Abstract
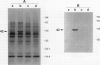
A 42-kilodalton cytoplasmic membrane protein is synthesized when high CO2-grown cells of Synechococcus PCC 7942 (Anacystis nidulans R2) are exposed to low CO2. The structural gene for this protein (cmpA) has been cloned and sequenced and shown to encode a 450 amino acid polypeptide with a molecular mass of 49 kilodalton. A deletion mutant lacking the 42-kilodalton protein was obtained by transformation of Synechococcus PCC 7942 following in vitro mutagenesis of the cloned gene. There were no significant differences between the mutant and wild-type cells in their growth rates under either low or high CO2 conditions. The activity of inorganic carbon (Ci) transport in the mutant was as high as that in the wild-type strain. In both types of cells, CO2 was the main species of Ci transported and the activities of CO2 and HCO3− transport increased when high CO2-grown cells were exposed to low CO2. We conclude that the 42-kilodalton protein is not directly involved in the Ci-accumulating mechanism of Synechococcus PCC 7942.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Photosynthesis and Inorganic Carbon Usage by the Marine Cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):517–523. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W. H., Henderson L. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:254–259. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus Y., Zenvirth D., Harel E., Kaplan A. Induction of HCO(3) Transporting Capability and High Photosynthetic Affinity to Inorganic Carbon by Low Concentration of CO(2) in Anabaena variabilis. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1008–1012. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masamoto K., Riethman H. C., Sherman L. A. Isolation and Characterization of a Carotenoid-Associated Thylakoid Protein from the Cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans R2. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):633–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Kaneda T., Omata T. A Mutant of Synechococcus PCC7942 Incapable of Adapting to Low CO(2) Concentration. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):711–715. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Ogawa T. Biosynthesis of a 42-kD Polypeptide in the Cytoplasmic Membrane of the Cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans Strain R2 during Adaptation to Low CO(2) Concentration. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):525–530. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Ogawa T., Marcus Y., Friedberg D., Kaplan A. Adaptation to Low CO(2) Level in a Mutant of Anacystis nidulans R(2) which Requires High CO(2) for Growth. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):892–894. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Ohmori M., Arai N., Ogawa T. Genetically engineered mutant of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC 7942 defective in nitrate transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6612–6616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Anomalous cleavage of aspartyl-proline peptide bonds during amino acid sequence determinations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90918-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. J., Masamoto K., Sherman D. M., Sherman L. A. DNA sequence and regulation of the gene (cbpA) encoding the 42-kilodalton cytoplasmic membrane carotenoprotein of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3486–3493. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3486-3493.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Austen B. The role of topogenic sequences in the movement of proteins through membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):249–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2460249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R., Friedberg D., Kaplan A. Is there a role for the 42 kilodalton polypeptide in inorganic carbon uptake by cyanobacteria? Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):284–288. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Kunisawa R., Mandel M., Cohen-Bazire G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):171–205. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.171-205.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volokita M., Zenvirth D., Kaplan A., Reinhold L. Nature of the Inorganic Carbon Species Actively Taken Up by the Cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):599–602. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Szalay A. A. Stable integration of foreign DNA into the chromosome of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus R2. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]