Abstract
Gibberellins (GAs) in suspensors and embryos of Phaseolus coccineus seeds at the heart stage of embryo development were analyzed by combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). From the suspensor four C19-GAs, GA1, GA4, GA5, GA6, and one C20 GA, GA44, were identified. From the embryo, five C19-GAs GA1, GA4, GA5, GA6, GA60 and two C20 GAs, GA19 and GA44 were identified. The data, in relation to previous results, suggest a dependence of the embryo on the suspensor during early stages of development.
Full text
PDF
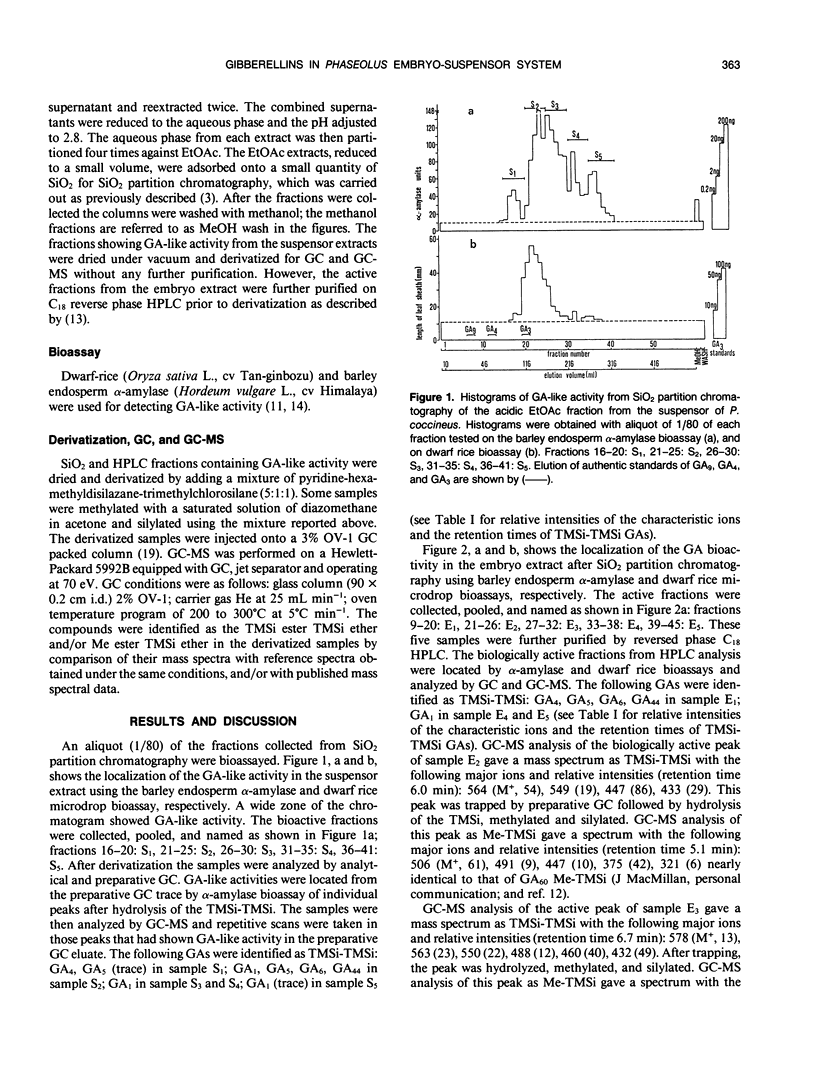
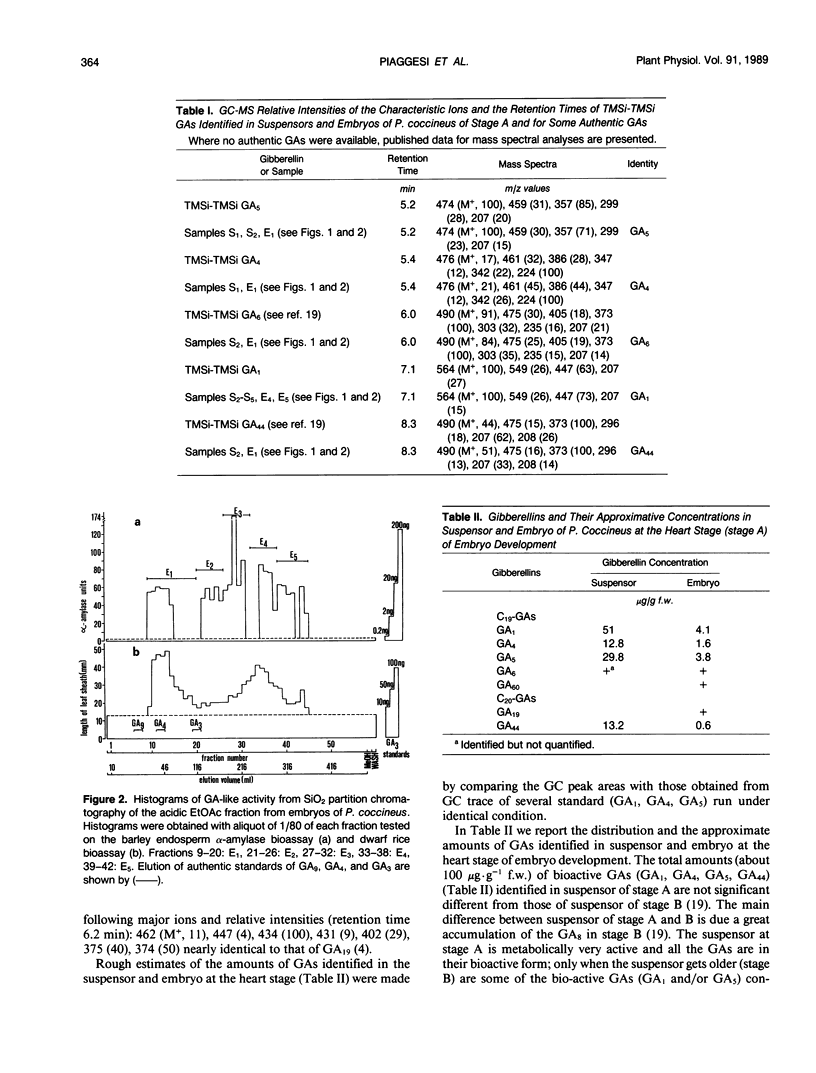


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Picciarelli P., Alpi A. Gibberellins in Suspensors of Phaseolus coccineus L. Seeds. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):298–300. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walthall E. D., Brady T. The effect of the suspensor and gibberellic acid on Phaseolus vulgaris embryo protein synthesis. Cell Differ. 1986 Jan;18(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(86)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


