Abstract
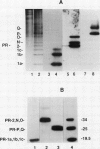
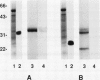
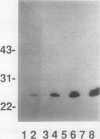
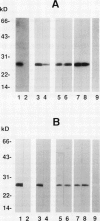
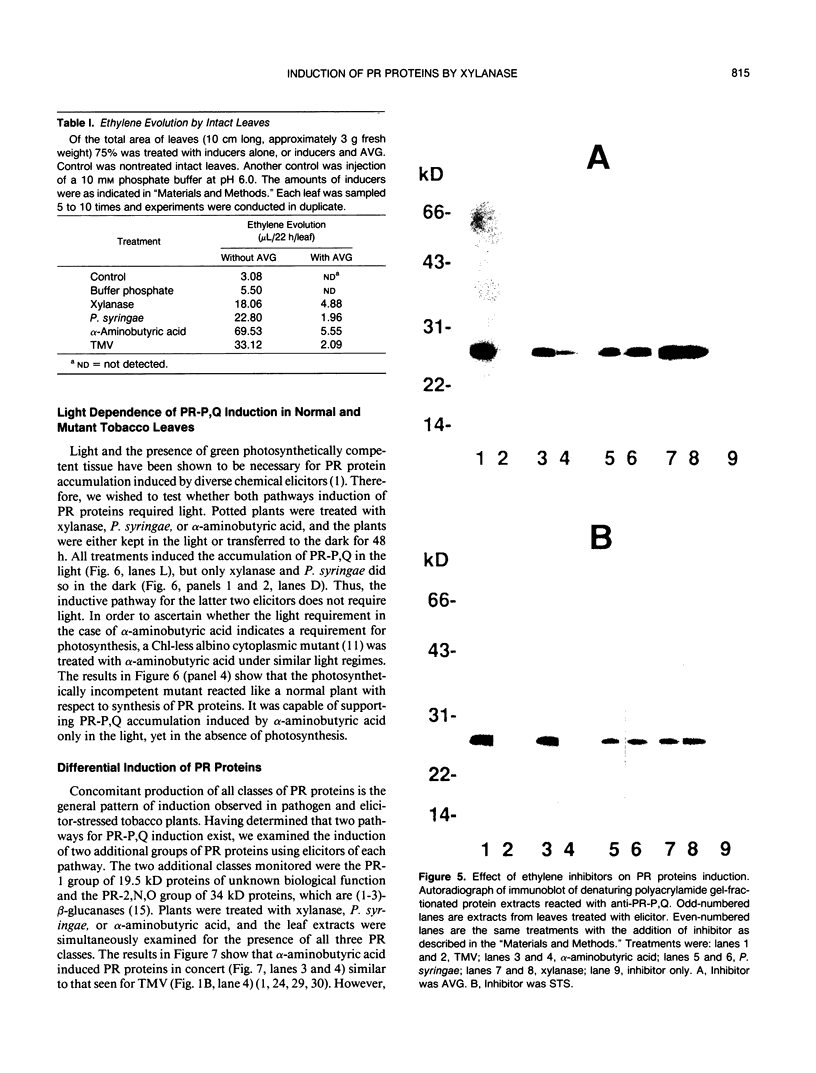
Antisera to acidic isoforms of pathogenesis-related proteins were used to measure the induction of these proteins in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) leaves. Endo-(1-4)-β-xylanase purified from culture filtrates of Trichoderma viride was a strong elicitor of pathogenesis-related protein synthesis in tobacco leaves. The synthesis of these proteins was localized to tissue at the area of enzyme application. The inhibitors of ethylene biosynthesis and ethylene action, 1-aminoethoxyvinylglycine and silver thiosulfate, inhibited accumulation of pathogenesis-related proteins induced by tobacco mosaic virus and α-aminobutyric acid, but did not inhibit elicitation by xylanase. Likewise, the induction of these proteins by the tobacco pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci was not affected by the inhibitors of ethylene biosynthesis and action. The leaf response to tobacco mosaic virus and α-aminobutyric acid was dependent on light in normal and photosynthetically incompetent leaves. In contrast, the response of leaves to xylanase was independent of light. Tobacco mosaic virus and α-aminobutyric acid induced concerted accumulation of pathogenesis-related proteins. However, xylanase elicited the accumulation of only a subset of these proteins. Specifically, the plant (1-3)-β-glucanases, which are normally a part of the concerted response, were underrepresented. These experiments have revealed the presence of a novel ethylene-independent pathway for pathogenesis-related protein induction that is activated by xylanase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bol J. F., van Kan J. A. The synthesis and possible functions of virus-induced proteins in plants. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Feb;5(2):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulcke M. V., Bauw G., Castresana C., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Characterization of vacuolar and extracellular beta(1,3)-glucanases of tobacco: Evidence for a strictly compartmentalized plant defense system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2673–2677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Helgeson J. P. An Extracellular Protein from Phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae Is Associated with Stress Metabolite Accumulation in Tobacco Callus. Plant Physiol. 1987 Nov;85(3):733–740. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink W., Liefland M., Mendgen K. Chitinases and beta-1,3-Glucanases in the Apoplastic Compartment of Oat Leaves (Avena sativa L.). Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):270–275. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Aviv D., Galun E., Edelman M. Efficient induction and selection of chloroplast-encoded antibiotic-resistant mutants in Nicotiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs Y., Saxena A., Gamble H. R., Anderson J. D. Ethylene biosynthesis-inducing protein from cellulysin is an endoxylanase. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):138–143. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann S., Legrand M., Geoffroy P., Fritig B. Biological function of ;pathogenesis-related' proteins: four PR proteins of tobacco have 1,3-beta-glucanase activity. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3209–3212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand M., Kauffmann S., Geoffroy P., Fritig B. Biological function of pathogenesis-related proteins: Four tobacco pathogenesis-related proteins are chitinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6750–6754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan T., Ori N., Fluhr R. Pathogenesis-related proteins are developmentally regulated in tobacco flowers. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):881–887. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Hadwiger L. A., Boller T. Ethylene: Symptom, Not Signal for the Induction of Chitinase and beta-1,3-Glucanase in Pea Pods by Pathogens and Elicitors. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):607–611. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Mauch-Mani B., Boller T. Antifungal Hydrolases in Pea Tissue : II. Inhibition of Fungal Growth by Combinations of Chitinase and beta-1,3-Glucanase. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):936–942. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Memelink J., Hoge J. H., Schilperoort R. A. Cytokinin stress changes the developmental regulation of several defence-related genes in tobacco. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3579–3583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roby D., Toppan A., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions : VI. Elicitors of Ethylene from Colletotrichum lagenarium Trigger Chitinase Activity in Melon Plants. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):228–233. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A. Oligosaccharide signalling in plants. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:295–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon L. C., van Kammen A. Polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis of the soluble leaf proteins from Nicotiana tabacum var. "Samsun" and "Samsun NN". II. Changes in protein constitution after infection with tobacco mosaic virus. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):190–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]