The synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of a new PdII cinnamaldehyde 4-thiosemicarbazone homoleptic complex is reported. As a result of H⋯S intramolecular interactions, graph-set motif S(5), the coordination sphere resembles a hydrogen-bonded macrocyclic environment-type. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by H⋯S interactions, with graph-set motifs
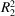 (8), forming a mono-periodic hydrogen-bonded polymer along [001].
(8), forming a mono-periodic hydrogen-bonded polymer along [001].
Keywords: palladium(II) thiosemicarbazone complex, cinnamaldehyde 4-phenylthiosemicarbazone, Hirshfeld surface analysis, crystal structure
Abstract
The reaction of (2E)-N-phenyl-2-[(2E)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ylidene]hydrazinecarbothioamide (common name: cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone) deprotonated with NaOH in ethanol with an ethanolic suspension of PdII chloride in a 2:1 molar ratio yielded the title compound, [Pd(C16H14N3S)2]. The anionic ligands act as metal chelators, κ2 N 1 S-donors, forming five-membered rings with a trans-configuration. The PdII ion is fourfold coordinated in a slightly distorted square-planar geometry. For each ligand, one H⋯S and one H⋯N intramolecular interactions are observed, with S(5) and S(6) graph-set motifs. Concerning the H⋯S interactions, the coordination sphere resembles a hydrogen-bonded macrocyclic environment-type. In the crystal, the complexes are linked via pairs of H⋯S interactions, with graph-set motif R 2 2(8), and building a mono-periodic hydrogen-bonded ribbon along [001]. The Hirshfeld surface analysis indicates that the major contributions for the crystal cohesion are: H⋯H (45.3%), H⋯C/C⋯H (28.0%), H⋯S/S⋯H (8.0%) and H⋯N/N⋯H (7.4%).
1. Chemical context
As far as we know, the thiosemicarbazone chemistry can be traced back to the beginning of the 1900s, when a thiosemicarbazide derivative, H2N—N(H)C(=S)NR 1 R 2, was used as chemical reagent for the characterization of aldehydes and ketones, R 3 R 4C=O. It was pointed out that the main product of the characterization reaction was a thiosemicarbazone derivative, R 3 R 4C=N—N(H)C(=S)NR 1 R 2 (Freund & Schander, 1902 ▸). In the second half of the 1950s, the use of 4-phenylthiosemicarbazide as reagent for the characterization of cinnamaldehyde was reported and the cinnamaldehyde 4-phenylthiosemicarbazone molecule, the ligand of the title compound, was the major product of the reaction (Tišler, 1956 ▸).
From early times, as a product of qualitative analysis reactions in the organic chemistry, thiosemicarbazone chemistry emerged as a large class of compounds present in a wide range of scientific disciplines. For example, the cinnamaldehyde 4-phenylthiosemicarbazone derivative shows anti-corrosion activity for copper in nitric acid media (Mostafa, 2000 ▸).
One of the most important applications of thiosemicarbazone derivatives is in coordination chemistry. The N—N(H)—C(=S) fragment can be easily deprotonated and the negative charge is then delocalized over the N—N—C—S entity, which enables chemical bonding with many different metal centers, with different Lewis acidity, and a diversity of coordination modes, e.g., chelating and bridging. Complexes with anionic thiosemicarbazone derivatives are more common as a result of the charge density and the geometry adopted by the ligands (Lobana et al., 2009 ▸).
Many complexes with thiosemicarbazone ligands show relevant biological activity. For example, PdII heteroleptic complexes with a cinnamaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone derivative turned out to be very active on in vitro Human Topoisomerase IIα inhibition, a biological target of prime importance for cancer research (Rocha et al., 2019 ▸). Other PdII homoleptic and heteroleptic complexes with cinnamaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone as ligands were reported to be active against five human cancer cell lines in vitro: colon (Caco-2), cervix (HeLa), hepatocellular (HepG2), breast (MCF-7) and prostate (PC-3) (Nyawadea et al., 2021 ▸). Finally, NiII homoleptic cinnamaldehyde-4-ethylthiosemicarbazone and cinnamaldehyde-4-methylthiosemicarbazone derivative complexes showed, also in in vitro assays, inhibition of cell growth for two selected human tumour cell lines: breast (MCF-7) and lung (A549) (Farias et al., 2021 ▸).
Another interesting approach for cinnamaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone chemistry is the synthesis of nanostructured materials through thermal and solvothermal decomposition techniques, where thiosemicarbazone complexes are employed as single-molecule precursors. It was reported that the thermal and solvothermal decomposition of ZnL 2 and ZnCl2(LH)2 homo- and heteroleptic complexes results in the formation of ZnS nanocrystallites (for this section only, L = the anionic form of cinnamaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone and LH = the neutral form of it) (Palve & Garje, 2011 ▸). Similarly, CdII heteroleptic complexes CdCl2(LH)2 and CdI2(LH)2 were used as starting materials to obtain CdS nanoparticles (Pawar et al., 2016 ▸) and CoS or Co9S8 nanocrystallites were synthesized from CoL 2 and CoCl2(LH)2 homo- and heteroleptic complexes (Pawar & Garje, 2015 ▸).
Motivated by the bioinorganic chemistry and materials science of the cinnamaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone complexes, we report herein the synthesis, crystal structure and Hirshfeld analysis of a new PdII homoleptic complex where the cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone molecules act as anionic ligands.
2. Structural commentary
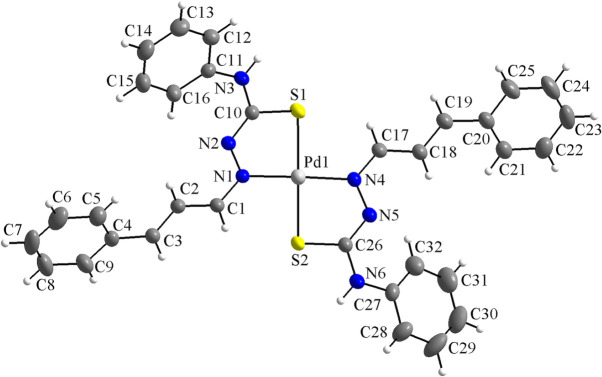
The asymmetric unit comprises one molecule of the title compound, with all atoms being located in general positions (Fig. 1 ▸). The complex consists of one PdII metal center and two deprotonated cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone ligands, which act as metal chelators, forming five-membered metallarings. The ligands are coordinated through N and S atoms in a trans-configuration, κ2 N 1 S-donors, and the N1—Pd1—N4 and the S1—Pd1—S2 angles are 178.31 (6) and 177.57 (2)°, respectively. The metal ion is fourfold coordinated in a slightly distorted square-planar geometry. The maximum deviation from the mean plane through the Pd1/N1/N4/S1/S2 fragment is 0.0227 (5) Å for Pd1 and the r.m.s. for the selected atoms is 0.0151 Å. Concerning the geometry of the N—N—C—S entities, the N1—N2—C10—S1 torsion angle is 0.6 (3)°, while N4—N5—C26—S2 is −0.4 (3)°. Both of the ligands are non-planar, with the angle between the mean planes through the C4–C9 and the C11–C16 aromatic rings being 15.7 (1)°, while that between the C20–C25 and the C27–C32 rings is 45.5 (8)°.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom labeling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level.
