Abstract
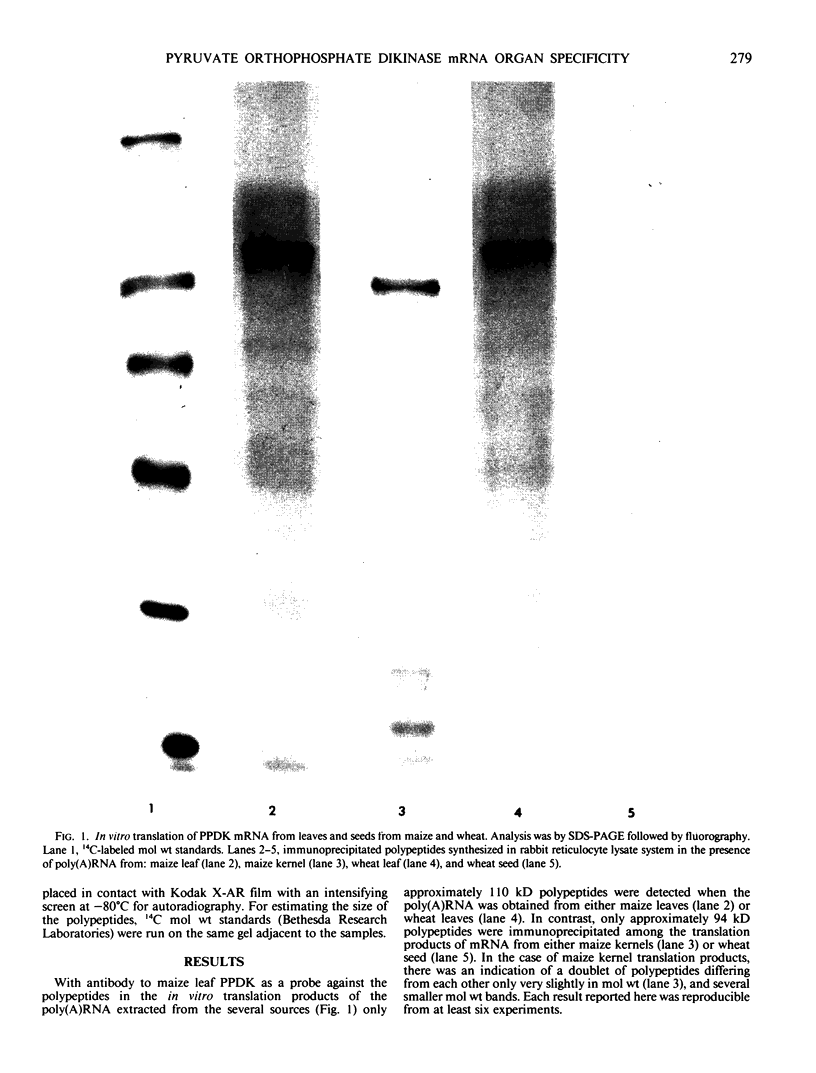
Polyadenylated RNA was isolated from leaves and seeds of a C3 plant (Triticum aestivum L. cv Cheyenne, CI 8885) and from a C4 plant (Zea mays L. cv Golden bantam). Each polyadenylated RNA preparation was translated in vitro with micrococcal nuclease-treated reticulocyte lysate. When the in vitro translation products were probed with antibodies to pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase (PPDK) (EC 2.7.9.1), two sizes of polypeptide were identified. A 110 kilodalton polypeptide was found in the in vitro translation products of mRNA isolated exclusively from leaves of both wheat and maize. A 94 kilodalton polypeptide, similar to the PPDK polypeptide which can be extracted after in vivo synthesis in maize and wheat leaves and seeds, was found in the in vitro translation products obtained from wheat seeds and maize kernels.
These results indicate that the mRNAs for PPDK polypeptides are organ-specific in both a C4 and a C3 plant. Hague et al. (1983 Nucleic Acids Res 11: 4853-4865) proposed that the larger size polypeptide of the in vitro translation polypeptide from maize leaf RNA contains a `transit sequence' which permits entry into the chloroplasts of a polypeptide synthesized in vivo in maize leaf cell cytoplasm. It appears that in wheat leaves also the transit of synthesized PPDK polypeptide through an intracellular membrane may be required, while such a transit sequence seems not to be required within cells of wheat and maize seeds.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):853–854. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase of c(3) seeds and leaves as compared to the enzyme from maize. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):387–392. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerff R., Kloppstech K. Structural diversity and differential light control of mRNAs coding for angiosperm glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7624–7628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee S. L., Ruzin S., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase: intracellular site of synthesis in maize leaf cells. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):189–191. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hague D. R., Uhler M., Collins P. D. Cloning of cDNA for pyruvate, Pi dikinase from maize leaves. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4853–4865. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. A new enzyme for the interconversion of pyruvate and phosphopyruvate and its role in the C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1060141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Harpster M. H., Mayfield S. P., Taylor W. C. Light-regulated gene expression during maize leaf development. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):558–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt S., Reich R., Witt H. T. Electrochromism of chlorophylls and carotenoids in multilayers and in chloroplasts. Naturwissenschaften. 1971 Aug;58(8):414–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00591523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]