Abstract
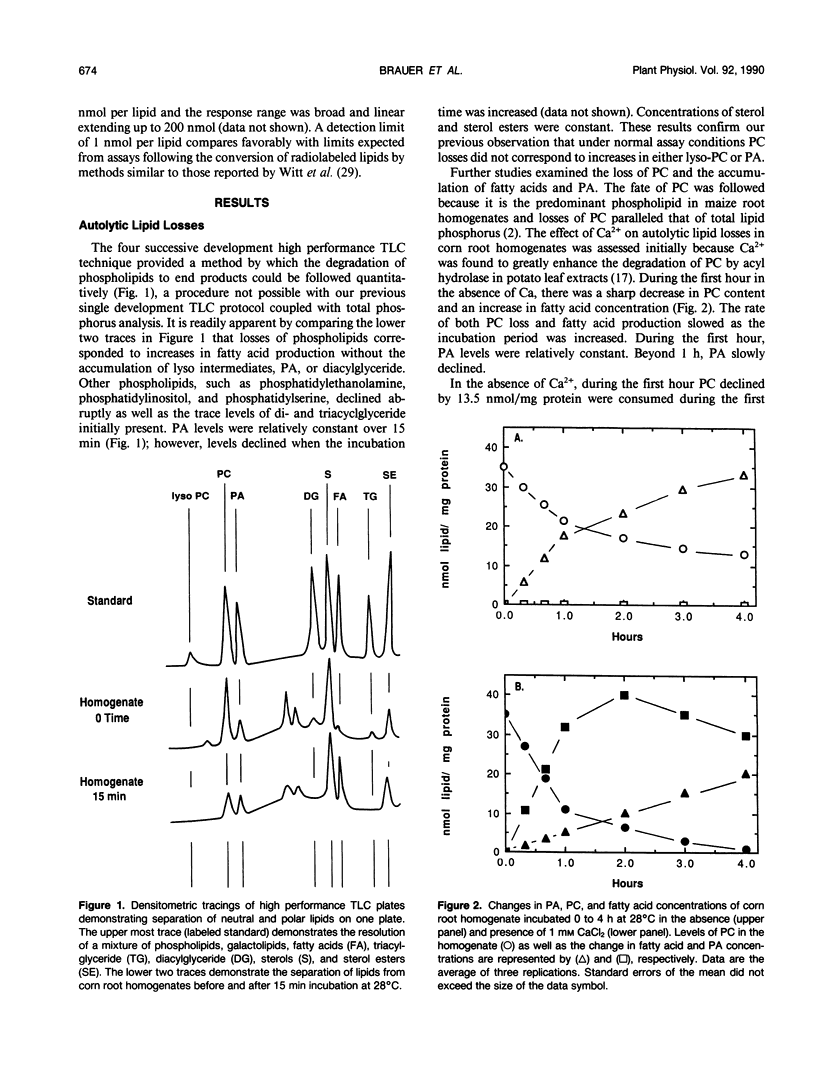
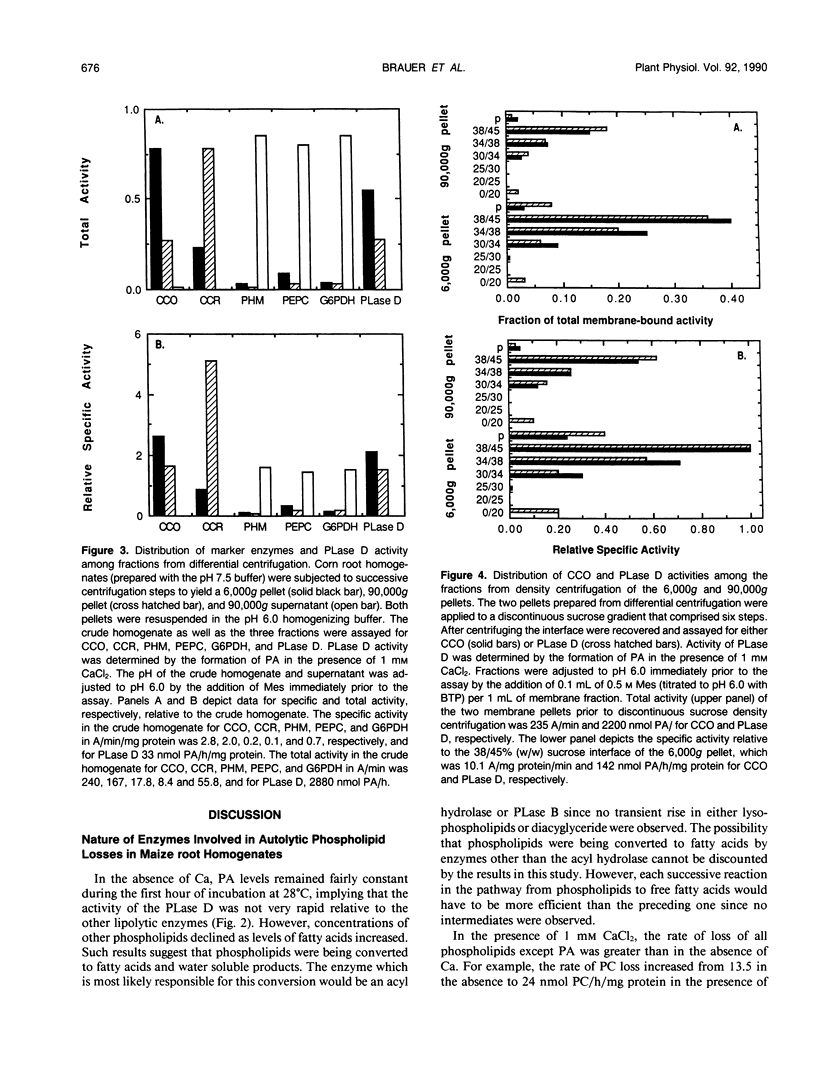
Autolytic lipid changes in corn (Zea mays L.) root crude homogenates and isolated membranes were examined by the use of high performance thin-layer chromatography. In the absence of added CaCl2, losses in phosphatidylcholine and other phospholipids corresponds to increase in fatty acids without the accumulation of either phosphatidic acid or lyso-phosphatidylcholine. However, in the presence of 1 millimolar CaCl2, phosphatidylcholine concentrations declined more rapidly with an immediate increase in phoshatidic acid, and slower rate of fatty acid accumulation. Autolytic phospholipid degradation yielded primarily free fatty acids in the absence of Ca and phosphatidic acid in the presence of 1 millimolar CaCl2, suggesting the presence of an acyl hydrolase and phospholipase D activities. Differential centrifugation studies indicate that 50 to 80% of the crude homogenate's phospholipase D activity is membrane-bound. Density centrifugation experiments suggest that the membrane-bound phospholipase D activity is localized primarily on mitochondrial membranes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauer D., Hsu A. F., Tu S. I. Factors associated with the instability of nitrate-insensitive proton transport by maize root microsomes. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jul;87(3):598–602. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman E. M., Chrispeels M. J. Characteristics and subcellular localization of phospholipase d and phosphatidic Acid phosphatase in mung bean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):1001–1007. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills M. J., Beevers H. Ca stimulated neutral lipase activity in castor bean lipid bodies. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):272–276. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kringstad R., Kenyon W. H., Black C. C. The rapid isolation of vacuoles from leaves of crassulacean Acid metabolism plants. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):379–382. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke I. R., Zeugner S. Quantitative high-performance thin-layer chromatography of lipids in plasma and liver homogenates after direct application of 0.5-microliter samples to the silica-gel layer. J Chromatogr. 1978 Sep 1;146(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81892-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hotchkiss C. W. Cation-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity and Cation Transport in Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):331–335. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell R. J., Marmer W. N. Systematic protocol for the accumulation of fatty acid data from multiple tissue samples: tissue handling, lipid extraction and class separation, and capillary gas chromatographic analysis. Lipids. 1983 Jul;18(7):453–459. doi: 10.1007/BF02535785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin P. M., Sommarin M., Sandelius A. S., Jergil B. Identification of Ca2+-stimulated polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C in isolated plant plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Jones L. M., Downes C. P., Creba J. A. The stimulation of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):123–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahashi G., Baker A. F. beta-Glucosidase Activity in Corn Roots: Problems in Subcellular Fractionation. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):861–864. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahashi J., Hiraike K. Effects of centrifugal force and centrifugation time on the sedimentation of plant organelles. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):546–548. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliyath G., Thompson J. E. Calcium- and calmodulin-regulated breakdown of phospholipid by microsomal membranes from bean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):63–68. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., Morré D. J. Action and Inhibition of Endogenous Phospholipases during Isolation of Plant Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):933–937. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom M., Maretzki A., Komor E. Vacuoles from Sugarcane Suspension Cultures : I. ISOLATION AND PARTIAL CHARACTERIZATION. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1315–1319. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu S. I., Nagahashi G., Brouillette J. N. Proton pumping kinetics and origin of nitrate inhibition of tonoplast-type H+-ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Aug 1;256(2):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90620-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters S. P., Noble E. R., Dalling M. J. Intracellular Localization of Peptide Hydrolases in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1982 Mar;69(3):575–579. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt W., Yelenosky G., Mayer R. T. Purification of phospholipase D from citrus callus tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 15;259(1):164–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90482-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