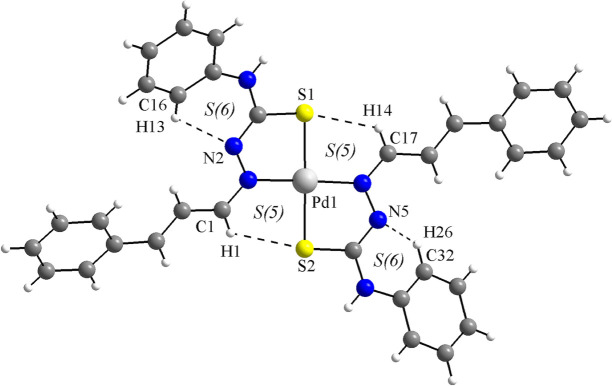
Four intramolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions are observed (Fig. 2 ▸, Table 1 ▸): C1—H1⋯S2 and C17—H14⋯S1, with graph-set motif S(5), and C16—H13⋯N2 and C32—H26⋯N5, with graph-set motif S(6). Considering the S(5) rings, a hydrogen-bonded macrocyclic coordination environment-type can be suggested for the PdII metal center, while the S(6) rings contribute to the stabilization of the molecular structure.
Figure 2.
C—H⋯S and C—H⋯N hydrogen intramolecular interactions of the title compound (dashed lines), forming rings of S(5) and S(6) graph-set motifs. A hydrogen-bonded macrocyclic coordination environment-type can be suggested for the PdII metal center.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1⋯S2 | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.230 (2) | 126 |
| C16—H13⋯N2 | 0.93 | 2.32 | 2.887 (3) | 119 |
| C17—H14⋯S1 | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.355 (2) | 126 |
| C32—H26⋯N5 | 0.93 | 2.39 | 2.911 (3) | 115 |
| N3—H27⋯S2i | 0.86 | 2.63 | 3.4805 (18) | 171 |
| N6—H28⋯S1ii | 0.86 | 2.84 | 3.6554 (19) | 159 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
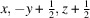 ; (ii)
; (ii)
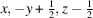 .
.
Finally, the anionic form of the ligands was assigned because of the absence of hydrazinic H atoms and the change in the bond lengths of the N—N—C—S entities. For the neutral or free, i.e., non-coordinating thiosemicarbazones, the N—N and C—S bonds have lengths of double-bond character, while the N—C bond shows lengths of single-bond type, which can be written as a N=N(H)—C=S fragment. When the acidic H atom of the hydrazinic fragment is removed, the negative charge is delocalized over the N—N—C—S chain and the bond lengths change to intermediate values. Thus, the N—N and the C—S bond lengths assume single-bond character, being longer, and the N—C bond lengths assume double-bond character, being shorter. Information about the bond lengths of the N—N—C—S entities for the cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone molecule, C16H15N3S, and the Ni(C16H14N3S)2 (Song et al., 2014 ▸) and Pd(C16H14N3S)2 complexes, this work, are summarized in Table 2 ▸. These data are in agreement with reported bond lengths values for thiosemicarbazone derivatives (Oliveira et al., 2014 ▸).
Table 2. Bond lengths (Å) for the N—N—C—S entities in cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone structures: as a neutral molecule and as an anionic ligand.
| N—N | N—C | C—S | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C16H15N3S a , c | 1.369 (2) | 1.354 (2) | 1.6704 (19) |
| Ni(C16H14N3S)2 b , c | 1.405 (5) | 1.301 (6) | 1.730 (5) |
| Pd(C16H14N3S)2 b , d | 1.390 (2) | 1.293 (2) | 1.7520 (19) |
| 1.393 (2) | 1.291 (2) | 1.7328 (19) |
Notes: (a) Neutral, non-coordinated form of the cinnamaldehyde 4-phenylthiosemicarbazone; (b) anionic, coordinated form of the cinnamaldehyde 4-phenylthiosemicarbazone; (c) Song et al. (2014 ▸); (d) this work.
3. Supramolecular features
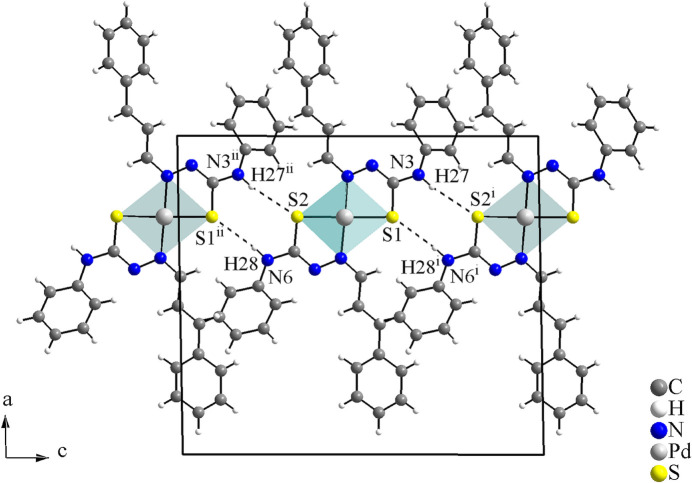
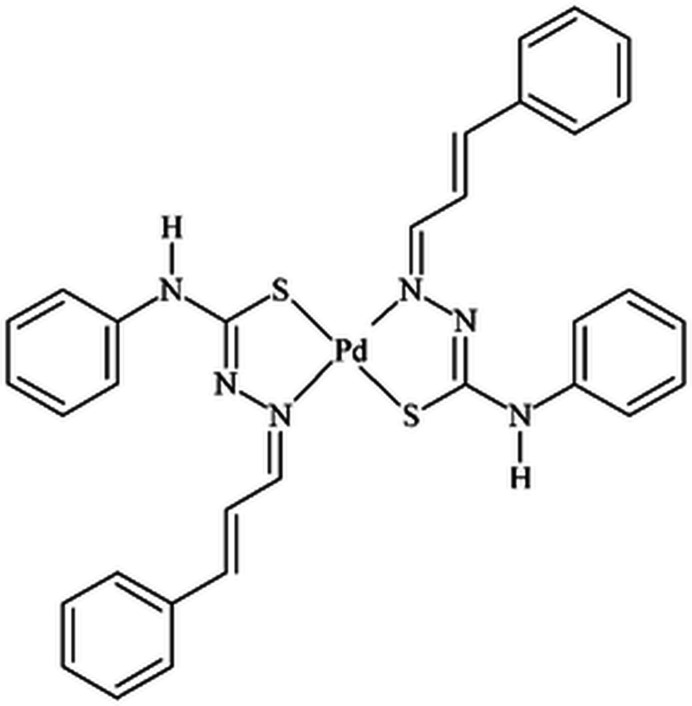
In the crystal, the molecules are connected via pairs of N—H⋯S interactions with graph-set motif
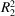 (8), forming a mono-periodic hydrogen-bonded ribbon along [001] (Fig. 3 ▸, Table 1 ▸).
