Abstract
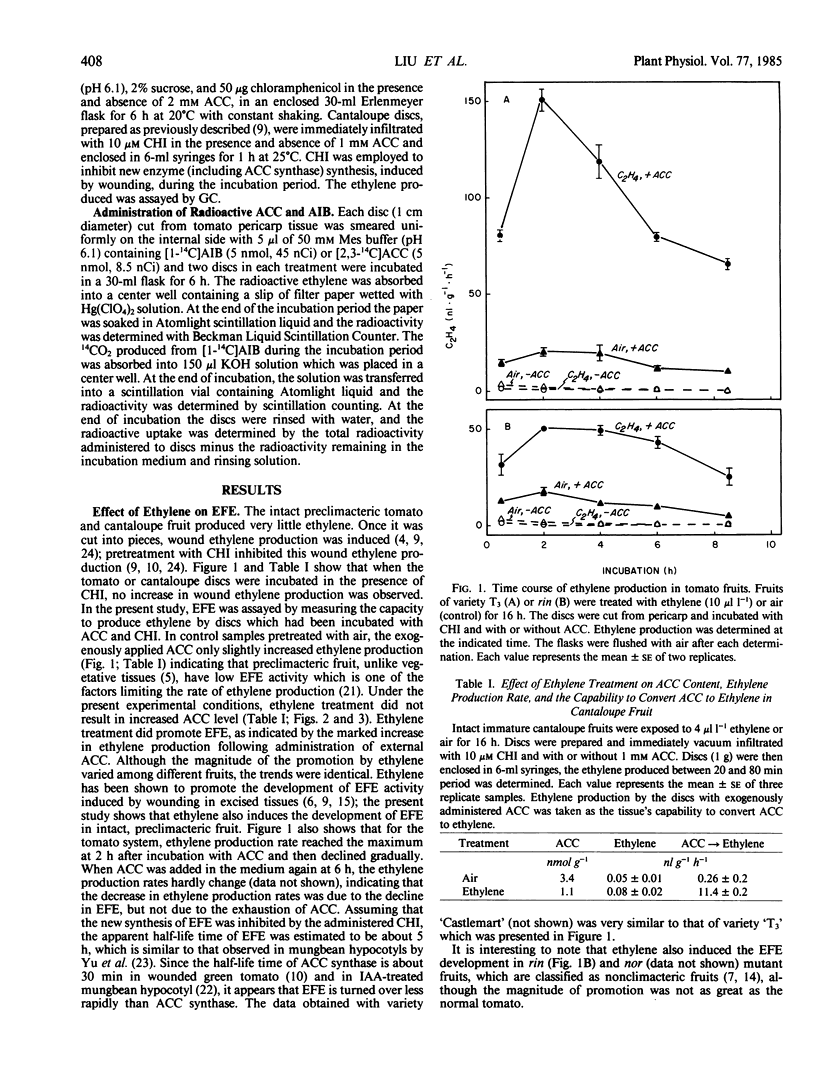
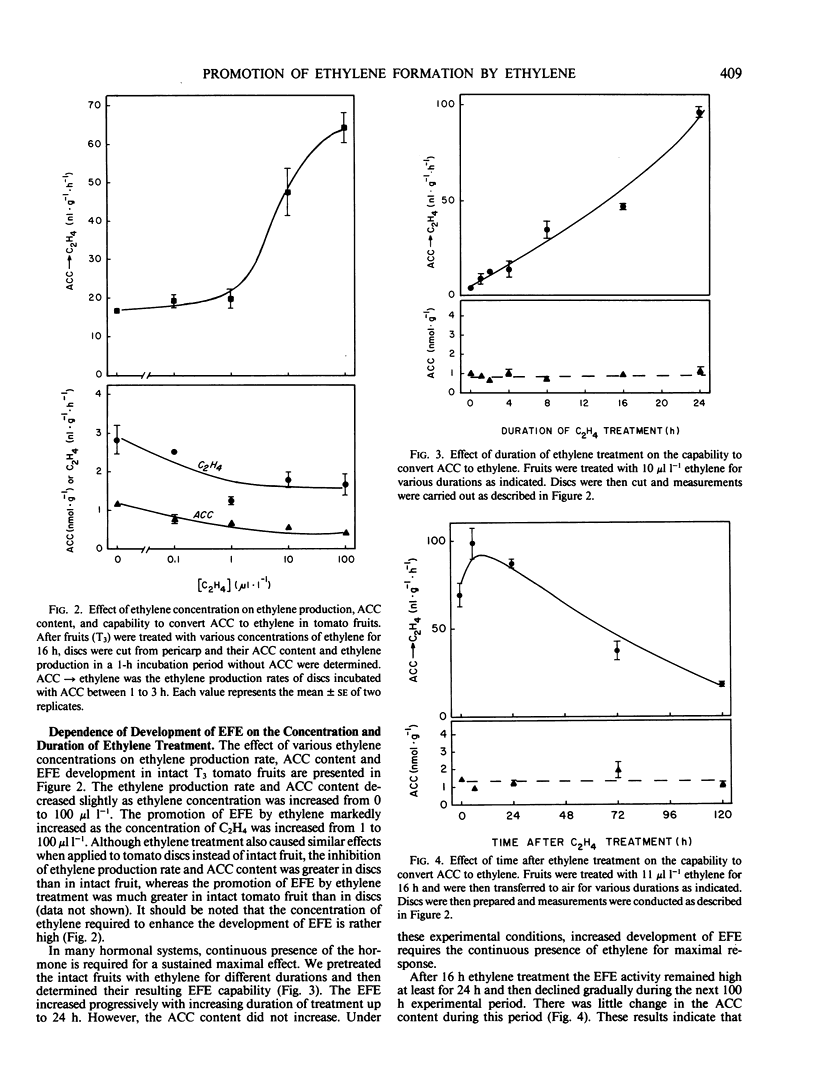
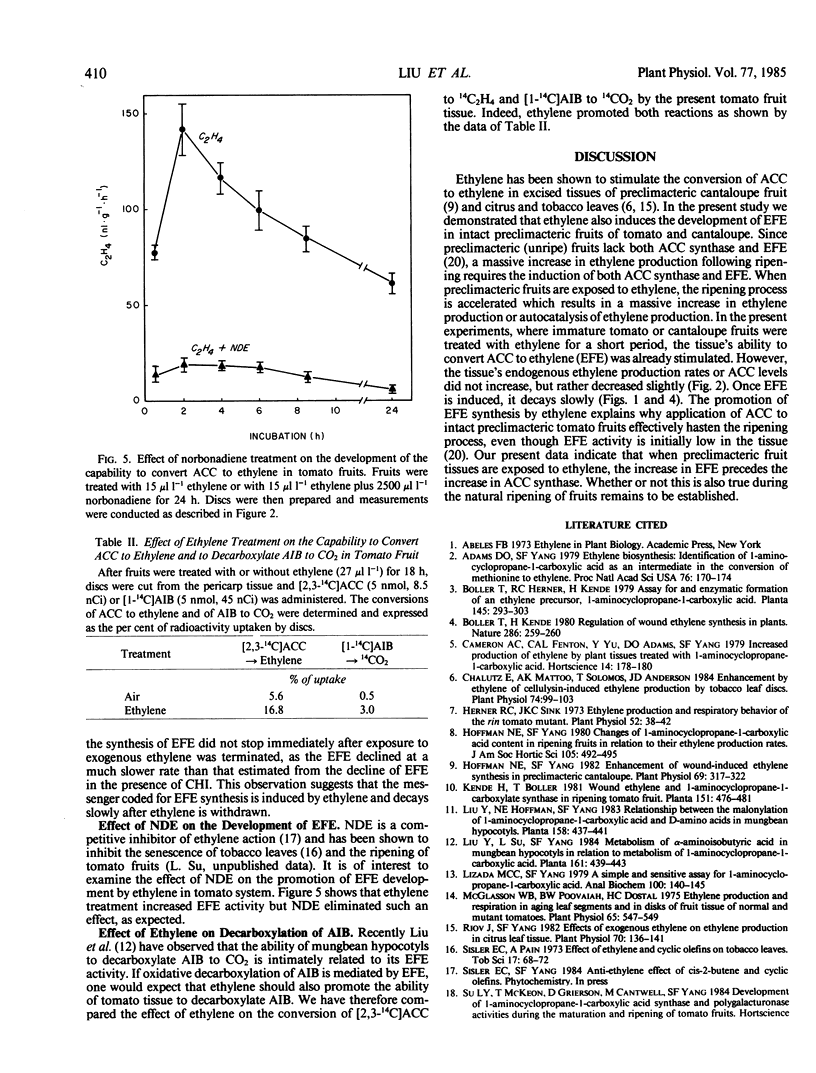
The intact fruits of preclimacteric tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) or cantaloupe (Cucumis melo L.) produced very little ethylene and had low capability of converting 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) to ethylene. When these unripe tomato or cantaloupe fruits were treated with ethylene for 16 hours there was no increase in ACC content or in ethylene production rate, but the tissue's capability to convert ACC to ethylene increased markedly. Such an effect was also observed in fruits of tomato mutants rin and nor, which do not undergo ripening and the climacteric increase in ethylene production during the senescence. The development of this ethylene-forming capability induced by ethylene increased with increasing ethylene concentration (from 0.1 to 100 microliters per liter) and duration (1 to 24 hours); when ethylene was removed this capability remained high for sometime (more than 24 hours). Norbornadiene, a competitive inhibitor of ethylene action, effectively eliminated the promotive effect of ethylene in tomato fruit. These data indicate that the development of the capability to convert ACC to ethylene in preclimacteric tomato and cantaloupe fruits are sensitive to ethylene treatment and that when these fruits are exposed to exogenous ethylene, the increase in ethylene-forming enzyme precedes the increase in ACC synthase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Yang S. F. Ethylene biosynthesis: Identification of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid as an intermediate in the conversion of methionine to ethylene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):170–174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalutz E., Mattoo A. K., Solomos T., Anderson J. D. Enhancement by ethylene of cellulysin-induced ethylene production by tobacco leaf discs. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):99–103. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herner R. C., Sink K. C. Ethylene Production and Respiratory Behavior of the rin Tomato Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):38–42. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Yang S. F. Enhancement of wound-induced ethylene synthesis by ethylene in preclimacteric cantaloupe. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):317–322. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizada M. C., Yang S. F. A simple and sensitive assay for 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):140–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlasson W. B., Poovaiah B. W., Dostal H. C. Ethylene production and respiration in aging leaf segments and in disks of fruit tissue of normal and mutant tomatoes. Plant Physiol. 1975 Oct;56(4):547–549. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riov J., Yang S. F. Effects of exogenous ethylene on ethylene production in citrus leaf tissue. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):136–141. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. B., Adams D. O., Yang S. F. Regulation of Auxin-induced Ethylene Production in Mung Bean Hypocotyls: Role of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):589–590. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. B., Yang S. F. Biosynthesis of wound ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):281–285. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


