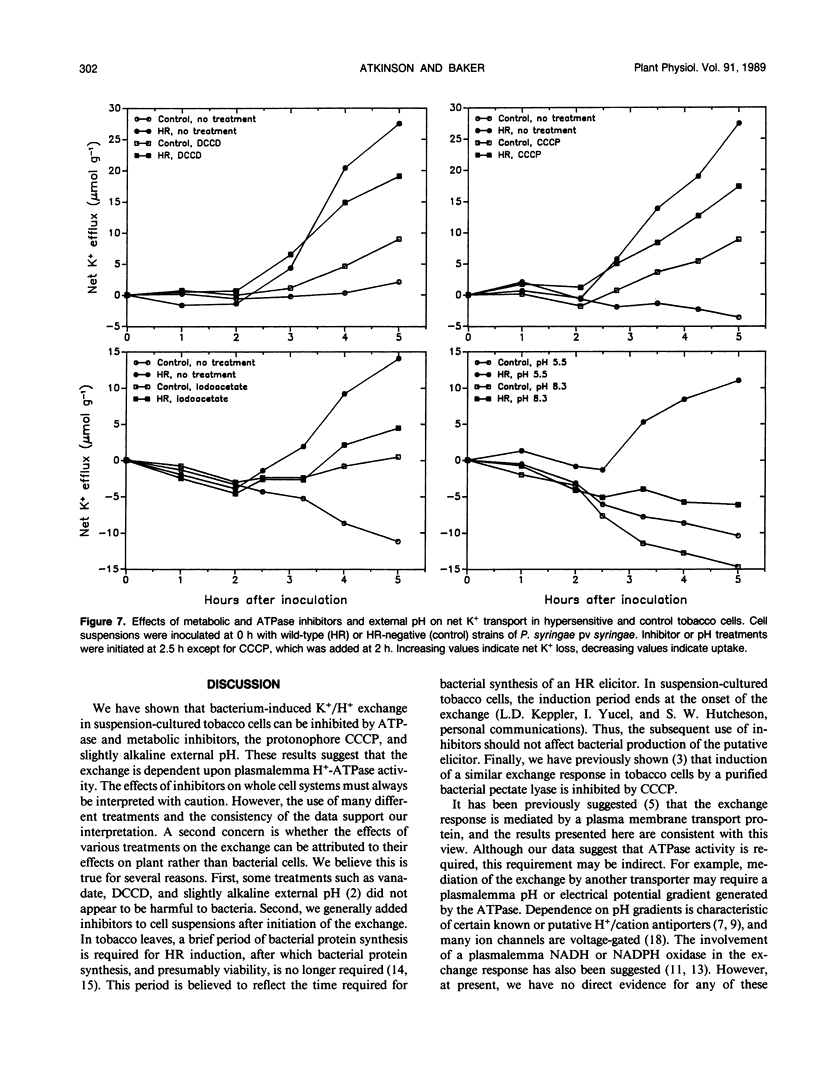
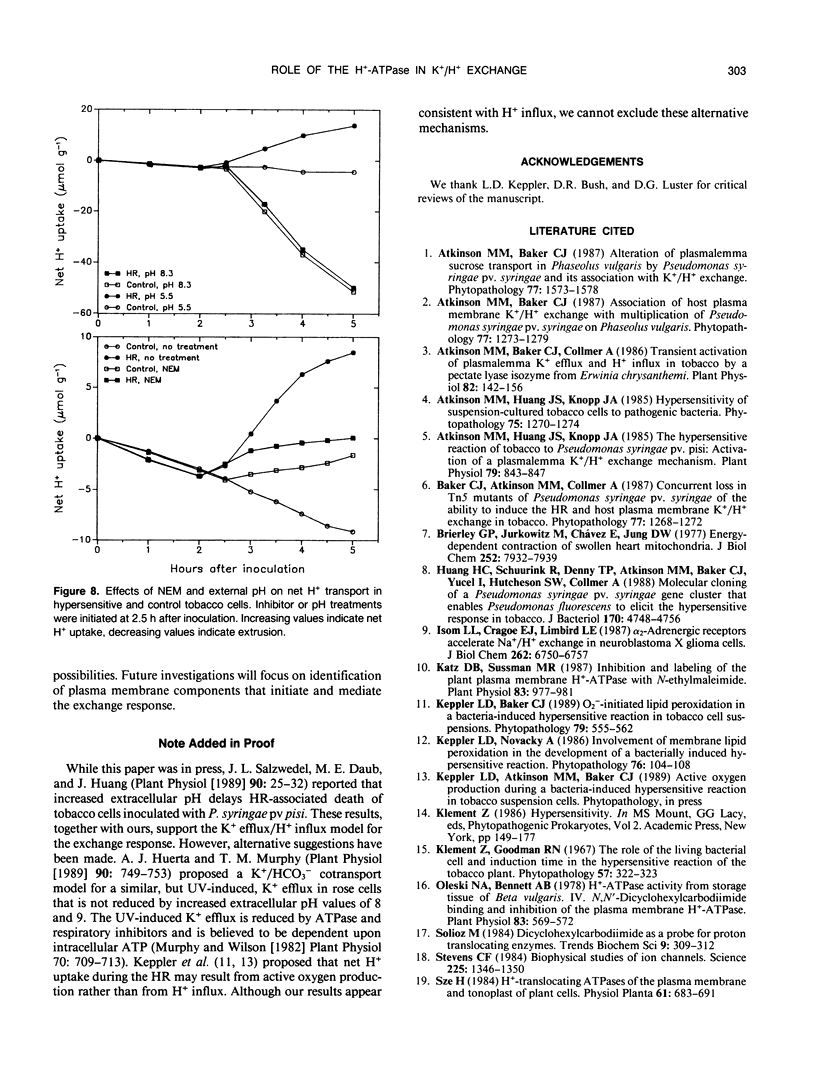
Activation of a host plasma membrane K+ efflux/net H+ uptake exchange by pathogenic pseudomonads plays an important role in the development of hypersensitivity in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Involvement of the plasmalemma H+-pumping ATPase in this response was investigated. The exchange response of suspension-cultured tobacco cells to Pseudomonas syringae pv syringae was reduced 90% or more by ATPase inhibitors including vanadate, N-ethylmaleimide, and N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. The exchange was also strongly inhibited by the protonophore carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone and by slightly alkaline external pH. Respiratory inhibitors such as oligomycin and sodium azide reduced the exchange by 50% to 75%, while glycolysis inhibitors such as sodium arsenite and sodium iodoacetate decreased exchange by approximately 90%. These results suggest that plasmalemma H+-ATPase activity is required for the exchange response and that this may reflect a requirement for a plasmalemma pH and/or electrical potential gradient.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. M., Baker C. J., Collmer A. Transient Activation of Plasmalemma K Efflux and H Influx in Tobacco by a Pectate Lyase Isozyme from Erwinia chrysanthemi. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):142–146. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. M., Huang J. S., Knopp J. A. The Hypersensitive Reaction of Tobacco to Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi: Activation of a Plasmalemma K/H Exchange Mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):843–847. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley G. P., Jurkowitz M., Chávez E., Jung D. W. Energy-dependent contraction of swollen heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7932–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Schuurink R., Denny T. P., Atkinson M. M., Baker C. J., Yucel I., Hutcheson S. W., Collmer A. Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae gene cluster that enables Pseudomonas fluorescens to elicit the hypersensitive response in tobacco plants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4748–4756. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4748-4756.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta A. J., Murphy T. M. Effects of Extracellular pH on UV-Induced K Efflux from Cultured Rose Cells. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jun;90(2):749–753. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Limbird L. E. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptors accelerate Na+/H+ exchange in neuroblastoma X glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6750–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. B., Sussman M. R. Inhibition and Labeling of the Plant Plasma Membrane H-ATPase with N-Ethylmaleimide. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):977–981. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. M., Wilson C. UV-Stimulated K Efflux from Rose Cells: Counterion and Inhibitor Studies. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):709–713. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleski N. A., Bennett A. B. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: IV. N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide Binding and Inhibition of the Plasma Membrane H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):569–572. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Biophysical studies of ion channels. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1346–1350. doi: 10.1126/science.6089347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


