Abstract
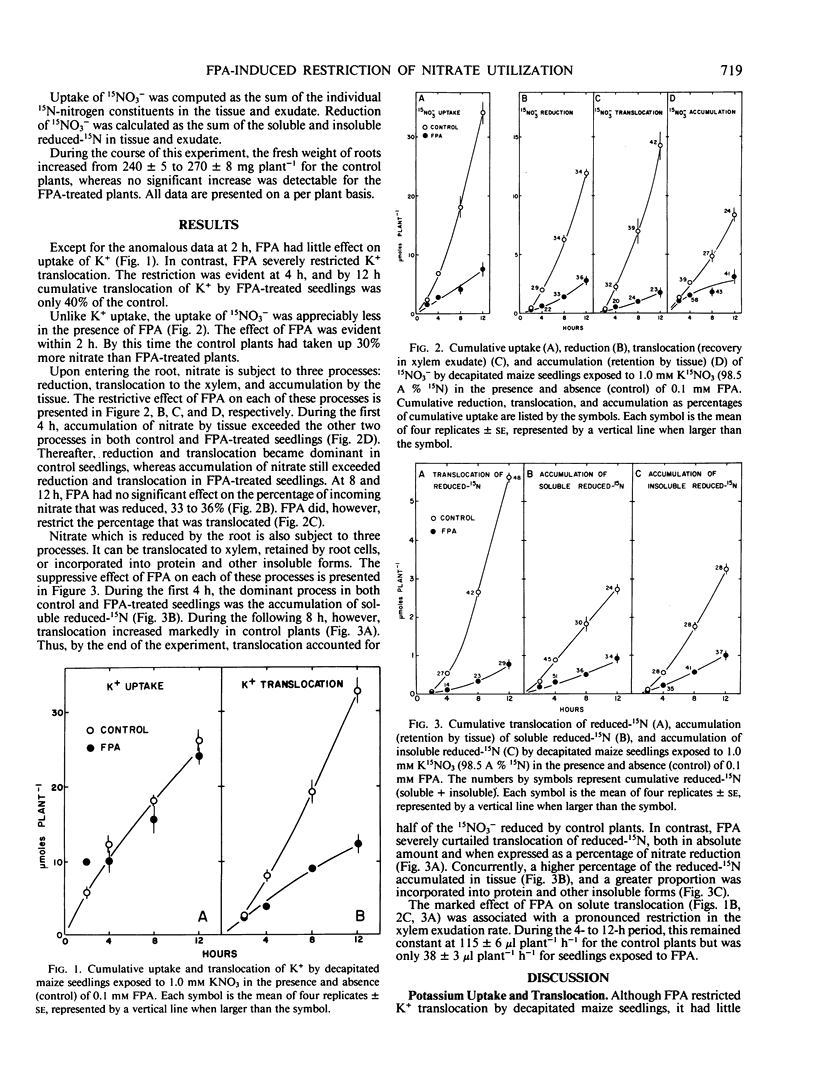
Roots of decapitated maize seedlings (Zea mays L.) were exposed for 12 hours to 1.0 millimolar KNO3 (98.5 atom per cent 15N) in the presence and absence (control) of 0.1 millimolar p-fluorophenylalanine (FPA), an analog of the amino acid phenylalanine. FPA decreased nitrate uptake but had little effect on potassium uptake. In contrast, accumulation of both ions in the xylem exudate was greatly restricted. The proportion of reduced 15N-nitrogen that was translocated at each time was also restricted by FPA. These observations are interpreted as indicating that synthesis of functional protein(s) is required for nitrate uptake and for transport of potassium, nitrate, and reduced-15N from xylem parenchyma cells into xylem elements. The effect of FPA on nitrate reduction is less clear. Initially, FPA limited nitrate reduction more than nitrate uptake, but by 8 hours the cumulative reduction of entering nitrate was similar (∼35%) in both control and FPA-treated roots. A relationship between nitrate uptake and nitrate reduction is implied. It is suggested that nitrate influx regulates the proportion of nitrate reductase in the active state, and thereby regulates concurrent nitrate reduction in decapitated maize seedlings.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aryan A. P., Batt R. G., Wallace W. Reversible Inactivation of Nitrate Reductase by NADH and the Occurrence of Partially Inactive Enzyme in the Wheat Leaf. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):582–587. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastain C. J., Lafayette P. R., Hanson J. B. Action of protein synthesis inhibitors in blocking electrogenic h efflux from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):832–835. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Macdonald I. R. Specificity of cycloheximide in higher plant systems. Plant Physiol. 1970 Aug;46(2):227–232. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.2.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezeta F. N., Jackson W. A. Nitrate translocation by detopped corn seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):148–156. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filner P. Regulation of nitrate reductase in cultured tobacco cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 5;118(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filner P., Varner J. E., Wray J. L. Environmental or developmental changes cause many enzyme activities of higher plants to rise or fall. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):358–367. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. A., Flesher D., Hageman R. H. Nitrate Uptake by Dark-grown Corn Seedlings: Some Characteristics of Apparent Induction. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–127. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks A., Wallace W., Stevens D. Synthesis and turnover of nitrate reductase in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1972 Dec;50(6):649–654. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.6.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace G. M., Mackown C. T., Volk R. J. Minimizing Nitrate Reduction during Kjeldahl Digestion of Plant Tissue Extracts and Stem Exudates : APPLICATION TO N STUDIES. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):32–36. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G., Wildes R. A., Schaefer N., Wellfare D. Effect of azetidine 2-carboxylic Acid on ion uptake and ion release to the xylem of excised barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):240–246. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. P., Rains D. W. Nitrate absorption by barley: I. Kinetics and energetics. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):55–58. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers D. A., Kuo T. M., Kleinhofs A., Warner R. L., Oaks A. Synthesis and degradation of barley nitrate reductase. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):949–952. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA A. Studies on the mechanism of protein synthesis; incorporation of p-fluorophenylalanine into alpha-amylase of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:98–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


