Abstract
Some properties of ornithine carbamoyltransferase from chloroplasts isolated from leaves of Pisum sativum L. (cv Marzia) were compared with those of the enzyme partially purified (316-fold) from shoots of seedlings after 3 weeks of cultivation.
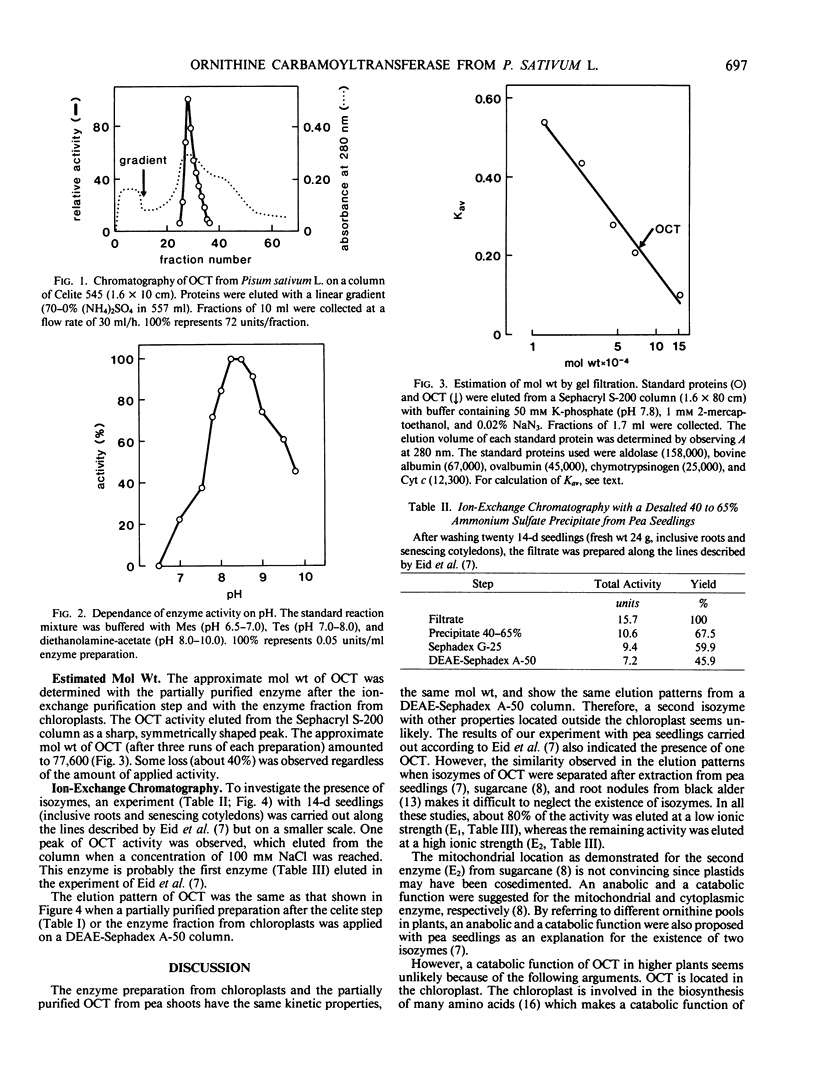
Both preparations showed a pH optimum at pH 8.3 and had the same affinity to ornithine (Km = 1.2 millimolar) as well as to carbamoyl phosphate (Km = 0.2 millimolar). The approximate molecular weight determined by gel sieving was 77,600.
A desalted ammonium sulfate precipitate from 14-day seedlings (inclusive roots and senescing cotyledons) was applied on a column of anion exchanger. The elution pattern showed one peak of ornithine carbamoyl-transferase activity. This elution pattern was the same as observed for the enzyme from chloroplasts.
The results suggest the presence of one form of ornithine carbamoyl-transferase in pea seedlings.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boggess S. F., Naylor A. W. Partial Purification and Properties of Ornithine Transcarbamoylase from Nostoc muscorum Kützing. Plant Physiol. 1975 Nov;56(5):640–644. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.5.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyde T. R., Rahmatullah M. Optimization of conditions for the colorimetric determination of citrulline, using diacetyl monoxime. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 15;107(2):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn E. Properties and subcellular distribution of two partially purified ornithine transcarbamoylases in cell suspensions of sugarcane. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):122–126. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLECZKOWSKI K., COHEN P. P. PURIFICATION OF ORNITHINE TRANSCARBAMYLASE FROM PEA SEEDLINGS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Aug;107:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90329-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain C., Stalon V., Noullez J. P., Mercenier A., Simon J. P., Broman K., Wiame J. M. Structure and function of ornithine carbamoyltransferases. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neway J. O., Switzer R. L. Purification, characterization, and physiological function of Bacillus subtilis ornithine transcarbamylase. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):512–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.512-521.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shargool P. D., Steeves T., Weaver M., Russell M. The localization within plant cells of enzymes involved in arginine biosynthesis. Can J Biochem. 1978 Apr;56(4):273–279. doi: 10.1139/o78-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. W., Titus J. S. The occurrence and nature of ornithine carbamoyltransferase in senescing apple leaf tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):382–385. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. A., Stewart G. R. Tissue and subcellular localization of enzymes of arginine metabolism in Pisum sativum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 31;101(4):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S. Chicken ornithine transcarbamylase: purification and some properties. J Biochem. 1983 Oct;94(4):1307–1315. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ruiter H., Kollöffel C. Arginine catabolism in the cotyledons of developing and germinating pea seeds. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):525–528. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


