Abstract
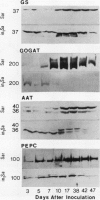
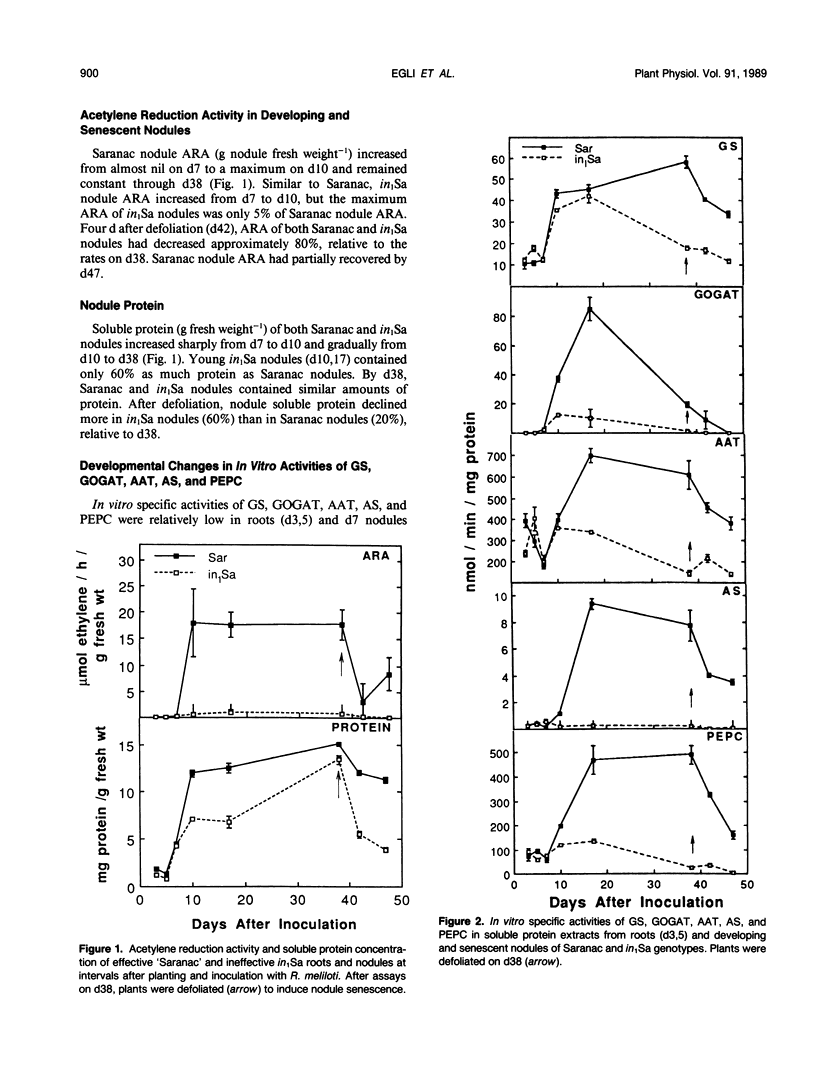
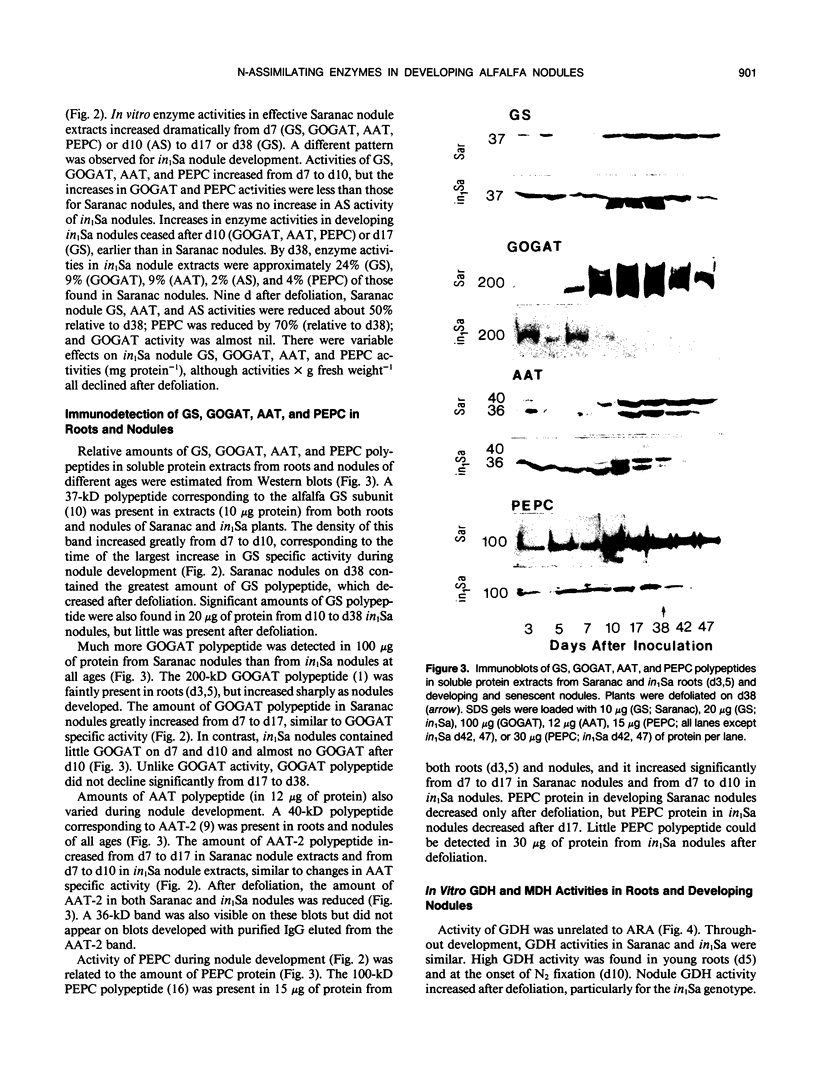
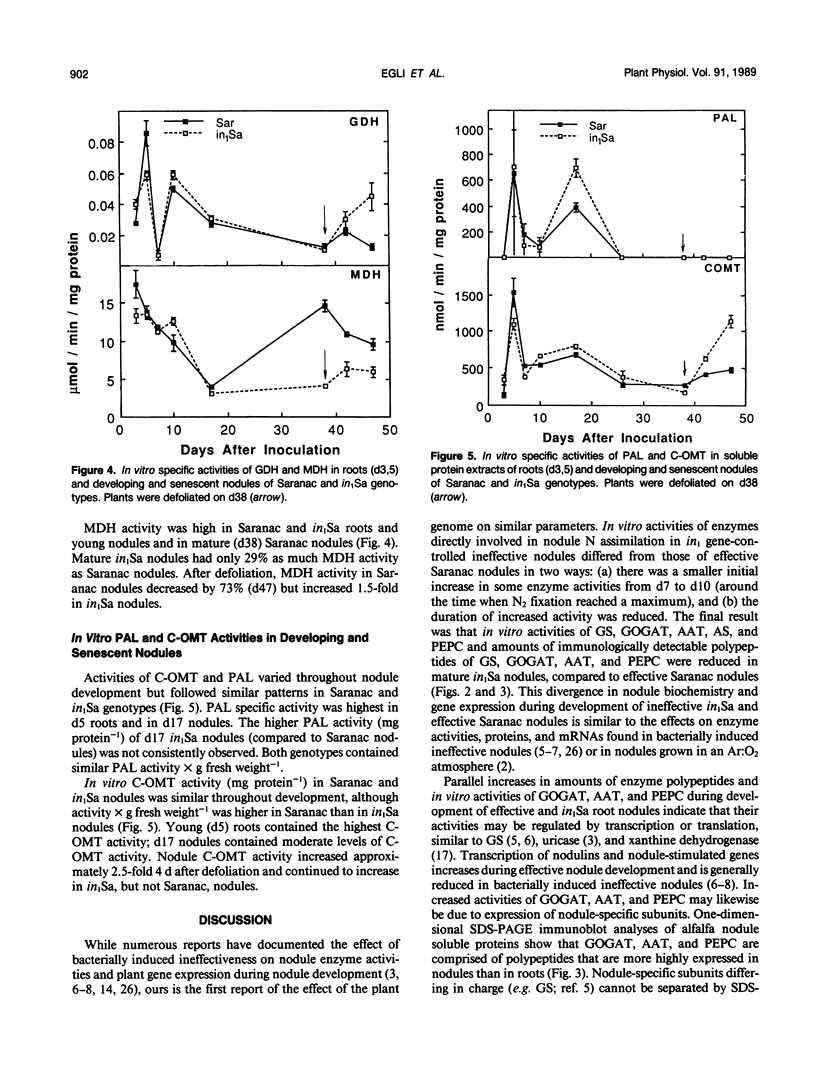
Effective (N2-fixing) alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and plant-controlled ineffective (non-N2-fixing) alfalfa recessive for the in1 gene were compared to determine the effects of the in1 gene on nodule development, acetylene reduction activity (ARA), and nodule enzymes associated with N assimilation and disease resistance. Effective nodule ARA reached a maximum before activities of glutamine synthetase (GS), glutamate synthase (GOGAT), aspartate aminotransferase (AAT), asparagine synthetase (AS), and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) peaked. Ineffective nodule ARA was only 5% of effective nodule ARA. Developmental profiles of GS, GOGAT, AAT, and PEPC activities were similar for effective and ineffective nodules, but activities in ineffective nodules were lower and declined earlier. Little AS activity was detected in developing ineffective nodules. Changes in GS, GOGAT, AAT, and PEPC activities in developing and senescent effective and ineffective nodules generally paralleled amounts of immunologically detectable enzyme polypeptides. Effective nodule GS, GOGAT, AAT, AS, and PEPC activities declined after defoliation. Activities of glutamate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase, phenylalanine ammonia lyase, and caffeic acid-o-methyltransferase were unrelated to nodule effectiveness. Maximum expression of nodule N-assimilating enzymes appeared to require the continued presence of a product associated with effective bacteroids that was lacking in in1 effective nodules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. P., Vance C. P., Heichel G. H., Miller S. S. Purification and Characterization of NADH-Glutamate Synthase from Alfalfa Root Nodules. Plant Physiol. 1989 May;90(1):351–358. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.1.