Abstract
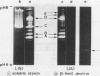
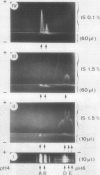
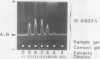
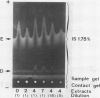
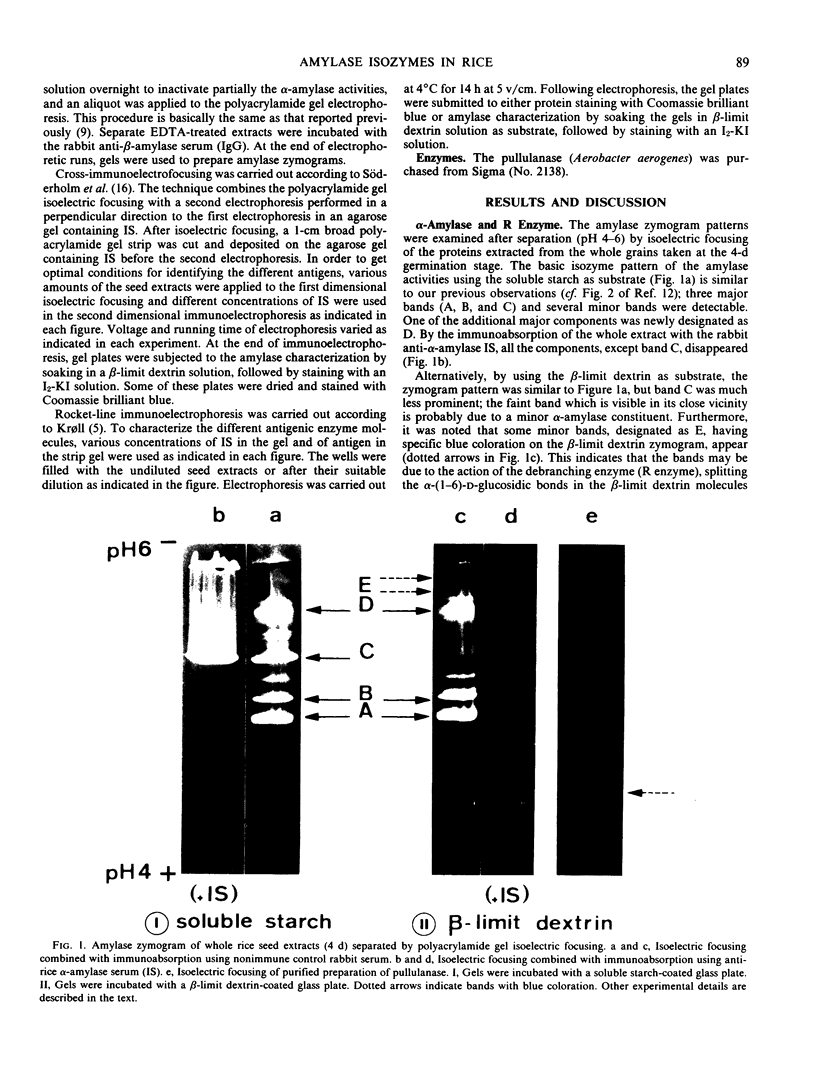
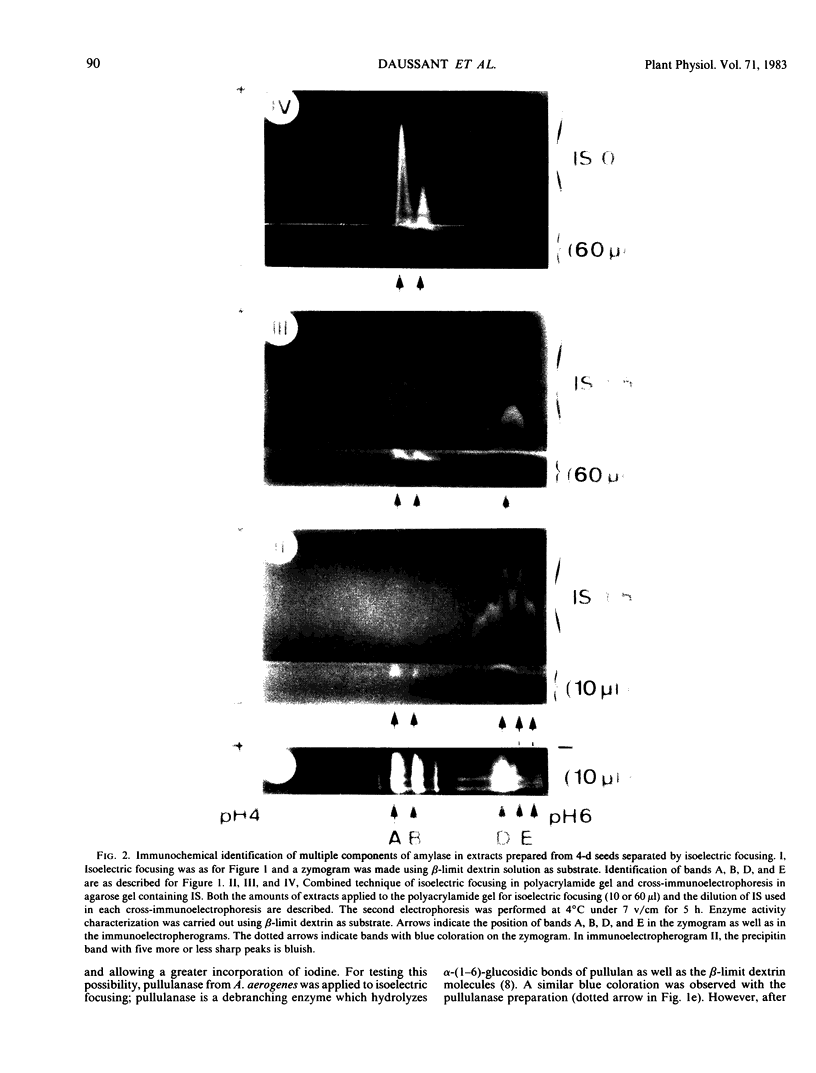
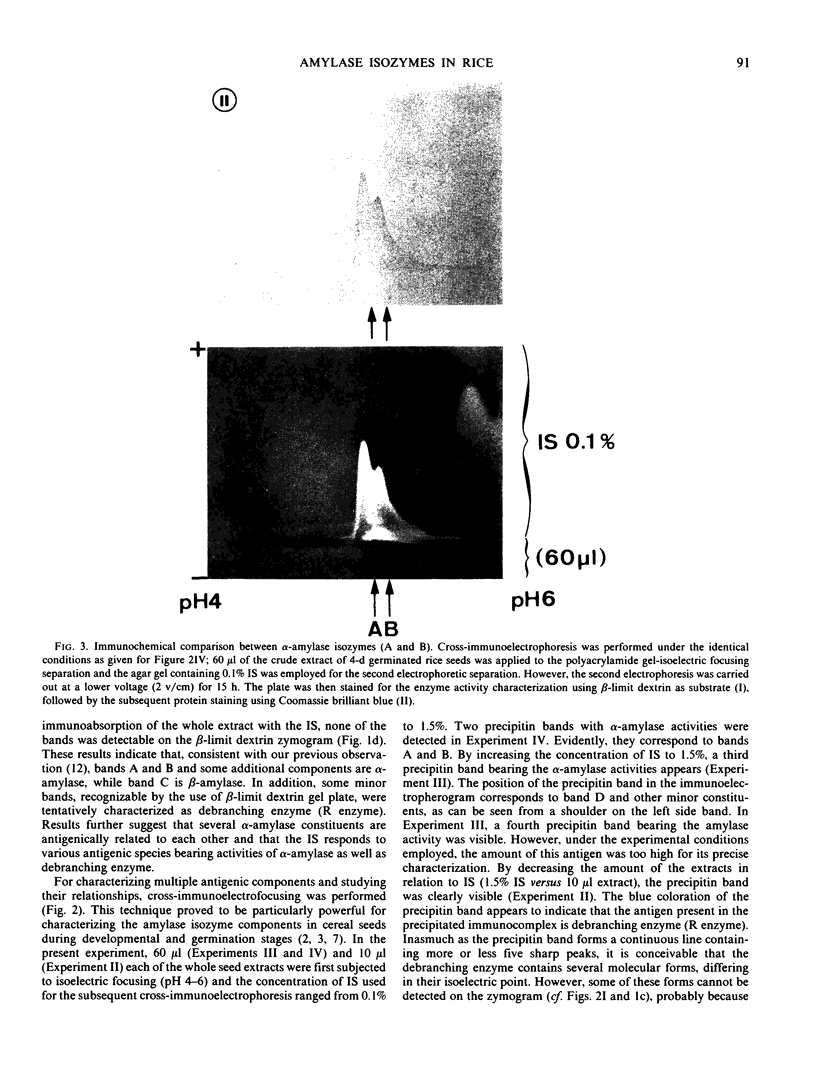
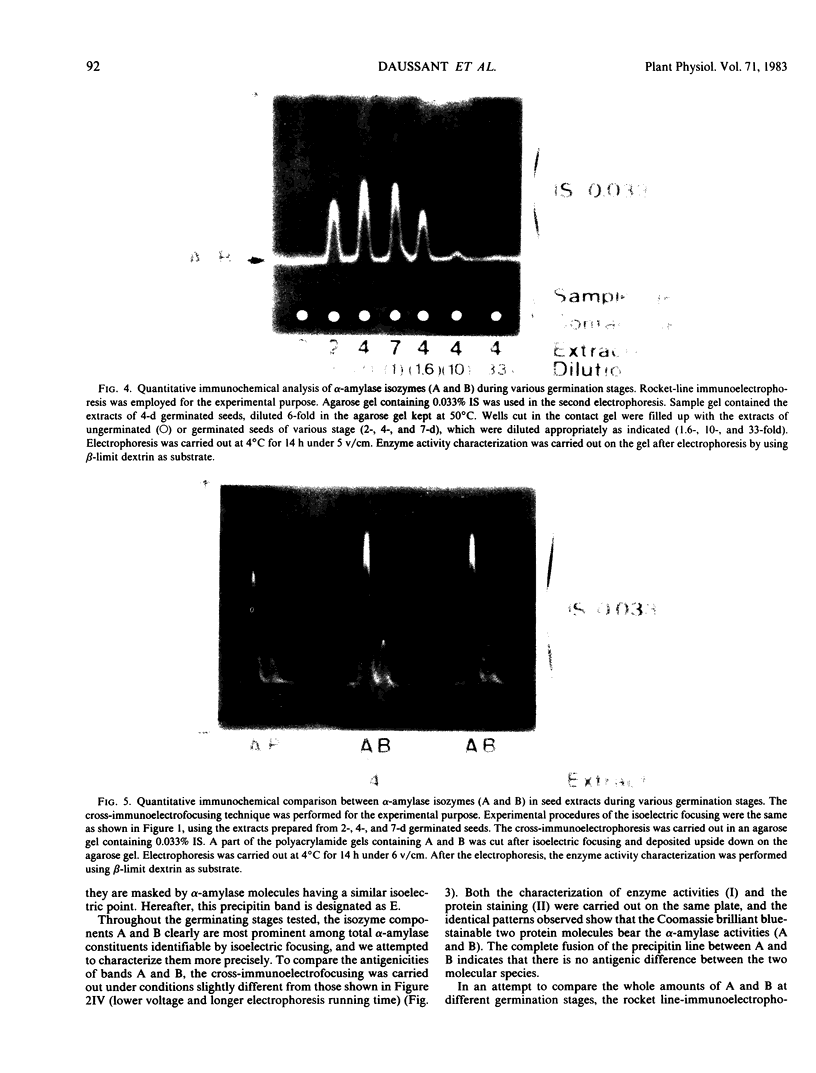
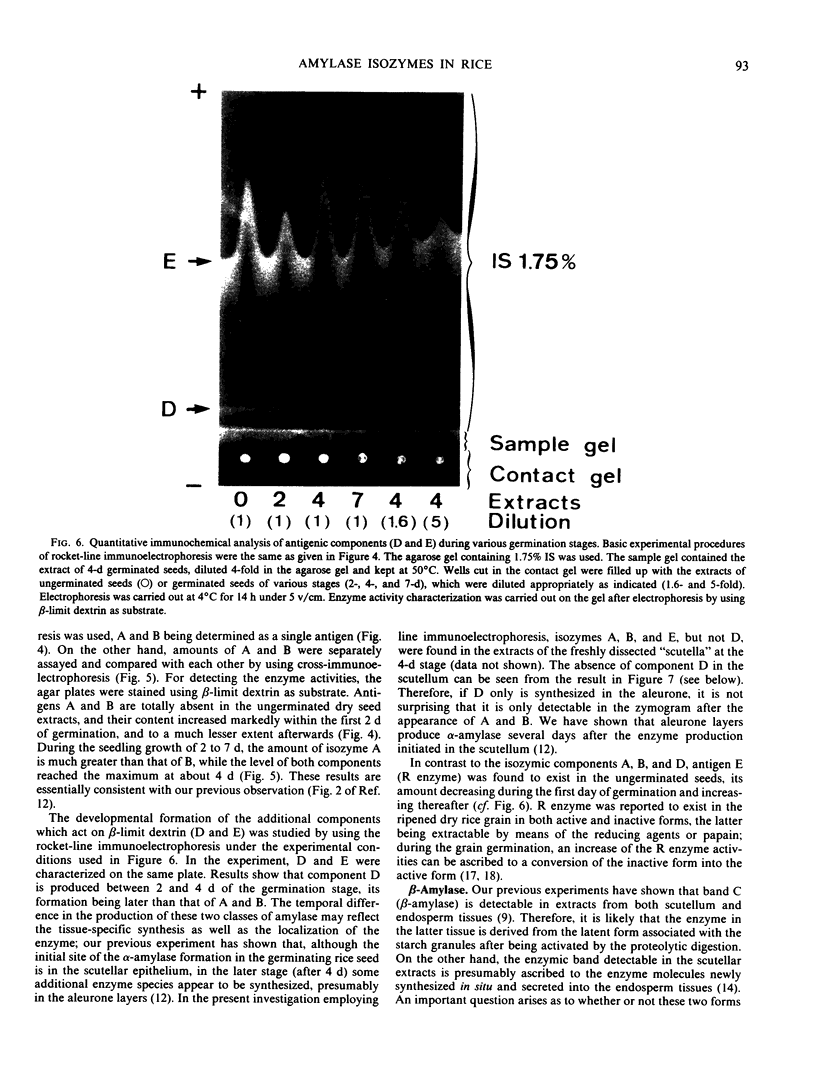
The formation of multiple forms of amylases in germinating rice (Oryza sativa L. cv Kimmaze) grains was examined by means of isoelectric focusing, cross-immunoelectrophoresis, and rocket-line immunoelectrophoresis followed by a reaction of enzymic characterization by using β-limit dextrin or starch as substrate. The constituents detected by isoelectric focusing were identified as three electrophoretically heterogeneous antigens. The major α-amylase bands A and B corresponded to a same antigen, the main portion of which was produced within 2 days' germination. The bulk of α-amylase D appeared between 2 and 4 days' germination. Component E, a debranching enzyme according to its action on the β-limit dextrin, already exists in the ungerminated seeds; its amount decreases within the first 2 days of germination and increases again thereafter.