(8), forming a mono-periodic hydrogen-bonded ribbon along [001] (Fig. 3 ▸, Table 1 ▸).
Figure 3.
Crystal structure section of the title compound viewed along the b-axis. The N—H⋯S interactions are drawn as dashed lines, forming rings of
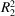 (8) graph-set motif and linking the molecules along the c-axis. [Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y +
(8) graph-set motif and linking the molecules along the c-axis. [Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y +
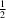 , z +
, z +
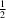 ; (ii) x, −y +
; (ii) x, −y +
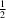 , z −
, z −
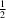 .]
.]
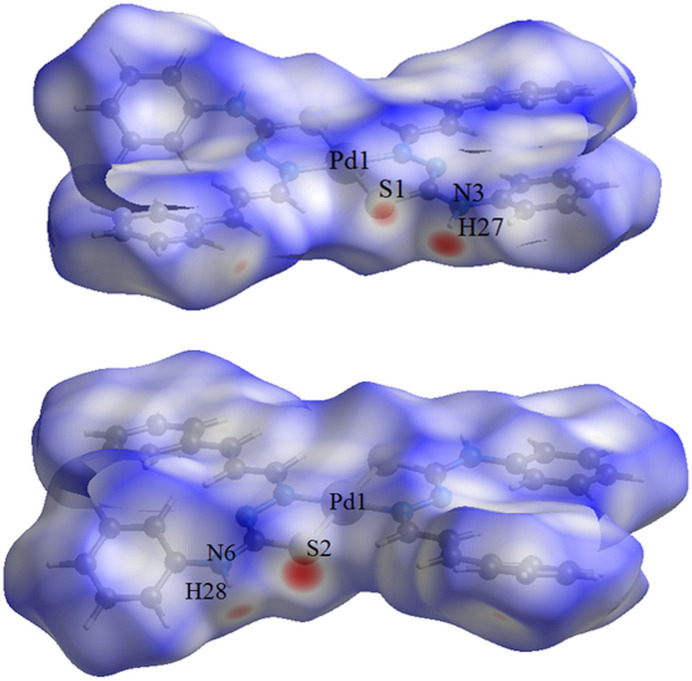
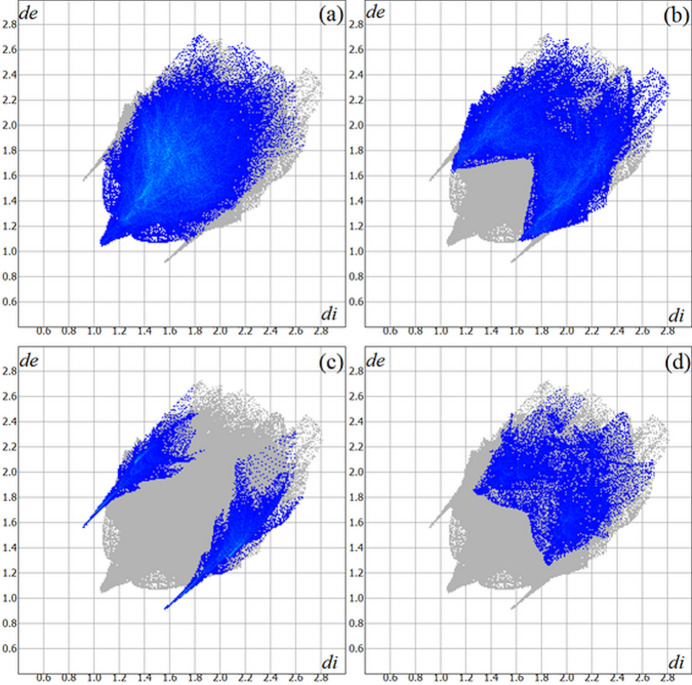
The Hirshfeld surface analysis (Hirshfeld, 1977 ▸) of the crystal structure was performed with Crystal Explorer (Wolff et al., 2012 ▸). The graphical representations of the Hirshfeld surface for the title compound are represented using a ball-and-stick model with transparency, in two side-views and separate figures for clarity (Fig. 4 ▸). The locations of the strongest intermolecular contacts, i.e, the regions around the S1, H27, S2 and H28 atoms, are indicated in magenta. These atoms are those involved in the N—H⋯S intermolecular interactions represented in the previous figure (Fig. 3 ▸): N3—H27⋯S2i and N6—H28⋯S1ii [symmetry codes: (i) x, −y +
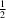 , z +
, z +
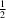 ; (ii) x, −y +
; (ii) x, −y +
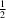 , z −
, z −
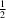 ]. The Hirshfeld surface analysis of the crystal structure also indicates that the most relevant intermolecular interactions for crystal packing are the following: (a) H⋯H (45.3%), (b) H⋯C/C⋯H (28.0%), (c) H⋯S/S⋯H (8.0%) and (d) H⋯N/N⋯H (7.4%). The contributions to the crystal packing are shown as two-dimensional Hirshfeld surface fingerprint plots with cyan dots (Fig. 5 ▸). The d
i (x-axis) and the d
e (y-axis) values are the closest internal and external distances from given points on the Hirshfeld surface (in Å).
]. The Hirshfeld surface analysis of the crystal structure also indicates that the most relevant intermolecular interactions for crystal packing are the following: (a) H⋯H (45.3%), (b) H⋯C/C⋯H (28.0%), (c) H⋯S/S⋯H (8.0%) and (d) H⋯N/N⋯H (7.4%). The contributions to the crystal packing are shown as two-dimensional Hirshfeld surface fingerprint plots with cyan dots (Fig. 5 ▸). The d
i (x-axis) and the d
e (y-axis) values are the closest internal and external distances from given points on the Hirshfeld surface (in Å).
Figure 4.
Two side-views in separate figures of the Hirshfeld surface graphical representation (d norm) for the title compound. The surface is drawn with transparency and simplified for clarity and the regions with strongest intermolecular interactions are shown in magenta. [d norm range: −0.289 to 1.415]
Figure 5.
The Hirshfeld surface two-dimensional fingerprint plot for the title compound showing the (a) H⋯H, (b) H⋯C/C⋯H, (c) H⋯S/S⋯H and (d) H⋯N/N⋯·H contacts in detail (cyan dots). The contributions of the interactions to the crystal cohesion amount to 45.3, 28.0, 8.0 and 7.4%, respectively. The d i (x-axis) and the d e (y-axis) values are the closest internal and external distances from given points on the Hirshfeld surface (in Å).
