Abstract
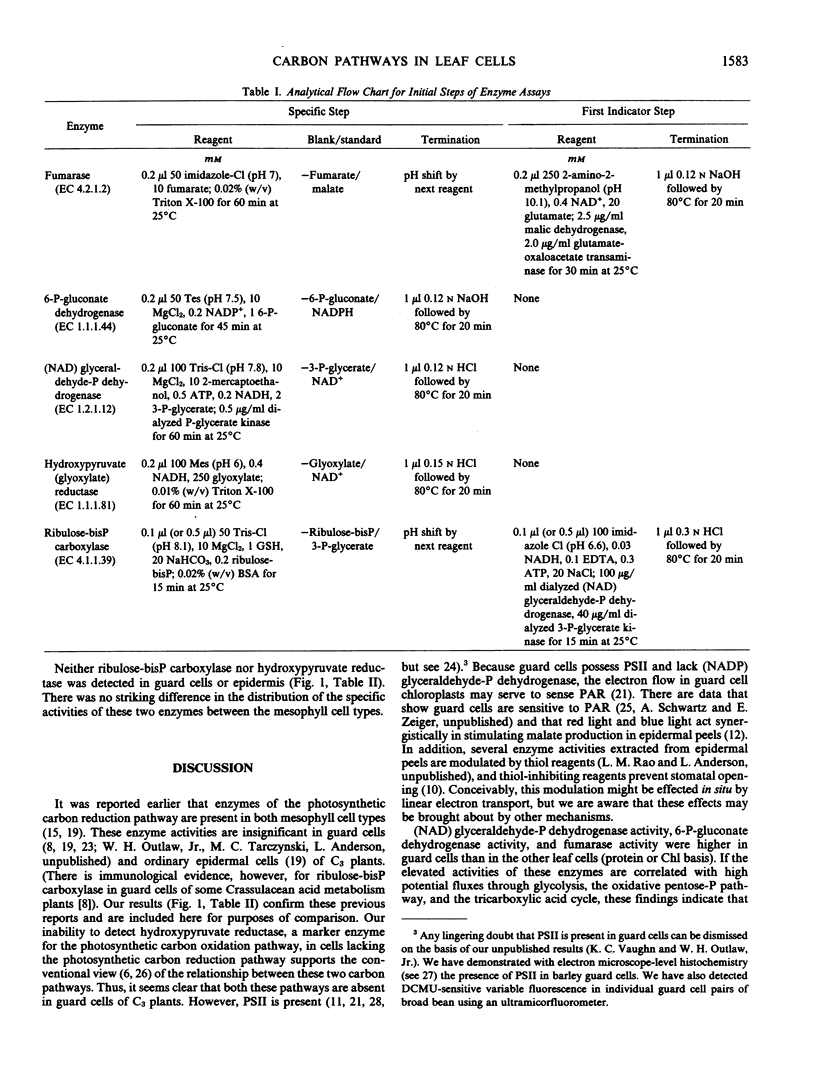
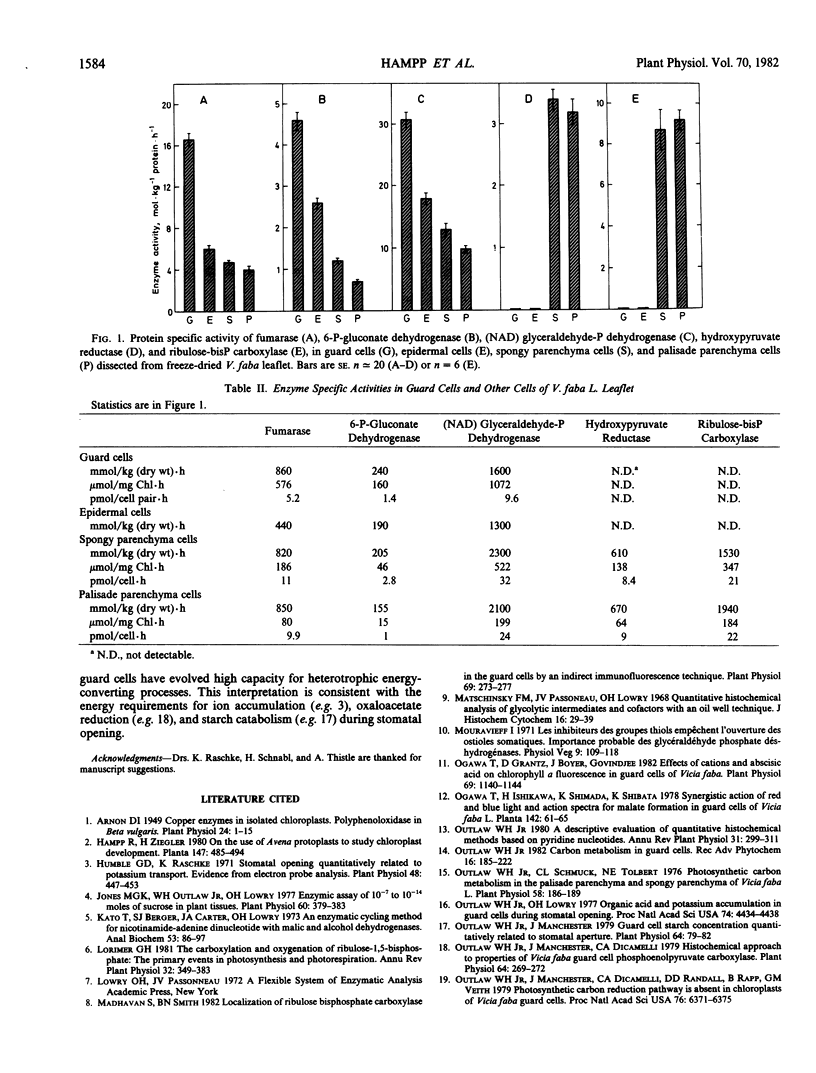
Guard cells and three other cell types from Vicia faba L. `Longpod' leaflets were assayed for enzymes that catalyze one step in each of five major carbon pathways in green plants: the photosynthetic carbon reduction pathway (ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase, EC 4.1.1.39), the photosynthetic carbon oxidation pathway (hydroxypyruvate reductase, EC 1.1.1.81), glycolysis ([NAD] glyceraldehyde-P dehydrogenase, EC 1.2.1.12), the oxidative pentose-P pathway (6-P-gluconate dehydrogenase, EC 1.1.1.44), and the tricarboxylic acid pathway (fumarase, EC 4.2.1.2). Neither ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase nor hydroxypyruvate reductase could be detected in guard cells or epidermal cells; high levels of these activities were present in mesophyll cells. The specific activity of fumarase (protein basis) was about 4-fold higher in guard cells than in epidermal, palisade parenchyma or spongy parenchyma cells. (NAD) glyceraldehyde-P and 6-P-gluconate dehydrogenases also were present at high protein specific activities in guard cells (2- to 4-fold that in meosphyll cells).
It was concluded that the capacity for metabolite flux through the catabolic pathways is high in guard cells. In addition, other support is provided for the view that photoreduction of CO2 by these guard cells is absent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humble G. D., Raschke K. Stomatal opening quantitatively related to potassium transport: evidence from electron probe analysis. Plant Physiol. 1971 Oct;48(4):447–453. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. G., Outlaw W. H., Lowry O. H. Enzymic assay of 10 to 10 moles of sucrose in plant tissues. Plant Physiol. 1977 Sep;60(3):379–383. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Berger S. J., Carter J. A., Lowry O. H. An enzymatic cycling method for nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide with malic and alcohol dehydrogenases. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):86–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90409-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhavan S., Smith B. N. Localization of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in the guard cells by an indirect, immunofluorescence technique. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):273–277. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M., Passonneau J. V., Lowry O. H. Quantitative histochemical analysis of glycolytic intermediates and cofactors with an oil well technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Jan;16(1):29–39. doi: 10.1177/16.