Abstract
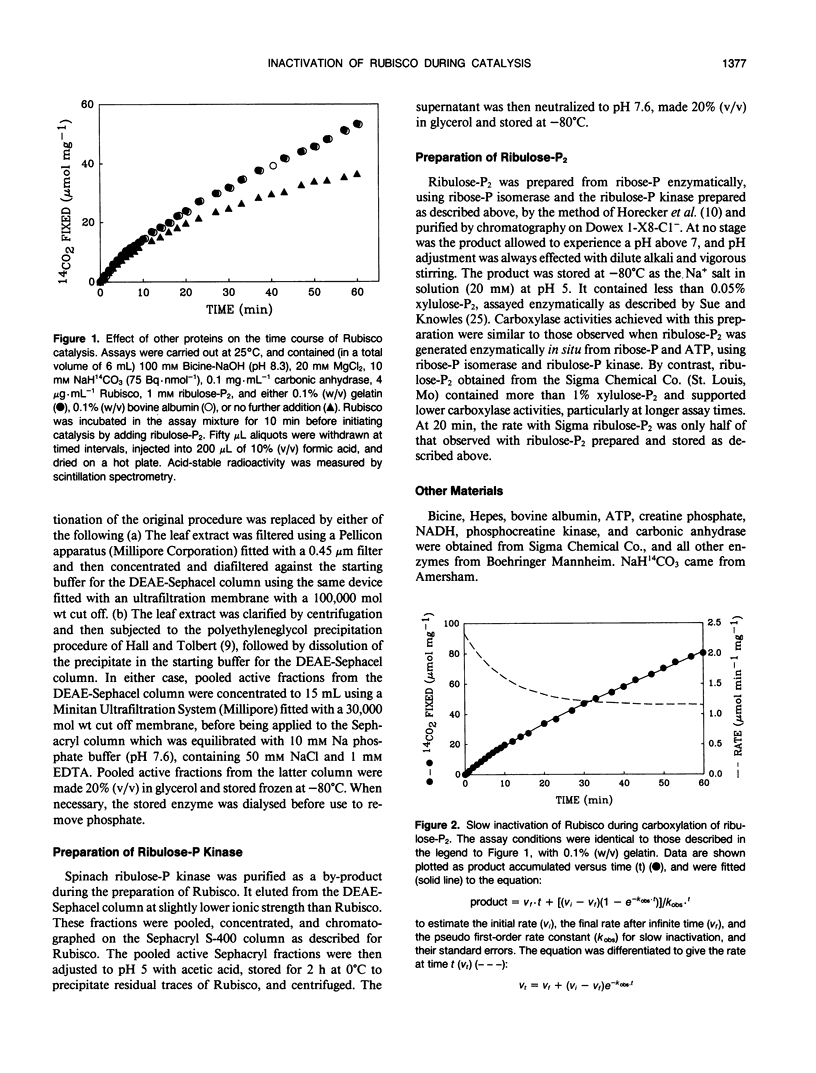
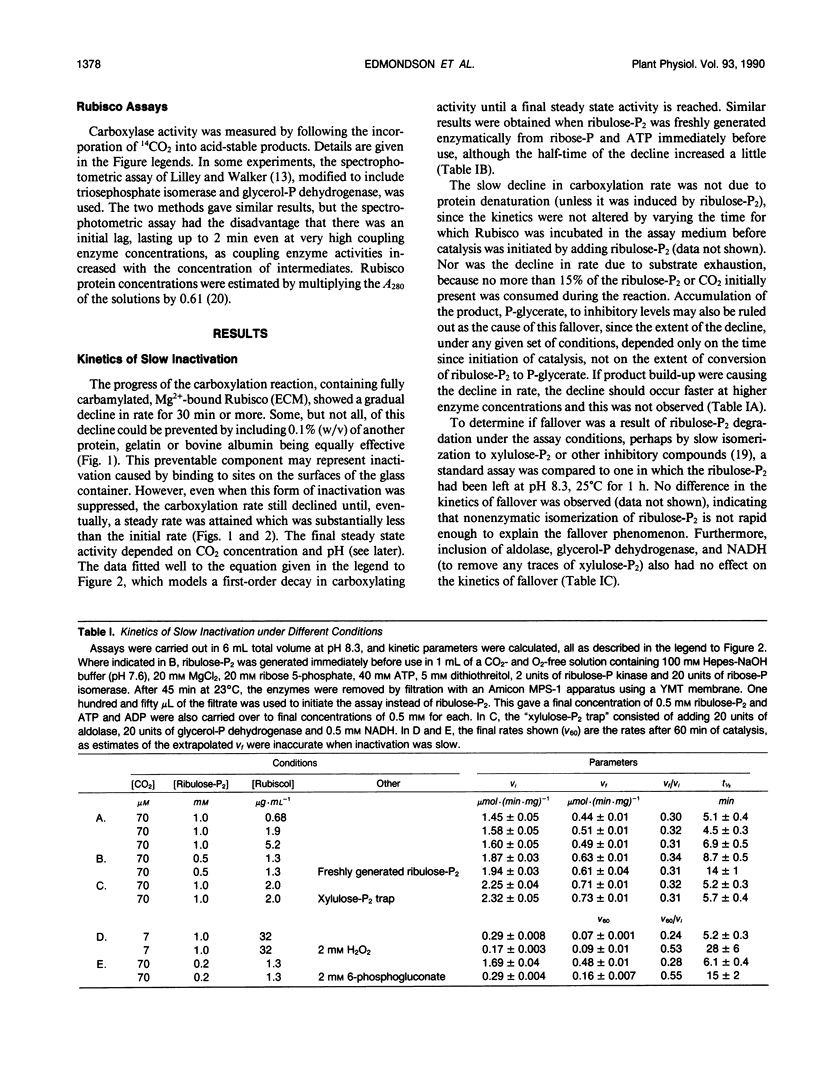
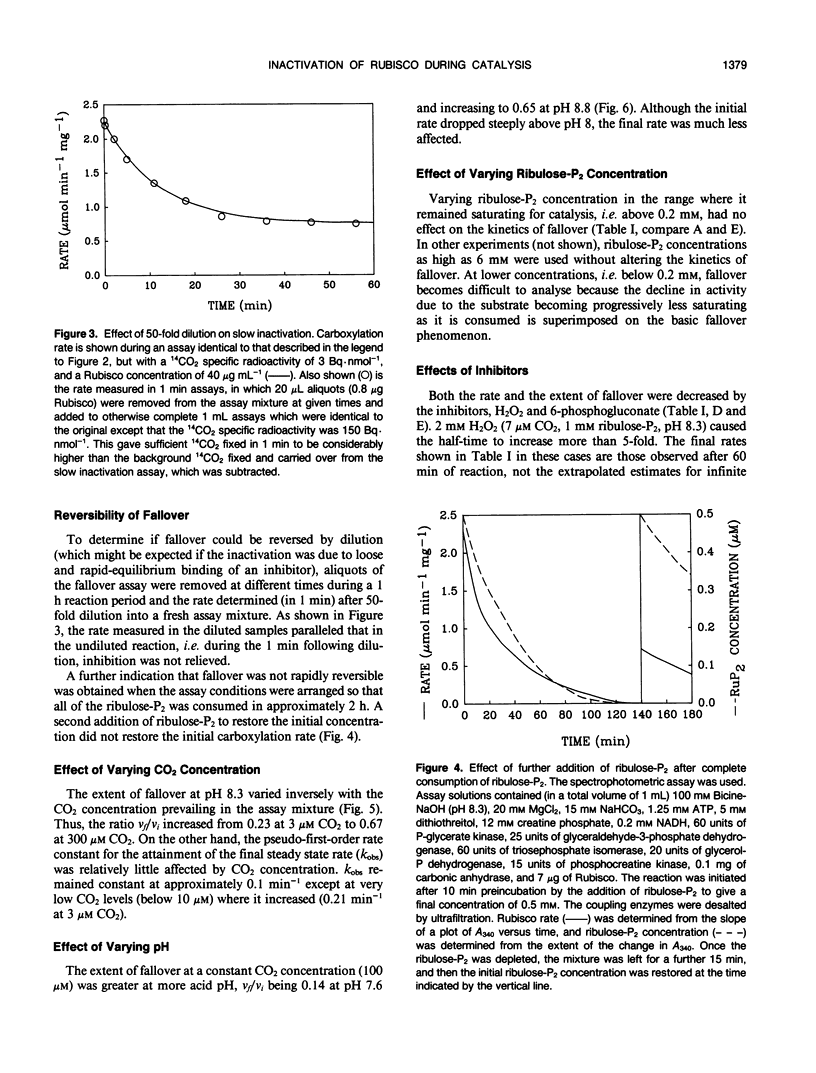
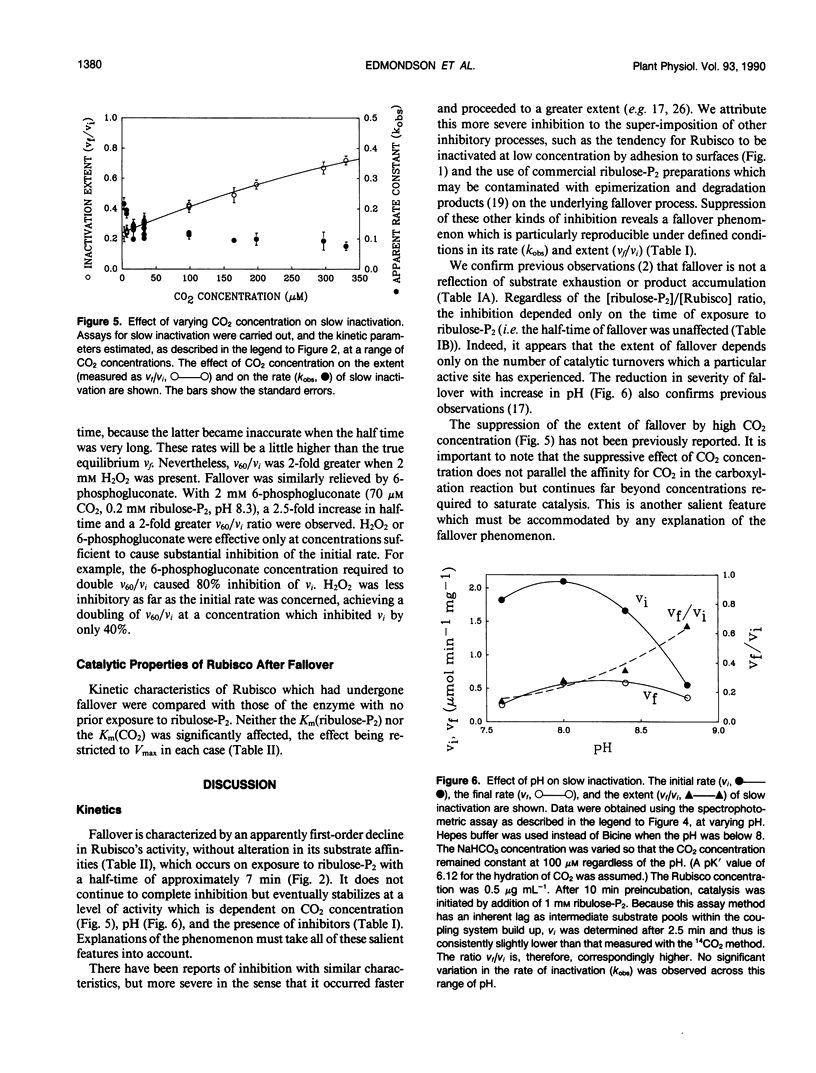
The catalytic activity of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) declined as soon as catalysis was initiated by exposure to its substrate, d-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (ribulose-P2). The decline continued exponentially, with a half-time of approximately 7 minutes until, eventually, a steady state level of activity was reached which could be as low as 15% of the initial activity. The ratio of the steady state activity to the initial activity was lower at low CO2 concentration and at low pH. The inhibitors 6-phosphogluconate and H2O2 alleviated the inactivation, increasing the final/initial rate ratio and the half-time. Varying ribulose-P2 concentration in the range above that required to saturate catalysis did not affect the kinetics of inactivation. The affinities for CO2 and ribulose-P2 were unaffected by the inactivation. The decline in activity occurred with preparations of ribulose-P2 which contained no detectable d-xylulose-1,5-bisphosphate and also with ribulose-P2 which had been generated enzymatically immediately before use. Inclusion of an aldolase system for removing d-xylulose-1,5-bisphosphate also did not alter the inactivation process. The inactivated Rubisco did not recover after complete exhaustion of ribulose-P2. We conclude that the inactivation is not caused by readily-reversible binding of ribulose-P2 at a site different from the active site and that it is unlikely to be attributable to inhibitory contaminants in ribulose-P2 preparations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews T. J., Ballment B. Active-site