4. Database survey
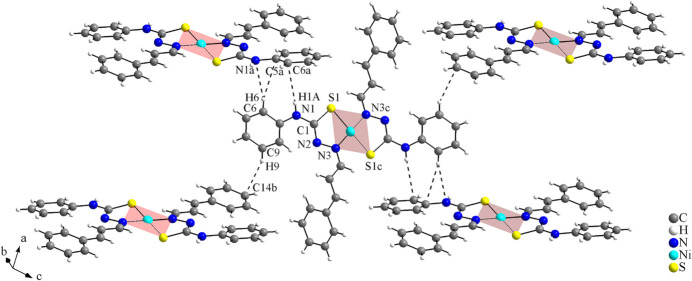
To the best of our knowledge and using database tools such as SciFinder TM (Chemical Abstracts Service, 2023 ▸), there is only one report of the crystal structure of a compound bearing cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone as non-coordinated molecule (C16H15N3S) and as a ligand, viz. in the homoleptic [Ni(C16H14N3S)2] complex (Song et al., 2014 ▸). The asymmetric unit of the reference coordination compound consists of one NiII ion, which lies on an inversion center, and two deprotonated cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone ligands, in one of which the atoms are general positions while the second is generated by symmetry (Fig. 6 ▸) [symmetry code: (c) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1]. The negative charge of the ligand was assigned by the absence of a hydrazinic H atom and the bond distances in the N—N—C—S chain (please see the remarks in the Structural commentary section of this work and also Table 2 ▸). The coordination environment of the NiII complex is quite similar to that for the PdII metal center of the title compound: the anionic ligands act as metal chelators, κ2 N 1 S-donors, with N and S atoms in trans-positions (180°), the metal center is fourfold coordinated in a square-planar geometry and the N—N—C—S entity torsion angle is 1.5 (6)°.
Figure 6.
Part of the crystal structure of the reference compound, the centrosymmetric [Ni(C16H14N3S)2] complex (Song et al., 2014 ▸). The H⋯C and H⋯N intermolecular contacts are drawn as dashed lines and the figure is simplified for clarity. [Symmetry codes: (a) −x + 1, y +
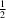 , −z +
, −z +
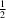 ; (b) −x, y +
; (b) −x, y +
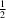 , −z +
, −z +
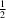 ; (c) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1.]
; (c) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1.]
Although the coordination sphere of the PdII title compound and the NiII analogue compound are similar, the supramolecular arrangement of the complexes is totally different. In the crystal, the molecules of the centrosymmetric NiII coordination compound are linked into a three-dimensional hydrogen-bonded network. The H⋯S intermolecular interactions, like those observed in the PdII complex (Fig. 3 ▸), are not present in this case and only very weak H⋯C and H⋯N intermolecular contacts are noted. The values for the hydrogen-bonding of the asymmetric part of the complex amount to: C6—H6⋯C5
a
= 2.90 (5) Å, C6—H6⋯N1
a
= 2.73 (5) Å, C9—H9⋯C14
b
= 2.86 (6) Å and N1—H1A⋯C6
a
= 2.90 (7) Å [symmetry codes: (a) −x + 1, y +
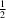 , −z +
, −z +
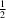 ; (b) −x, y +
; (b) −x, y +
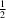 , −z +
, −z +
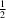 ] (Fig. 6 ▸). The H⋯C and H⋯N distances are slightly above the sum of the van der Waals radii for the respective atoms (Bondi, 1964 ▸; Rowland & Taylor, 1996 ▸) and they are the only intermolecular contacts observed for the supramolecular structure of the NiII complex.
] (Fig. 6 ▸). The H⋯C and H⋯N distances are slightly above the sum of the van der Waals radii for the respective atoms (Bondi, 1964 ▸; Rowland & Taylor, 1996 ▸) and they are the only intermolecular contacts observed for the supramolecular structure of the NiII complex.
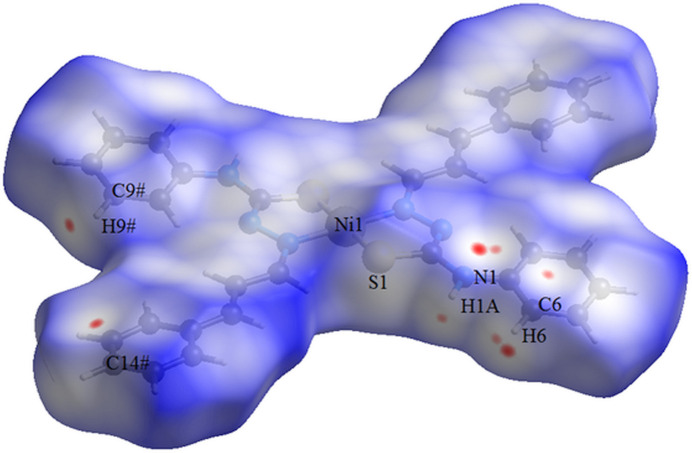
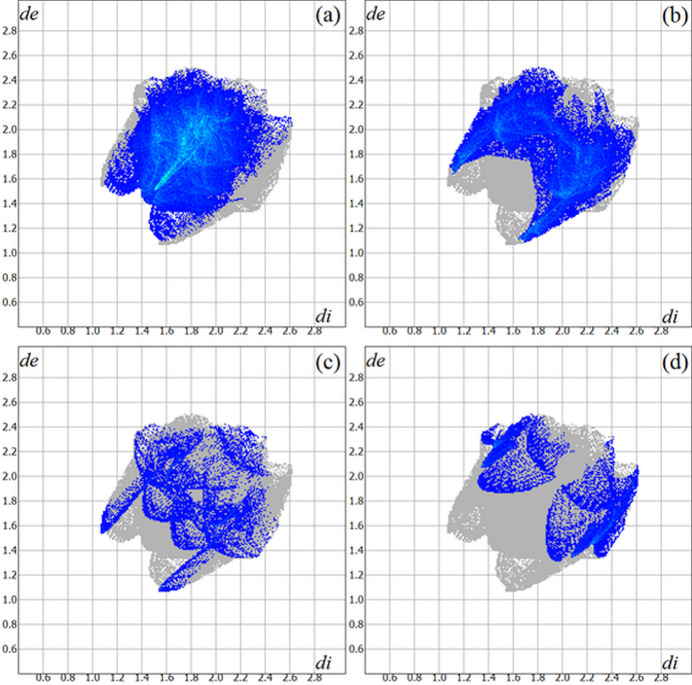
The Hirshfeld surface analysis (Hirshfeld, 1977 ▸) of the crystal structure of the NiII coordination compound was also performed with CrystalExplorer (Wolff et al., 2012 ▸). The graphical representation of the Hirshfeld surface is represented using a ball-and-stick model with transparency and the locations of the strongest intermolecular contacts are draw in magenta, i.e., the regions around the C6, H6, N1, H1A, H9# and C14# atoms (Fig. 7 ▸) [symmetry code: (#) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1]. These data are in agreement with the weak H⋯C and H⋯N intermolecular contacts observed in the previous figure (Fig. 6 ▸). The contributions to the crystal packing are shown as two-dimensional Hirshfeld surface fingerprint plots with cyan dots (Fig. 8 ▸). The Hirshfeld surface analysis of the crystal structure also suggests that the most important intermolecular interactions for crystal packing are the following: (a) H⋯H (47.4%), (b) H⋯C/C⋯H (27.6%), (c) H⋯N/N⋯H (7.0%) and (d) H⋯S/S⋯H (6.5%). The d i (x-axis) and the d e (y-axis) values are the closest internal and external distances from given points on the Hirshfeld surface contacts (in Å). While for the PdII title compound and the NiII reference compound the most important intermolecular contacts are H⋯H and the H⋯C/C⋯H, the order of importance changes for the H⋯S/S⋯H and H⋯N/N⋯H contacts. For the crystal packing of the PdII complex, the H⋯S/S⋯H contacts are more important then H⋯N/N⋯H contacts, while for the NiII complex this order is the opposite.
