Abstract
An efficient and largely genotype-independent transformation method for Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea was established based on neo or bar as selectable marker genes. Hypocotyl explants of Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea cultivars were infected with Agrobacterium strains containing chimeric neo and bar genes. The use of AgNO3 was a prerequisite for efficient shoot regeneration under selective conditions. Vitrification was avoided by decreasing the water potential of the medium, by decreasing the relative humidity in the tissue culture vessel, and by lowering the cytokinin concentration. In this way, rooted transformed shoots were obtained with a 30% efficiency in 9 to 12 weeks. Southern blottings and genetic analysis of S1-progeny showed that the transformants contained on average between one and three copies of the chimeric genes. A wide range of expression levels of the chimeric genes was observed among independent transformants. Up to 25% of the transformants showed no detectable phosphinotricin acetyltransferase or neomycin phosphotransferase II enzyme activities although Southern blottings demonstrated that these plants were indeed transformed.
Full text
PDF

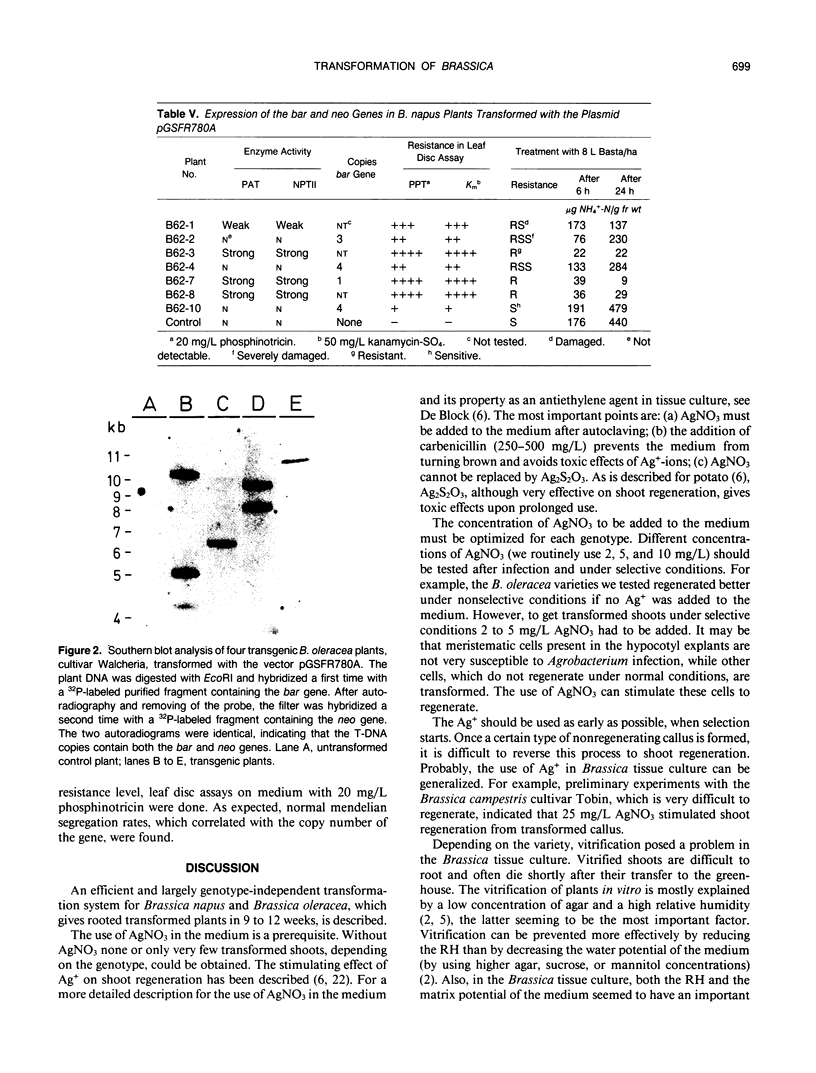


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block M. D., Botterman J., Vandewiele M., Dockx J., Thoen C., Gosselé V., Movva N. R., Thompson C., Montagu M. V., Leemans J. Engineering herbicide resistance in plants by expression of a detoxifying enzyme. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2513–2518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamborg O. L., Miller R. A., Ojima K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Apr;50(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella L., Block M. D., Messens E., Hernalsteens J. P., Montagu M. V., Schell J. Chimeric genes as dominant selectable markers in plant cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):987–995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss B., Sprengel R., Schaller H. Protein fusions with the kanamycin resistance gene from transposon Tn5. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3317–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velten J., Schell J. Selection-expression plasmid vectors for use in genetic transformation of higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6981–6998. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]