carbamate formation and reaction-intermediate-analog binding by ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in the absence of its small subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3660–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. J., Hatch M. D. Properties and mechanism of action of pyruvate, phosphate dikinase from leaves. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):117–125. doi: 10.1042/bj1140117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R., Andrews T. J., Canvin D. T., Lorimer G. H. Interactions of hydrogen peroxide with ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham J. A., Krohne S., Lendzian K. In vivo control mechanism of the carboxylation reaction. Basic Life Sci. 1978;11:77–93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8106-8_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butz N. D., Sharkey T. D. Activity ratios of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase accurately reflect carbamylation ratios. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):735–739. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. L., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Slow Inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase during Catalysis Is Caused by Accumulation of a Slow, Tight-Binding Inhibitor at the Catalytic Site. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1390–1397. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. L., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Slow Inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase during Catalysis Is Not Due to Decarbamylation of the Catalytic Site. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. An improved spectrophotometric assay for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurry S. D., Pierce J., Tolbert N. E., Orme-Johnson W. H. On the mechanism of effector-mediated activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6623–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Mildvan A. S. Electron paramagnetic resonance, 1-H, and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the interaction of manganese and bicarbonate with ribulose 1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2743–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Berry J. A. Effects of pH on Activity and Activation of Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase at Air Level CO(2). Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):77–82. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paech C., Pierce J., McCurry S. D., Tolbert N. E. Inhibition of ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate epimerization and degradation products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen J. M., Lane M. D. Spinach ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2350–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., Portis A. R. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase protein prevents the in vitro decline in activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Hatch A. L., Stumpf D. K., Jensen R. G. Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate and activation of the carboxylase in the chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):252–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sue J. M., Knowles J. R. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase: primary deuterium kinetic isotope effect using [3-2H]ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5410–5414. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