Figure 7.
The Hirshfeld surface graphical representation [d norm range: −0.045 to 1.492] for the centrosymmetric NiII complex (Song et al., 2014 ▸). The surface is drawn with transparency and simplified for clarity. The surface regions with strongest intermolecular contacts are shown in magenta. [Symmetry code: (#) −x + 1, -y+2, −z + 1.]
Figure 8.
The Hirshfeld surface two-dimensional fingerprint plot for the NiII coordination compound (Song et al., 2014 ▸) showing the (a) H⋯H, (b) H⋯C/C⋯H, (c) H⋯N/N⋯H and (d) H⋯S/S⋯·H contacts in detail (cyan dots). The contributions of the interactions to the crystal cohesion amount to 47.4, 27.6, 7.0 and 6.5%, respectively. The d i (x-axis) and the d e (y-axis) values are the closest internal and external distances from given points on the Hirshfeld surface (in Å).
5. Synthesis and crystallization
The starting materials are commercially available and were used without further purification. The synthesis of the ligand was adapted from a previously reported procedure (Freund & Schander, 1902 ▸; Tišler, 1956 ▸). Cinnamaldehyde-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone was dissolved in ethanol (4 mmol, 50 mL) and deprotonated with one pellet of NaOH with stirring maintained for 2 h until the solution turned yellow. Simultaneously, an ethanolic suspension of palladium(II) chloride (2 mmol, 50 mL) was prepared under continuous stirring. A yellow-colored mixture of the ethanolic solution and the ethanolic suspension was maintained with stirring at room temperature for 8 h, until the PdCl2 was consumed. Orange single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by the slow evaporation of the solvent.
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. Hydrogen atoms were located in a difference-Fourier map, but were positioned with idealized geometry and refined isotropically using a riding model (HFIX command), with U iso(H) = 1.2 U eq(C, N), and with C—H = 0.93 Å and N—H = 0.86 Å.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Pd(C16H14N3S)2] |
| M r | 667.12 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 299 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 15.084 (5), 11.418 (4), 17.097 (6) |
| β (°) | 91.097 (9) |
| V (Å3) | 2944.0 (16) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.81 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.18 × 0.11 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Venture Photon 100 area detector diffractometer |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.699, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 87933, 7344, 6204 |
| R int | 0.042 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.668 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.026, 0.063, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 7344 |
| No. of parameters | 370 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.34, −0.50 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, publication_text. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023008654/zn2032sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023008654/zn2032Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2163054
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
APLM thanks CAPES for the award of a PhD scholarship. The authors thank the Department of Chemistry of the Federal University of Santa Maria/Brazil for the access to the X-ray diffraction facility.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Pd(C16H14N3S)2] | F(000) = 1360 |
| Mr = 667.12 | Dx = 1.505 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 15.084 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 9138 reflections |
| b = 11.418 (4) Å | θ = 2.2–28.3° |
| c = 17.097 (6) Å | µ = 0.81 mm−1 |
| β = 91.097 (9)° | T = 299 K |
| V = 2944.0 (16) Å3 | Block, orange |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.18 × 0.11 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Venture Photon 100 area detector diffractometer | 6204 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: microfocus X ray tube | Rint = 0.042 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −20→20 |
| Tmin = 0.699, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −15→15 |
| 87933 measured reflections | l = −22→22 |
| 7344 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.026 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.063 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0241P)2 + 1.5227P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 7344 reflections | Δρmax = 0.34 e Å−3 |
| 370 parameters | Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.93114 (12) | 0.25646 (18) | 0.41478 (10) | 0.0408 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.911357 | 0.222755 | 0.368099 | 0.049* | |
| C2 | 1.02188 (12) | 0.29262 (18) | 0.41878 (11) | 0.0429 (4) | |
| H2 | 1.042322 | 0.334403 | 0.462190 | 0.052* | |
| C3 | 1.07777 (12) | 0.26780 (19) | 0.36174 (11) | 0.0434 (4) | |
| H3 | 1.054715 | 0.228656 | 0.318196 | 0.052* | |
| C4 | 1.17186 (12) | 0.29659 (18) | 0.36156 (11) | 0.0436 (4) | |
| C5 | 1.20873 (15) | 0.3801 (2) | 0.41107 (14) | 0.0566 (5) | |
| H4 | 1.172634 | 0.422924 | 0.444057 | 0.068* | |
| C6 | 1.29897 (17) | 0.4000 (3) | 0.41148 (17) | 0.0738 (8) | |
| H5 | 1.323135 | 0.457206 | 0.444183 | 0.089* | |
| C7 | 1.35360 (16) | 0.3362 (3) | 0.36419 (19) | 0.0765 (8) | |
| H6 | 1.414532 | 0.348617 | 0.366163 | 0.092* | |
| C8 | 1.31865 (17) | 0.2555 (3) | 0.31492 (18) | 0.0745 (8) | |
| H7 | 1.355493 | 0.212955 | 0.282440 | 0.089* | |
| C9 | 1.22814 (15) | 0.2358 (2) | 0.31256 (14) | 0.0613 (6) | |
| H8 | 1.204591 | 0.181127 | 0.277638 | 0.074* | |
| C10 | 0.85343 (12) | 0.31504 (17) | 0.59615 (10) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.95766 (12) | 0.42049 (17) | 0.68829 (10) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.95571 (14) | 0.48633 (19) | 0.75646 (11) | 0.0466 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.904012 | 0.489377 | 0.785175 | 0.056* | |
| C13 | 1.02970 (15) | 0.5473 (2) | 0.78205 (13) | 0.0559 (5) | |
| H10 | 1.027308 | 0.591307 | 0.827731 | 0.067* | |
| C14 | 1.10674 (15) | 0.5437 (2) | 0.74084 (14) | 0.0584 (6) | |
| H11 | 1.156512 | 0.585126 | 0.757969 | 0.070* | |
| C15 | 1.10894 (14) | 0.4777 (2) | 0.67371 (14) | 0.0597 (6) | |
| H12 | 1.161063 | 0.474407 | 0.645610 | 0.072* | |
| C16 | 1.03566 (13) | 0.4160 (2) | 0.64695 (12) | 0.0516 (5) | |
| H13 | 1.038671 | 0.371677 | 0.601430 | 0.062* | |
