Abstract
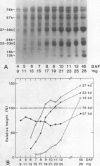
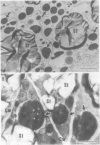
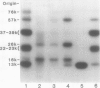
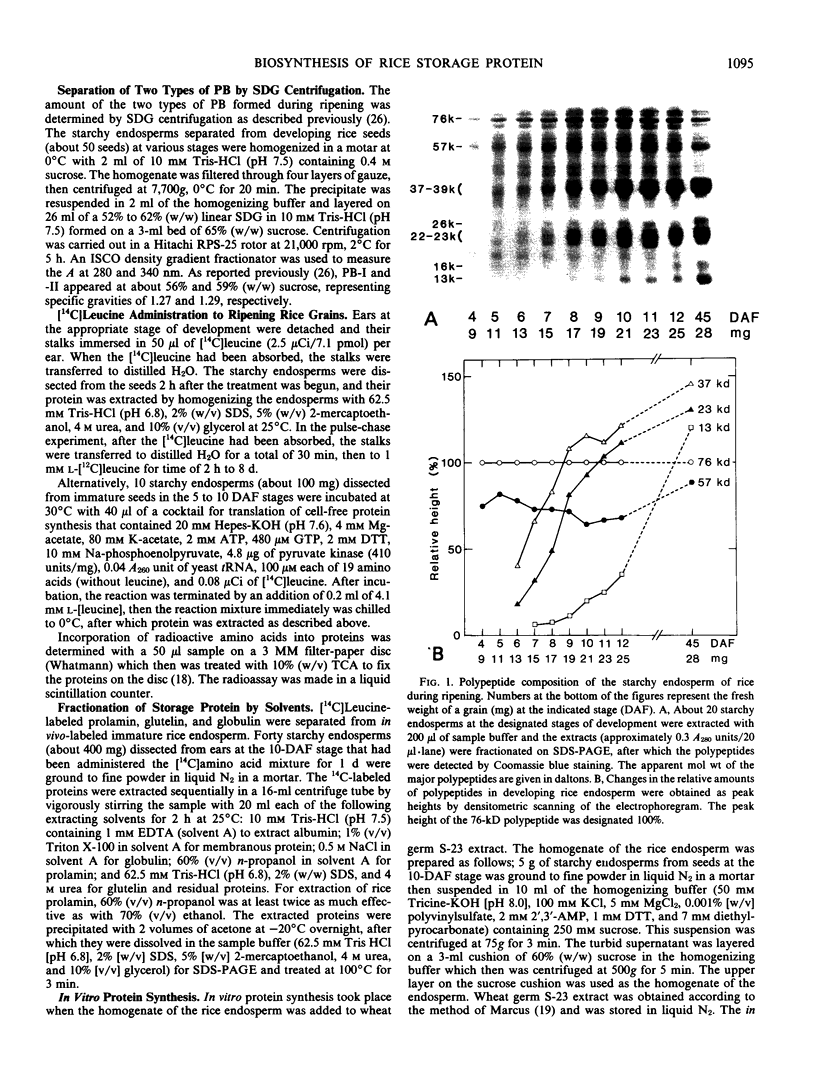
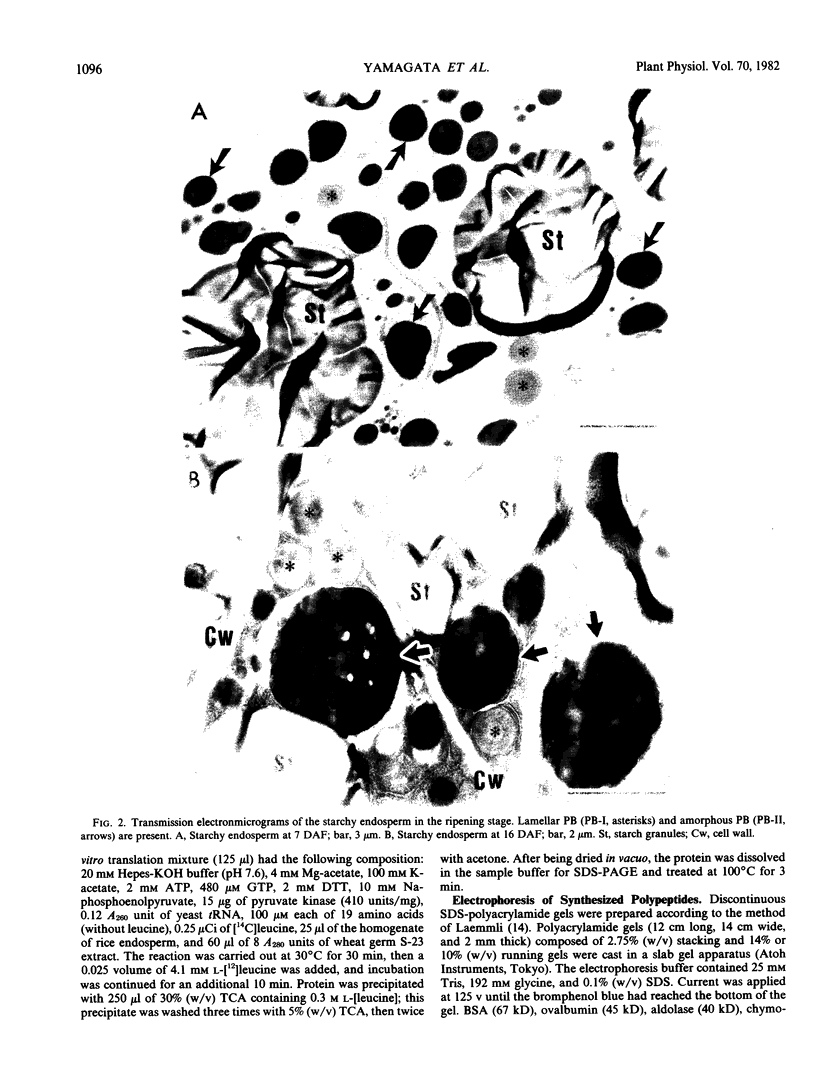
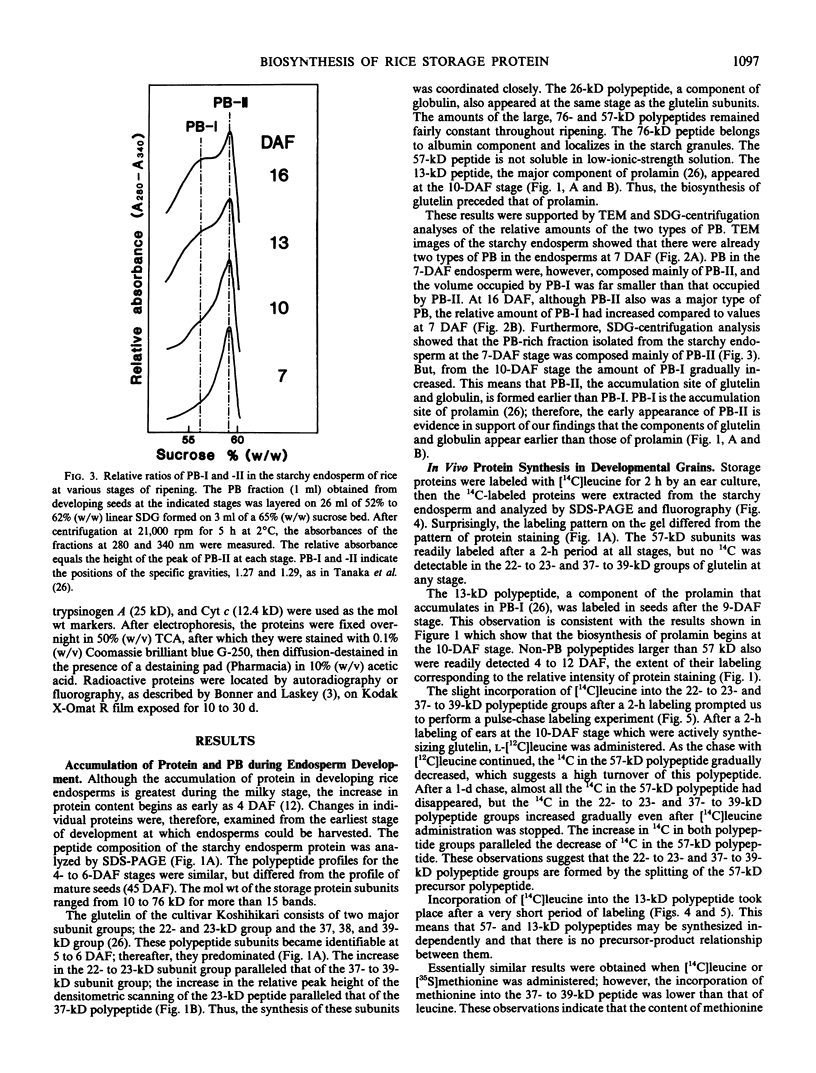
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of the starchy endosperm protein of rice (Oryza sativa L. Japonica cv Koshihikari) during seed development confirmed that storage protein begins to accumulate about 5 days after flowering. Two polypeptide groups, 22 to 23 and 37 to 39 kilodaltons, the components of glutelin, the major storage protein in rice seed, appeared 5 days after flowering. A 26-kilodalton polypeptide, the globulin component, also appeared 5 days after flowering. Smaller polypeptides (10- to 16-kilodaltons) including prolamin components, appeared about 10 days after flowering. In contrast, the levels of the 76- and 57-kilodalton polypeptides were fairly constant throughout seed development. Transmission electron microscopy and fractionation by sucrose density gradient centrifugation of the starchy endosperms at various stages of development showed that protein body type II, the accumulation site of glutelin and globulin, was formed faster than protein body type I, the accumulation site of prolamin.
