Abstract
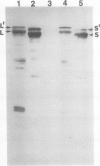
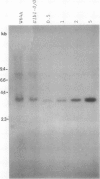
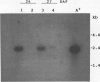
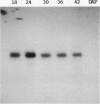
One of the most abundant proteins in maize (Zea mays L.) embryos is the molecular weight 63,000 globulin encoded by the Glb1 gene. To obtain DNA clones corresponding to Glb1, a cDNA library corresponding to RNA from developing maize embryos was constructed in a lambda expression vector and screened with antibodies specific for Glb1-encoded proteins. Here we report the complete nucleotide sequence, as determined from two overlapping clones, of pcGlb 1S, a 2009 base pair clone containing the entire translated region of Glb1. The deduced amino acid sequence of pcGlb 1S shows similarities to 7S-type seed storage proteins of wheat and legumes. Southern blot analysis of maize DNA confirms previous genetic studies which had indicated the presence of a single copy of Glb1 per haploid genome. Northern blot analysis indicates that Glb1 transcripts are present throughout most of embryo development and that expression of this gene is limited to seed tissues. Embryos homozygous for a Glb1 null allele, in which Glb1-encoded proteins are not detectable, contain low levels of Glb1 transcripts which are a different size from those encoded by functional alleles. This suggests that the defect in the null allele is at the level of gene transcription or RNA processing.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz A. L., Boston R. S., Larkins B. A. Structural and transcriptional analysis of DNA sequences flanking genes that encode 19 kilodalton zeins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):90–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00331495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz A. L. Characterization of embryo globulins encoded by the maize Glb genes. Biochem Genet. 1989 Apr;27(3-4):239–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02401804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz A. L., Schwartz D. Synthesis of globulins in maize embryos. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycett G. W., Delauney A. J., Gatehouse J. A., Gilroy J., Croy R. R., Boulter D. The vicilin gene family of pea (Pisum sativum L.): a complete cDNA coding sequence for preprovicilin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2367–2380. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Rapid identification of M13 phage deletions for sequence analysis. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):510–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J. C. An allele of the Prot locus in maize is a variant for the site of protein processing. Biochem Genet. 1988 Aug;26(7-8):463–474. doi: 10.1007/BF02399413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Dean D., Heck G. R. Aleurain: a barley thiol protease closely related to mammalian cathepsin H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6512–6516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a French bean storage protein gene: Phaseolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. D., Quatrano R. S. ABA-Regulation of Two Classes of Embryo-Specific Sequences in Mature Wheat Embryos. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):208–215. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]