| C17 | 0.55839 (12) | 0.16720 (18) | 0.50233 (11) | 0.0416 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.578917 | 0.185524 | 0.552491 | 0.050* | |
| C18 | 0.46597 (12) | 0.14045 (18) | 0.49358 (11) | 0.0429 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.444566 | 0.115183 | 0.445071 | 0.052* | |
| C19 | 0.40947 (13) | 0.15030 (19) | 0.55209 (12) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.433316 | 0.172755 | 0.600361 | 0.057* | |
| C20 | 0.31419 (13) | 0.12958 (18) | 0.54837 (12) | 0.0454 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.27211 (14) | 0.0746 (2) | 0.48604 (13) | 0.0513 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.305174 | 0.047797 | 0.444312 | 0.062* | |
| C22 | 0.18134 (15) | 0.0590 (2) | 0.48519 (16) | 0.0644 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.153934 | 0.021536 | 0.442935 | 0.077* | |
| C23 | 0.13142 (16) | 0.0979 (3) | 0.54540 (18) | 0.0713 (8) | |
| H19 | 0.070293 | 0.087173 | 0.544212 | 0.086* | |
| C24 | 0.17159 (17) | 0.1526 (3) | 0.60741 (18) | 0.0739 (8) | |
| H20 | 0.137628 | 0.180199 | 0.648339 | 0.089* | |
| C25 | 0.26240 (16) | 0.1673 (2) | 0.60978 (15) | 0.0653 (6) | |
| H21 | 0.289272 | 0.202928 | 0.653032 | 0.078* | |
| C26 | 0.63696 (12) | 0.14116 (18) | 0.31857 (11) | 0.0406 (4) | |
| C27 | 0.52836 (12) | 0.06730 (19) | 0.21755 (12) | 0.0456 (5) | |
| C28 | 0.50883 (17) | 0.0809 (2) | 0.13948 (14) | 0.0657 (7) | |
| H22 | 0.547569 | 0.121832 | 0.107827 | 0.079* | |
| C29 | 0.4319 (2) | 0.0341 (3) | 0.10764 (19) | 0.0878 (10) | |
| H23 | 0.418657 | 0.044846 | 0.054772 | 0.105* | |
| C30 | 0.37560 (18) | −0.0272 (3) | 0.1525 (2) | 0.0837 (9) | |
| H24 | 0.323855 | −0.058496 | 0.130698 | 0.100* | |
| C31 | 0.39511 (18) | −0.0431 (3) | 0.23033 (19) | 0.0803 (8) | |
| H25 | 0.356585 | −0.085945 | 0.261047 | 0.096* | |
| C32 | 0.47140 (16) | 0.0038 (2) | 0.26388 (15) | 0.0633 (6) | |
| H26 | 0.484228 | −0.007087 | 0.316803 | 0.076* | |
| N1 | 0.87363 (10) | 0.26614 (14) | 0.47008 (8) | 0.0375 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.90767 (10) | 0.31587 (16) | 0.53850 (9) | 0.0428 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.87873 (10) | 0.36111 (16) | 0.66658 (9) | 0.0442 (4) | |
| H27 | 0.841082 | 0.352842 | 0.703313 | 0.053* | |
| N4 | 0.61600 (10) | 0.16837 (14) | 0.44748 (9) | 0.0383 (3) | |
| N5 | 0.58090 (10) | 0.13619 (16) | 0.37463 (9) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| N6 | 0.61038 (11) | 0.11296 (18) | 0.24427 (9) | 0.0521 (5) | |
| H28 | 0.649000 | 0.124627 | 0.208750 | 0.063* | |
| Pd1 | 0.74528 (2) | 0.21629 (2) | 0.46039 (2) | 0.03379 (5) | |
| S1 | 0.74605 (3) | 0.25655 (5) | 0.59231 (3) | 0.04797 (12) | |
| S2 | 0.74676 (3) | 0.18416 (6) | 0.32859 (3) | 0.04861 (13) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0320 (9) | 0.0589 (11) | 0.0314 (9) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0020 (7) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0327 (9) | 0.0625 (12) | 0.0337 (9) | −0.0045 (8) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0337 (9) | 0.0606 (12) | 0.0358 (9) | −0.0037 (9) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0326 (9) | 0.0575 (12) | 0.0407 (10) | −0.0026 (8) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0101 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0445 (12) | 0.0656 (14) | 0.0596 (13) | −0.0060 (10) | −0.0040 (10) | 0.0032 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0551 (15) | 0.0816 (18) | 0.0838 (18) | −0.0223 (14) | −0.0209 (14) | 0.0151 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0348 (12) | 0.094 (2) | 0.100 (2) | −0.0080 (13) | −0.0040 (13) | 0.0419 (18) |
| C8 | 0.0416 (13) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0858 (19) | 0.0078 (13) | 0.0206 (13) | 0.0207 (17) |
| C9 | 0.0445 (12) | 0.0805 (17) | 0.0594 (14) | −0.0030 (11) | 0.0151 (10) | −0.0011 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0314 (9) | 0.0475 (10) | 0.0343 (9) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0351 (9) | 0.0486 (10) | 0.0354 (9) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0001 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0446 (11) | 0.0557 (12) | 0.0396 (10) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0016 (8) | −0.0032 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0578 (13) | 0.0596 (13) | 0.0499 (12) | −0.0054 (11) | −0.0067 (10) | −0.0103 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0443 (12) | 0.0655 (14) | 0.0650 (14) | −0.0103 (10) | −0.0128 (10) | −0.0005 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0341 (10) | 0.0826 (17) | 0.0624 (14) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0010 (10) | −0.0032 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0735 (14) | 0.0453 (11) | 0.0009 (10) | 0.0016 (8) | −0.0096 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0360 (9) | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0347 (9) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0036 (7) | −0.0037 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0356 (9) | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0392 (10) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0053 (8) | −0.0008 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0413 (10) | 0.0586 (12) | 0.0420 (10) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0078 (8) | −0.0009 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0390 (10) | 0.0505 (11) | 0.0471 (11) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0116 (8) | 0.0071 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0609 (13) | 0.0516 (12) | 0.0024 (10) | 0.0072 (9) | 0.0081 (10) |
| C22 | 0.0468 (13) | 0.0740 (16) | 0.0722 (16) | −0.0050 (12) | −0.0071 (11) | 0.0167 (13) |
| C23 | 0.0379 (12) | 0.0804 (18) | 0.096 (2) | 0.0040 (12) | 0.0149 (13) | 0.0283 (16) |
| C24 | 0.0539 (14) | 0.0804 (18) | 0.089 (2) | 0.0055 (13) | 0.0362 (14) | 0.0086 (16) |
| C25 | 0.0539 (14) | 0.0782 (16) | 0.0645 (15) | −0.0027 (12) | 0.0246 (11) | −0.0050 (13) |
| C26 | 0.0315 (9) | 0.0554 (11) | 0.0351 (9) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0021 (7) | −0.0016 (8) |
| C27 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0553 (12) | 0.0488 (11) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0040 (8) | −0.0101 (9) |
| C28 | 0.0631 (15) | 0.0751 (16) | 0.0582 (14) | −0.0127 (13) | −0.0205 (12) | 0.0074 (12) |
| C29 | 0.084 (2) | 0.095 (2) | 0.083 (2) | −0.0132 (18) | −0.0477 (17) | 0.0046 (17) |
