Abstract
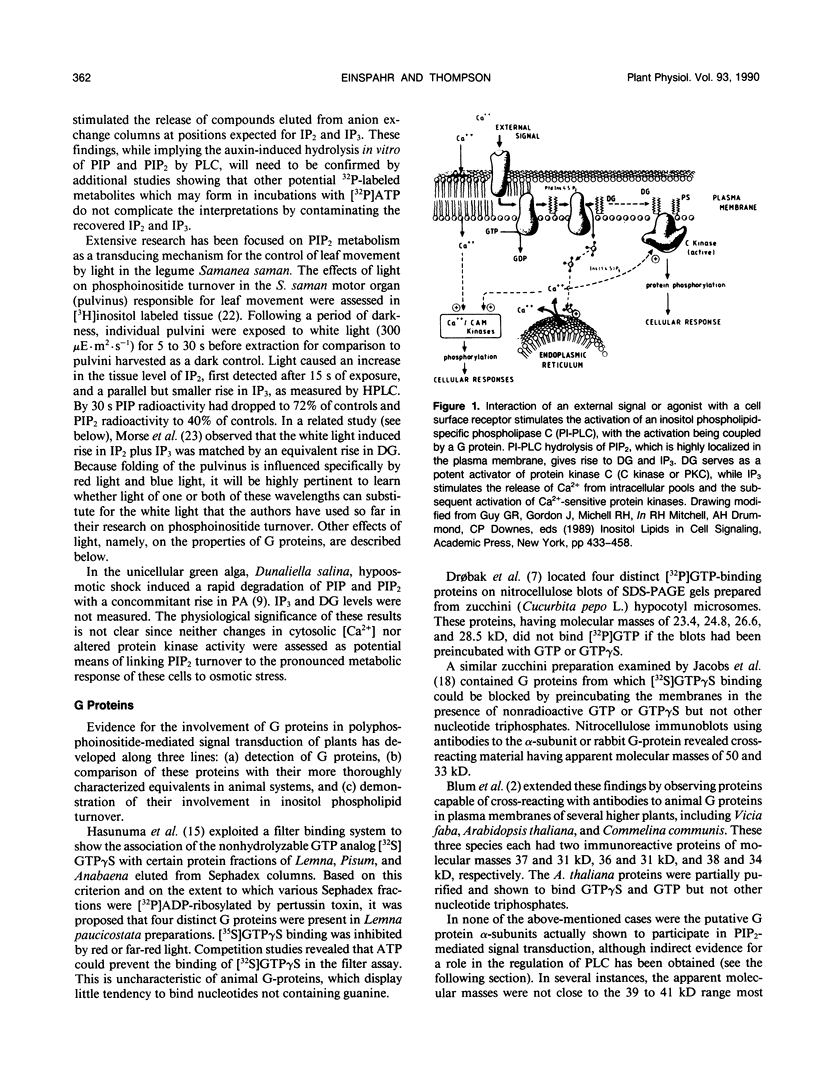
Recent investigations have confirmed the presence of the polyphosphoinositides, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), as well as inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C in higher plant and microalgal cells. In addition, it has been shown that stimulation of some photosynthetic cell types by environmental or hormonal challenge is accompanied by degradation of the polyphosphoinositides. The products of phospholipase C-catalyzed PIP2 hydrolysis, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol, appear to be capable of releasing organelle-bound Ca2+ and stimulating protein kinase C-like activity in vitro. However, a direct cause and effect relationship between stimulated PIP2 breakdown and changes in intracellular calcium, protein phosphorylation, or cell function has not yet been unequivocally established. Despite a number of technical difficulties slowing progress in this field, it is likely that photosynthetic organisms will soon be shown to transmit physiologically significant extracellular signals across their plasma membranes by a PIP2-mediated transduction mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan E., Dawson A., Drøbak B., Roberts K. GTP causes calcium release from a plant microsomal fraction. Cell Signal. 1989;1(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W., Hinsch K. D., Schultz G., Weiler E. W. Identification of GTP-binding proteins in the plasma membrane of higher plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):954–959. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coté G. G., Depass A. L., Quarmby L. M., Tate B. F., Morse M. J., Satter R. L., Crain R. C. Separation and Characterization of Inositol Phospholipids from the Pulvini of Samanea saman. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1422–1428. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobak B. K., Allan E. F., Comerford J. G., Roberts K., Dawson A. P. Presence of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in a plant hypocotyl microsomal fraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):899–903. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90713-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drøbak B. K., Ferguson I. B., Dawson A. P., Irvine R. F. Inositol-containing lipids in suspension-cultured plant cells: an isotopic study. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):217–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einspahr K. J., Peeler T. C., Thompson G. A., Jr Rapid changes in polyphosphoinositide metabolism associated with the response of Dunaliella salina to hypoosmotic shock. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5775–5779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einspahr K. J., Peeler T. C., Thompson G. A. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate Phospholipase C and Phosphomonoesterase in Dunaliella salina Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):1115–1120. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. C., Kokke Y. S. Cross-reaction of a plant protein kinase with antiserum raised against a sequence from bovine brain protein kinase C regulatory sub-unit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 30;145(3):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91541-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettlinger C., Lehle L. Auxin induces rapid changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolites. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):176–178. doi: 10.1038/331176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Drøbak B. K., Dawson A. P., Musgrave A. Phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate and Phosphatidylinositol(4)phosphate in Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):888–892. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Thelen M. P., Farndale R. W., Astle M. C., Rubery P. H. Specific guanine nucleotide binding by membranes from Cucurbita pepo seedlings. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1478–1484. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray W. C., Irvine R. F. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase in higher plants. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):877–881. doi: 10.1042/bj2490877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin P. M., Sommarin M., Sandelius A. S., Jergil B. Identification of Ca2+-stimulated polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C in isolated plant plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Memon A. R., Rincon M., Boss W. F. Inositol Trisphosphate Metabolism in Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Cells. Plant Physiol. 1989 Oct;91(2):477–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. J., Crain R. C., Coté G. G., Satter R. L. Light-Stimulated Inositol Phospholipid Turnover in Samanea saman Pulvini : Increased Levels of Diacylglycerol. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):724–727. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. J., Crain R. C., Satter R. L. Light-stimulated inositolphospholipid turnover in Samanea saman leaf pulvini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7075–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy A. S., Poovaiah B. W. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate induced calcium release from corn coleoptile microsomes. J Biochem. 1987 Mar;101(3):569–573. doi: 10.1093/jb/101.3.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincón M., Chen Q., Boss W. F. Characterization of Inositol Phosphates in Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Cells. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):126–132. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker K. S., Sze H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from vacuolar membrane vesicles of oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3944–3946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagh S. S., Menon K. K., Natarajan V. Evidence for the incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate into leaf inositol phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 23;962(2):178–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