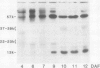
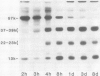
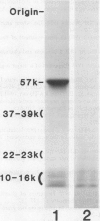
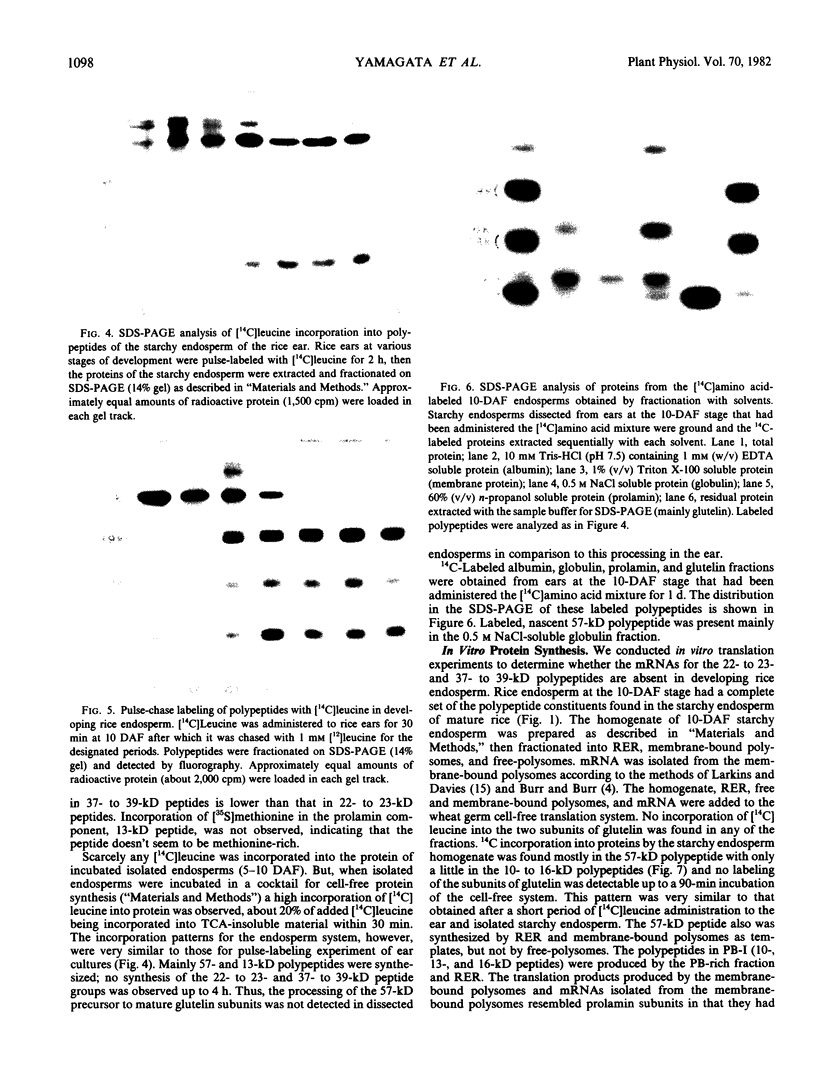
The 57-kilodalton polypeptide but not the glutelin subunits was labeled in a 2-hour treatment with [14C]leucine given between 4 and 12 days after flowering to developing ears. In vivo pulse-chase labeling studies showed the 57-kilodalton polypeptide to be a precursor of the 22 to 23 and 37 to 39 kilodalton subunits. The 57-kilodalton polypeptide was salt-soluble, but the mature glutelin subunits were almost salt insoluble.
In vitro protein synthesis also showed that the mRNAs directly coding the 22 to 23 and 37 to 39 kilodalton components were absent in developing seeds and that the 57-kilodalton polypeptide was the major product. Thus, it was concluded that the two subunits of rice glutelin are formed through post-translational cleavage of the 57-kilodalton polypeptide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene F. C. In Vitro Synthesis of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Storage Proteins. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):778–783. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Ma Y., Buchbinder B. U., Pyne J. W., Sun S. M., Bliss F. A. Messenger RNA for G1 protein of French bean seeds: Cell-free translation and product characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3196–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph T., Higgins V., Spencer D. Precursor Forms of Pea Vicilin Subunits: MODIFICATION BY MICROSOMAL MEMBRANES DURING CELL-FREE TRANSLATION. Plant Physiol. 1981 Feb;67(2):205–211. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Davies E. Polyribosomes from Peas: V. An Attempt to Characterize the Total Free and Membrane-bound Polysomal Population. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):749–756. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Hurkman W. J. Synthesis and deposition of zein in protein bodies of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):256–263. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Efron D., Weeks D. P. The wheat embryo cell-free system. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:749–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumer N. E., Thanh V. H., Nielsen N. C. Purification and characterization of mRNA from soybean seeds. Identification of glycinin and beta-conglycinin precursors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8756–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]