| C30 | 0.0520 (15) | 0.089 (2) | 0.109 (2) | −0.0128 (14) | −0.0269 (16) | −0.0201 (18) |
| C31 | 0.0566 (15) | 0.087 (2) | 0.098 (2) | −0.0283 (14) | 0.0074 (15) | −0.0243 (17) |
| C32 | 0.0520 (13) | 0.0787 (16) | 0.0592 (14) | −0.0154 (12) | 0.0031 (11) | −0.0121 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0299 (7) | 0.0523 (9) | 0.0303 (7) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0009 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0324 (8) | 0.0645 (10) | 0.0316 (8) | −0.0058 (7) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0059 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0348 (8) | 0.0659 (11) | 0.0319 (8) | −0.0070 (8) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0067 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0304 (7) | 0.0496 (9) | 0.0349 (8) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0023 (7) |
| N5 | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0646 (11) | 0.0342 (8) | −0.0057 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0055 (7) |
| N6 | 0.0341 (8) | 0.0878 (14) | 0.0346 (8) | −0.0110 (9) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0081 (8) |
| Pd1 | 0.02574 (7) | 0.04563 (8) | 0.03007 (7) | −0.00040 (5) | 0.00212 (5) | −0.00124 (5) |
| S1 | 0.0344 (2) | 0.0749 (3) | 0.0349 (2) | −0.0119 (2) | 0.00699 (18) | −0.0100 (2) |
| S2 | 0.0275 (2) | 0.0866 (4) | 0.0319 (2) | −0.0068 (2) | 0.00370 (17) | −0.0071 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N1 | 1.300 (2) | C18—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.430 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.457 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C19—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.332 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.381 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C20—C25 | 1.389 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.457 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.380 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C21—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (3) | C22—C23 | 1.361 (4) |
| C4—C9 | 1.389 (3) | C22—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (3) | C23—C24 | 1.363 (4) |
| C5—H4 | 0.9300 | C23—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.374 (4) | C24—C25 | 1.380 (3) |
| C6—H5 | 0.9300 | C24—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.349 (4) | C25—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H6 | 0.9300 | C26—N5 | 1.291 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.383 (3) | C26—N6 | 1.363 (2) |
| C8—H7 | 0.9300 | C26—S2 | 1.7328 (19) |
| C9—H8 | 0.9300 | C27—C28 | 1.370 (3) |
| C10—N2 | 1.293 (2) | C27—C32 | 1.384 (3) |
| C10—N3 | 1.362 (2) | C27—N6 | 1.410 (2) |
| C10—S1 | 1.7520 (19) | C28—C29 | 1.380 (3) |
| C11—C16 | 1.385 (3) | C28—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C12 | 1.388 (3) | C29—C30 | 1.351 (4) |
| C11—N3 | 1.413 (2) | C29—H23 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.380 (3) | C30—C31 | 1.369 (4) |
| C12—H9 | 0.9300 | C30—H24 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.371 (3) | C31—C32 | 1.384 (3) |
| C13—H10 | 0.9300 | C31—H25 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C15 | 1.374 (3) | C32—H26 | 0.9300 |
| C14—H11 | 0.9300 | N1—N2 | 1.390 (2) |
| C15—C16 | 1.381 (3) | N1—Pd1 | 2.0217 (16) |
| C15—H12 | 0.9300 | N3—H27 | 0.8600 |
| C16—H13 | 0.9300 | N4—N5 | 1.393 (2) |
| C17—N4 | 1.291 (2) | N4—Pd1 | 2.0333 (16) |
| C17—C18 | 1.432 (3) | N6—H28 | 0.8600 |
| C17—H14 | 0.9300 | Pd1—S2 | 2.2836 (9) |
| C18—C19 | 1.331 (3) | Pd1—S1 | 2.3016 (9) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 126.30 (17) | C25—C20—C19 | 119.0 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 116.8 | C22—C21—C20 | 120.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 116.8 | C22—C21—H17 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.49 (18) | C20—C21—H17 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.3 | C23—C22—C21 | 120.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.3 | C23—C22—H18 | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 125.73 (19) | C21—C22—H18 | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 117.1 | C22—C23—C24 | 119.6 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 117.1 | C22—C23—H19 | 120.2 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.0 (2) | C24—C23—H19 | 120.2 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.27 (19) | C23—C24—C25 | 120.3 (2) |
| C9—C4—C3 | 119.7 (2) | C23—C24—H20 | 119.8 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.0 (2) | C25—C24—H20 | 119.8 |
| C6—C5—H4 | 120.0 | C24—C25—C20 | 120.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—H4 | 120.0 | C24—C25—H21 | 119.6 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.8 (3) | C20—C25—H21 | 119.6 |
| C7—C6—H5 | 119.6 | N5—C26—N6 | 119.74 (17) |
| C5—C6—H5 | 119.6 | N5—C26—S2 | 125.25 (14) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.9 (2) | N6—C26—S2 | 115.00 (13) |
| C8—C7—H6 | 120.1 | C28—C27—C32 | 119.5 (2) |
| C6—C7—H6 | 120.1 | C28—C27—N6 | 116.4 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.2 (3) | C32—C27—N6 | 123.9 (2) |
| C7—C8—H7 | 119.9 | C27—C28—C29 | 120.3 (3) |
| C9—C8—H7 | 119.9 | C27—C28—H22 | 119.9 |
| C8—C9—C4 | 121.0 (3) | C29—C28—H22 | 119.9 |
| C8—C9—H8 | 119.5 | C30—C29—C28 | 120.6 (3) |
| C4—C9—H8 | 119.5 | C30—C29—H23 | 119.7 |
| N2—C10—N3 | 120.03 (17) | C28—C29—H23 | 119.7 |
| N2—C10—S1 | 124.91 (14) | C29—C30—C31 | 119.7 (2) |
| N3—C10—S1 | 115.06 (13) | C29—C30—H24 | 120.2 |
| C16—C11—C12 | 118.73 (18) | C31—C30—H24 | 120.2 |
| C16—C11—N3 | 124.58 (18) | C30—C31—C32 | 120.9 (3) |
| C12—C11—N3 | 116.68 (17) | C30—C31—H25 | 119.6 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.6 (2) | C32—C31—H25 | 119.6 |
| C13—C12—H9 | 119.7 | C31—C32—C27 | 119.0 (2) |
| C11—C12—H9 | 119.7 | C31—C32—H26 | 120.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.7 (2) | C27—C32—H26 | 120.5 |
| C14—C13—H10 | 119.7 | C1—N1—N2 | 113.95 (15) |
| C12—C13—H10 | 119.7 | C1—N1—Pd1 | 124.60 (13) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 118.7 (2) | N2—N1—Pd1 | 121.45 (11) |
| C13—C14—H11 | 120.7 | C10—N2—N1 | 114.18 (15) |
| C15—C14—H11 | 120.7 | C10—N3—C11 | 129.63 (16) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.6 (2) | C10—N3—H27 | 115.2 |
| C14—C15—H12 | 119.2 | C11—N3—H27 | 115.2 |
| C16—C15—H12 | 119.2 | C17—N4—N5 | 113.40 (15) |
| C15—C16—C11 | 119.6 (2) | C17—N4—Pd1 | 125.56 (13) |