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann H., Preddie E., Verma D. P. Nodulin-35: a subunit of specific uricase (uricase II) induced and localized in the uninfected cells of soybean nodules. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2333–2339. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A., Sutton W. D. Carbon Dioxide Fixation by Lupin Root Nodules: I. Characterization, Association with Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase, and Correlation with Nitrogen Fixation during Nodule Development. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):47–50. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn K., Dickstein R., Feinbaum R., Burnett B. K., Peterman T. K., Thoidis G., Goodman H. M., Ausubel F. M. Developmental regulation of nodule-specific genes in alfalfa root nodules. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1988 Feb;1(2):66–74. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-1-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith S. M., Vance C. P. Aspartate aminotransferase in alfalfa root nodules : I. Purification and partial characterization. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1622–1629. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schrader L. E. Isolation and Immunochemical Characterization of Plant Glutamine Synthetase in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Nodules. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1759–1761. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Vance C. P. Root Nodule Enzymes of Ammonia Assimilation in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) : DEVELOPMENTAL PATTERNS AND RESPONSE TO APPLIED NITROGEN. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jun;67(6):1198–1203. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.6.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirel B., Bouet C., King B., Layzell D., Jacobs F., Verma D. P. Glutamine synthetase genes are regulated by ammonia provided externally or by symbiotic nitrogen fixation. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1167–1171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen K., Jochimsen B. U. Appearance of purine-catabolizing enzymes in fix and fix root nodules on soybean and effect of oxygen on the expression of the enzymes in callus tissue. Plant Physiol. 1987 Oct;85(2):452–456. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. S., Boylan K. L., Vance C. P. Alfalfa Root Nodule Carbon Dioxide Fixation : III. Immunological Studies of Nodule Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):501–508. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. H., Boland M. J., Blevins D. G., Schubert K. R., Randall D. D. Enzymes of amide and ureide biogenesis in developing soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1334–1338. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapp S. S., Vance C. P. Asparagine Biosynthesis in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Root Nodules. Plant Physiol. 1986 Oct;82(2):390–395. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stulen I., Oaks A. Asparagine synthetase in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1977 Nov;60(5):680–683. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.5.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulebele G., Silverstein E. Malate dehydrogenase and aspartate aminotransferase of Phycomyces blakesleeanus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Sep;133(2):425–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90472-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance C. P., Heichel G. H., Barnes D. K., Bryan J. W., Johnson L. E. Nitrogen Fixation, Nodule Development, and Vegetative Regrowth of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) following Harvest. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jul;64(1):1–8. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance C. P., Stade S., Maxwell C. A. Alfalfa root nodule carbon dioxide fixation : I. Association with nitrogen fixation and incorporation into amino acids. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):469–473. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]