Abstract
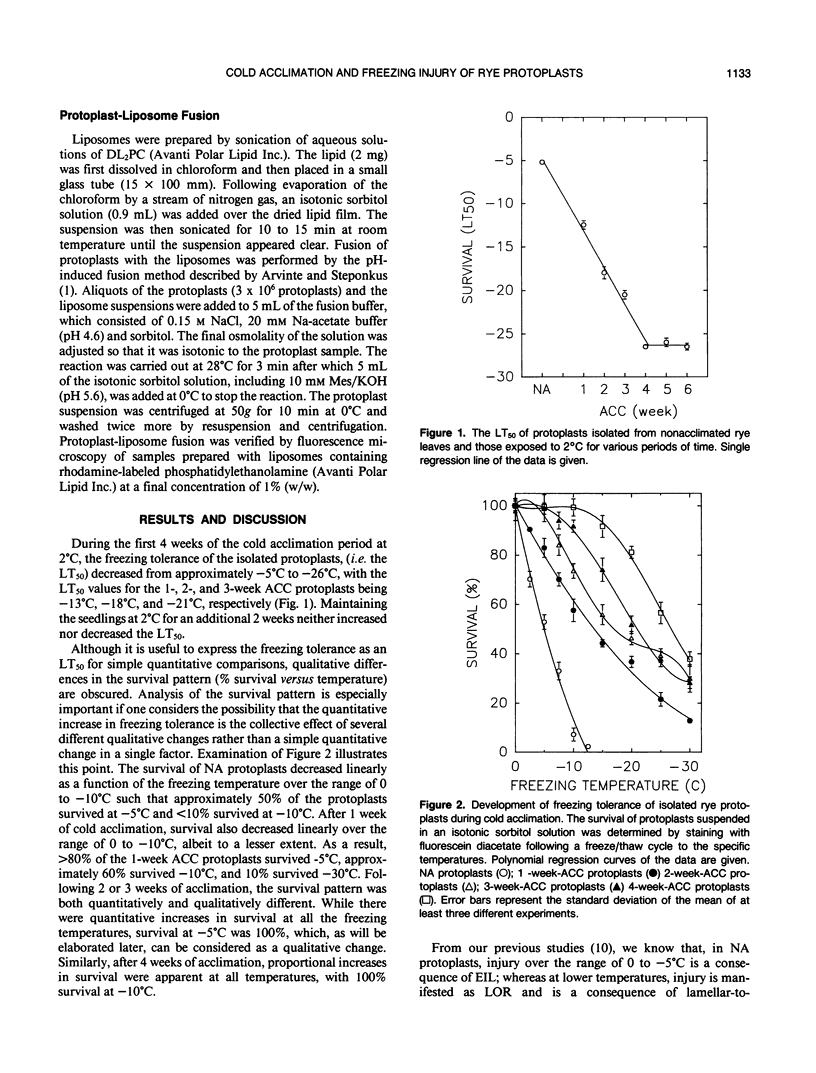
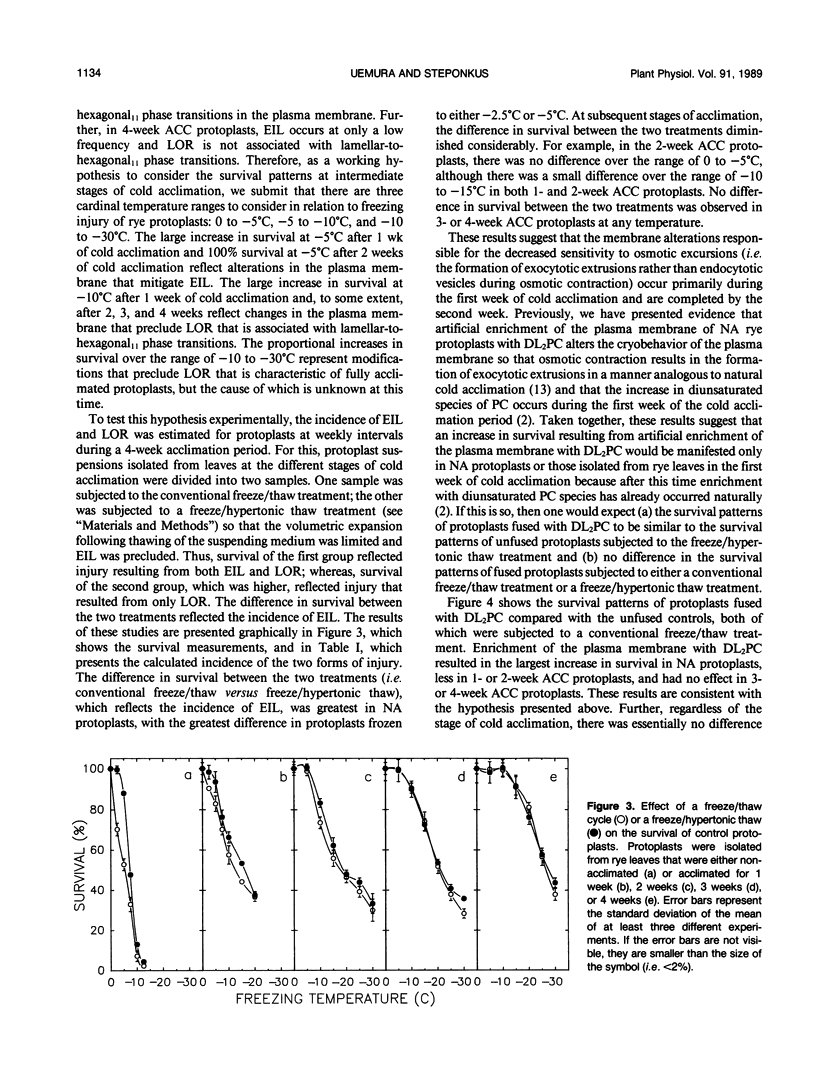
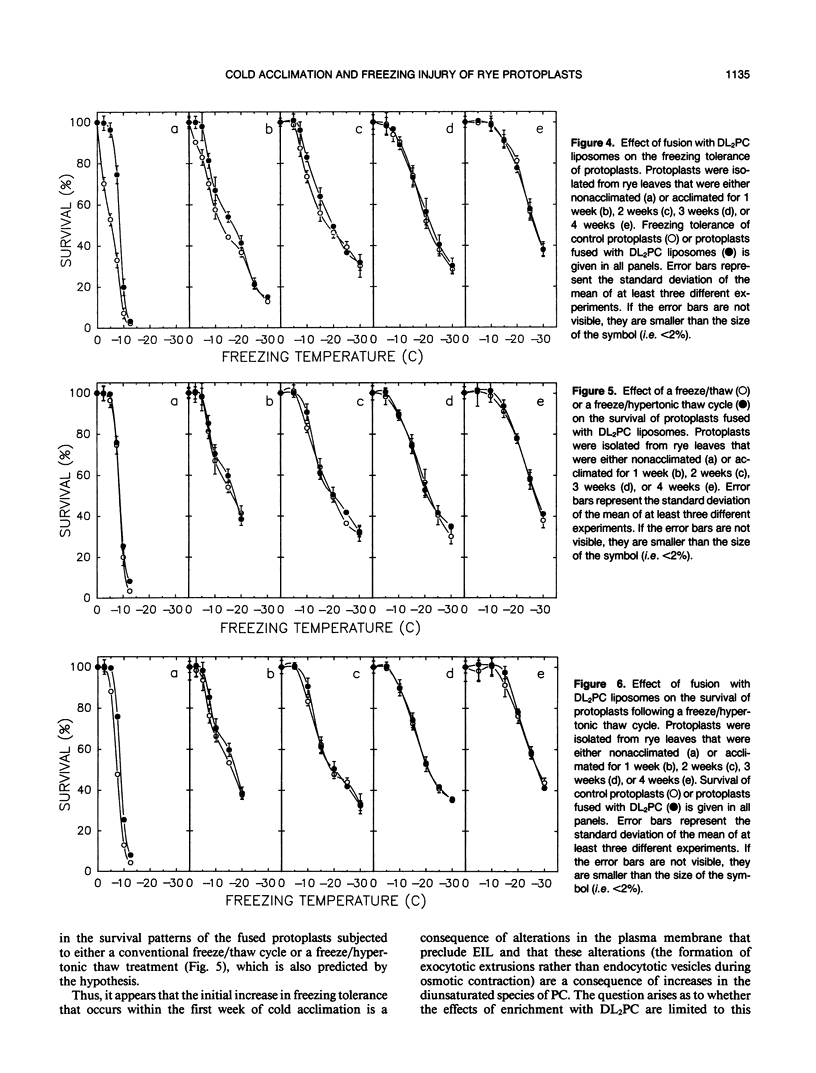
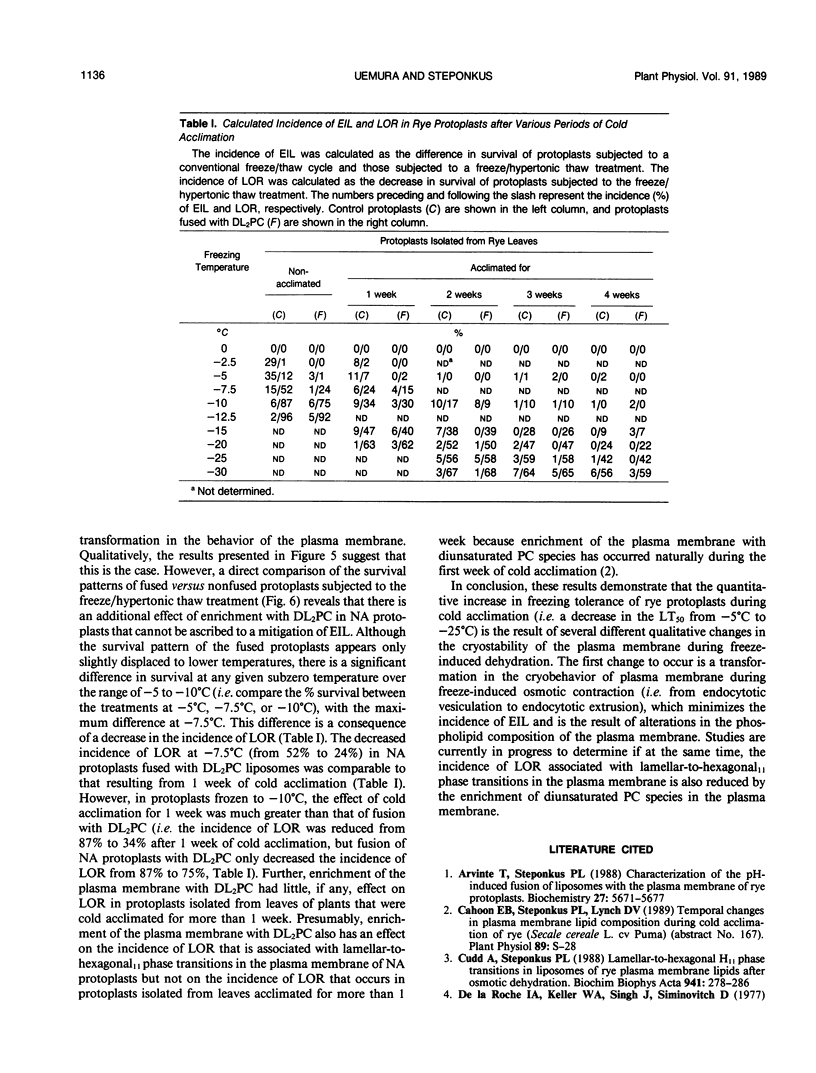
The freezing tolerance and incidence of two forms of freezing injury (expansion-induced lysis and loss of osmotic responsiveness) were determined for protoplasts isolated from rye leaves (Secale cereale L. cv Puma) at various times during cold acclimation. During the first 4 weeks of the cold acclimation period, the LT50 (i.e. the minimum temperature at which 50% of the protoplasts survived) decreased from −5°C to −25°C. In protoplasts isolated from nonacclimated leaves (NA protoplasts), expansion-induced lysis (EIL) was the predominant form of injury at the LT50. However, after only 1 week of cold acclimation, the incidence of EIL was reduced to less than 10% at any subzero temperature; and loss of osmotic responsiveness was the predominant form of injury, regardless of the freezing temperature. Fusion of either NA protoplasts or protoplasts isolated from leaves of seedlings cold acclimated for 1 week (1-week ACC protoplasts) with liposomes of dilinoleoylphosphatidylcholine also