| C15—C16—H13 | 120.2 | N5—N4—Pd1 | 121.01 (11) |
| C11—C16—H13 | 120.2 | C26—N5—N4 | 114.13 (15) |
| N4—C17—C18 | 126.43 (17) | C26—N6—C27 | 129.03 (17) |
| N4—C17—H14 | 116.8 | C26—N6—H28 | 115.5 |
| C18—C17—H14 | 116.8 | C27—N6—H28 | 115.5 |
| C19—C18—C17 | 122.63 (19) | N1—Pd1—N4 | 178.31 (6) |
| C19—C18—H15 | 118.7 | N1—Pd1—S2 | 95.66 (4) |
| C17—C18—H15 | 118.7 | N4—Pd1—S2 | 82.94 (4) |
| C18—C19—C20 | 126.8 (2) | N1—Pd1—S1 | 82.92 (4) |
| C18—C19—H16 | 116.6 | N4—Pd1—S1 | 98.45 (4) |
| C20—C19—H16 | 116.6 | S2—Pd1—S1 | 177.57 (2) |
| C21—C20—C25 | 117.9 (2) | C10—S1—Pd1 | 95.74 (6) |
| C21—C20—C19 | 123.10 (18) | C26—S2—Pd1 | 96.65 (6) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 172.9 (2) | C32—C27—C28—C29 | 1.5 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.50 (19) | N6—C27—C28—C29 | 177.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −17.8 (3) | C27—C28—C29—C30 | −1.1 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | 159.6 (2) | C28—C29—C30—C31 | 0.0 (5) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.8 (3) | C29—C30—C31—C32 | 0.6 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 176.7 (2) | C30—C31—C32—C27 | −0.1 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.2 (4) | C28—C27—C32—C31 | −0.9 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 2.0 (4) | N6—C27—C32—C31 | −176.0 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.8 (4) | C2—C1—N1—N2 | −0.7 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C4 | −1.3 (4) | C2—C1—N1—Pd1 | 178.74 (16) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | 2.0 (4) | N3—C10—N2—N1 | 179.95 (17) |
| C3—C4—C9—C8 | −175.5 (2) | S1—C10—N2—N1 | 0.6 (3) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.8 (3) | C1—N1—N2—C10 | −173.45 (18) |
| N3—C11—C12—C13 | −179.92 (19) | Pd1—N1—N2—C10 | 7.1 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.3 (3) | N2—C10—N3—C11 | 4.6 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.3 (4) | S1—C10—N3—C11 | −175.92 (16) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.4 (4) | C16—C11—N3—C10 | −18.5 (3) |
| C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.2 (4) | C12—C11—N3—C10 | 162.2 (2) |
| C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.7 (3) | C18—C17—N4—N5 | −2.1 (3) |
| N3—C11—C16—C15 | −180.0 (2) | C18—C17—N4—Pd1 | 176.05 (16) |
| N4—C17—C18—C19 | −174.5 (2) | N6—C26—N5—N4 | −179.31 (18) |
| C17—C18—C19—C20 | 177.5 (2) | S2—C26—N5—N4 | −0.4 (3) |
| C18—C19—C20—C21 | 13.0 (4) | C17—N4—N5—C26 | 177.55 (18) |
| C18—C19—C20—C25 | −166.5 (2) | Pd1—N4—N5—C26 | −0.7 (2) |
| C25—C20—C21—C22 | 0.5 (3) | N5—C26—N6—C27 | −6.0 (4) |
| C19—C20—C21—C22 | −178.9 (2) | S2—C26—N6—C27 | 175.02 (18) |
| C20—C21—C22—C23 | 0.3 (4) | C28—C27—N6—C26 | 160.2 (2) |
| C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.2 (4) | C32—C27—N6—C26 | −24.6 (4) |
| C22—C23—C24—C25 | −0.8 (4) | N2—C10—S1—Pd1 | −6.03 (18) |
| C23—C24—C25—C20 | 1.7 (4) | N3—C10—S1—Pd1 | 174.54 (14) |
| C21—C20—C25—C24 | −1.5 (4) | N5—C26—S2—Pd1 | 1.1 (2) |
| C19—C20—C25—C24 | 178.0 (2) | N6—C26—S2—Pd1 | 179.99 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1···S2 | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.230 (2) | 126 |
| C16—H13···N2 | 0.93 | 2.32 | 2.887 (3) | 119 |
| C17—H14···S1 | 0.93 | 2.72 | 3.355 (2) | 126 |
| C32—H26···N5 | 0.93 | 2.39 | 2.911 (3) | 115 |
| N3—H27···S2i | 0.86 | 2.63 | 3.4805 (18) | 171 |
| N6—H28···S1ii | 0.86 | 2.84 | 3.6554 (19) | 159 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – Brazil (CAPES), Finance code 001.
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bondi, A. (1964). J. Phys. Chem. 68, 441–451.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2015). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chemical Abstracts Service (2023). Columbus, Ohio, USA (accessed via SciFinder on September 1, 2023).
- Farias, R. L., Polez, A. M. R., Silva, A. D. E. S., Zanetti, R. D., Moreira, M. B., Batista, V. S., Reis, B. L., Nascimento-Júnior, N. M., Rocha, F. V., Lima, M. A., Oliveira, A. B., Ellena, J., Scarim, C. B., Zambom, C. R., Brito, L. D., Garrido, S. S., Melo, A. P. L., Bresolin, L., Tirloni, B., Pereira, J. C. M. & Netto, A. V. G. (2021). Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 121, 111815, 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Freund, M. & Schander, A. (1902). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 35, 2602–2606.
- Hirshfeld, H. L. (1977). Theor. Chim. Acta, 44, 129–138.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lobana, T. S., Sharma, R., Bawa, G. & Khanna, S. (2009). Coord. Chem. Rev. 253, 977–1055.
- Mostafa, H. A. (2000). Electrochim. Acta, 18, 45–53.
- Nyawadea, E. A., Sibuyi, N. R. S., Meyer, M., Lalancette, R. & Onani, M. O. (2021). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 515, 120036, 1–10.
- Oliveira, A. B. de, Feitosa, B. R. S., Näther, C. & Jess, I. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, 101–103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Palve, A. M. & Garje, S. S. (2011). J. Cryst. Growth, 326, 157–162.
- Pawar, A. S. & Garje, S. S. (2015). Bull. Mater. Sci. 38, 1843–1850.
- Pawar, A. S., Masikane, S. C., Mlowe, S., Garje, S. S. & Revaprasadu, N. (2016). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 366–372.
- Rocha, F. V., Farias, R. L., Lima, M. A., Batista, V. S., Nascimento-Júnior, N. M., Garrido, S. S., Leopoldino, A. M., Goto, R. N., Oliveira, A. B., Beck, J., Landvogt, C., Mauro, A. E. & Netto, A. V. G. (2019). J. Inorg. Biochem. 199, 110725, 1–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rowland, R. S. & Taylor, R. (1996). J. Phys. Chem. 100, 7384–7391.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Song, J., Zhu, F., Wang, H. & Zhao, P. (2014). Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 129, 227–234. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tišler, M. (1956). Z. Anal. Chem. 149, 164–172.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., McKinnon, J. J., Turner, M. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2012). Crystal Explorer 3.1. University of Western Australia, Australia.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, publication_text. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023008654/zn2032sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023008654/zn2032Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2163054
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report