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Grantz D., Boyer J., Govindjee Effects of Cations and Abscisic Acid on Chlorophyll a Fluorescence in Guard Cells of Vicia faba. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1140–1144. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Lowry O. H. Organic acid and potassium accumulation in guard cells during stomatal opening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4434–4438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Manchester J., Dicamelli C. A. Histochemical Approach to Properties of Vicia faba Guard Cell Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):269–272. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Manchester J., Dicamelli C. A., Randall D. D., Rapp B., Veith G. M. Photosynthetic carbon reduction pathway is absent in chloroplasts of Vicia faba guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6371–6375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Manchester J. Guard cell starch concentration quantitatively related to stomatal aperture. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jul;64(1):79–82. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Manchester J., Zenger V. E. The relationship between protein content and dry weight of guard cells and other single cell samples of Vicia faba L. leaflet. Histochem J. 1981 Mar;13(2):329–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01006886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Mayne B. C., Zenger V. E., Manchester J. Presence of Both Photosystems in Guard Cells of Vicia faba L: IMPLICATIONS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL SIGNAL PROCESSING. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):12–16. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Schmuck C. L., Tolbert N. E. Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism in the Palisade Parenchyma and Spongy Parenchyma of Vicia faba L. Plant Physiol. 1976 Aug;58(2):186–189. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Raschke K. Effect of Light Quality on Stomatal Opening in Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1170–1174. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert N. E. Metabolic pathways in peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn K. C., Duke S. O. Cytochemical localization of photosystem II donor sites. Histochemistry. 1981 Dec;73(3):363–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00495650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger E., Armond P., Melis A. Fluorescence Properties of Guard Cell Chloroplasts: EVIDENCE FOR LINEAR ELECTRON TRANSPORT AND LIGHT-HARVESTING PIGMENTS OF PHOTOSYSTEMS I AND II. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):17–20. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