decreased the incidence of EIL to less than 10%. Fusion of protoplasts with dilinoleoylphosphatidylcholine diminished the incidence of loss of osmotic responsiveness, but only in NA protoplasts or 1-week ACC protoplasts that were frozen to temperatures over the range of -5 to -10°C. These results suggest that the cold acclimation process, which results in a quantitative increase in freezing resistance, involves several different qualitative changes in the cryobehavior of the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dowgert M. F., Steponkus P. L. Behavior of the Plasma Membrane of Isolated Protoplasts during a Freeze-Thaw Cycle. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1139–1151. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett W. F., Dunn M. F. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars in Infected Leaves of Susceptible Hosts. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):5–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon-Kamm W. J., Steponkus P. L. Lamellar-to-hexagonalII phase transitions in the plasma membrane of isolated protoplasts after freeze-induced dehydration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6373–6377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. V., Steponkus P. L. Plasma Membrane Lipid Alterations Associated with Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):761–767. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steponkus P. L., Lynch D. V. Freeze/thaw-induced destabilization of the plasma membrane and the effects of cold acclimation. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Feb;21(1):21–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00762210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steponkus P. L., Uemura M., Balsamo R. A., Arvinte T., Lynch D. V. Transformation of the cryobehavior of rye protoplasts by modification of the plasma membrane lipid composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9026–9030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura M., Yoshida S. Involvement of Plasma Membrane Alterations in Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):818–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widholm J. M. The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):189–194. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