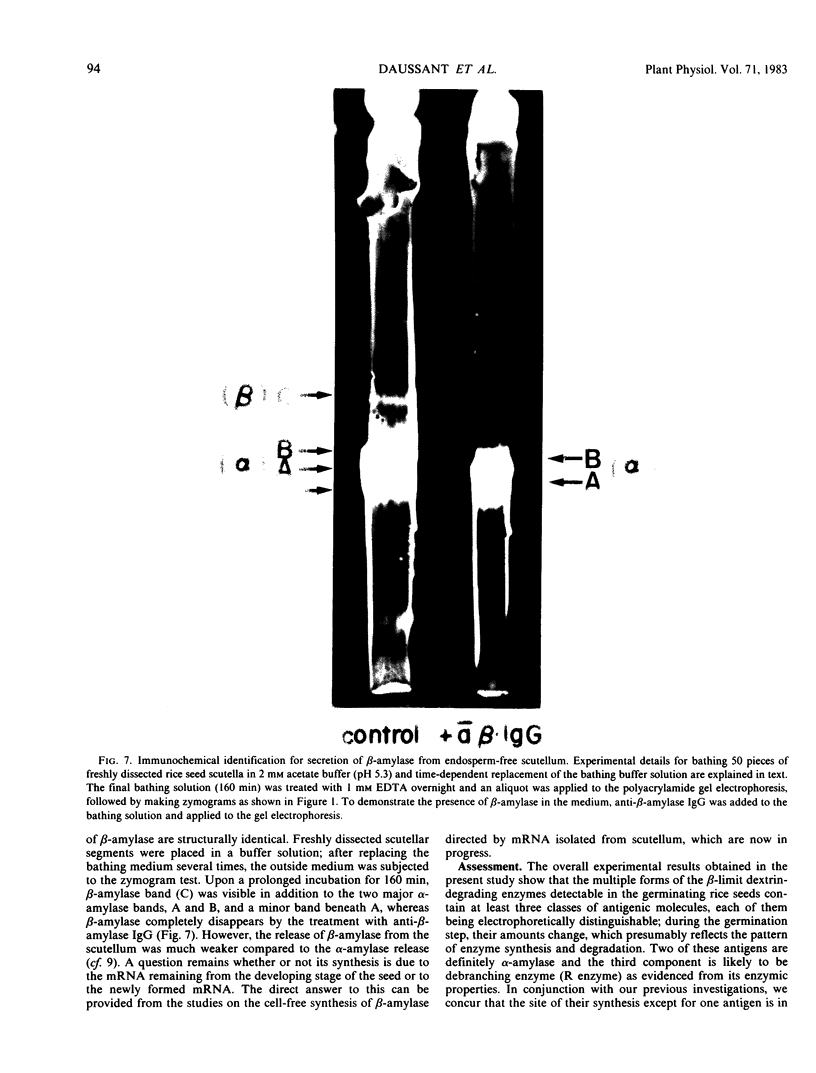
Evidence showing that β-amylase (band C) is produced by the scutellum at an early stage of germination was provided. The enzyme appeared in a suspension of the scutellum after a prolonged incubation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daussant J., MacGregor A. W. Combined immunoabsorption and isoelectric focusing of barley and malt amylases in polyacrylamine gel. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):261–266. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daussant J., Skakoun A. Immunochemical approaches to studies of isozyme regulation in higher plants. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1981;5:175–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Rocket-line immunoelectrophoresis (76). Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:83–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier C., Frantz B. M., Whelan W. J. An improved purification of cell-bound pullulanase from Aerobacter aerogenes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata S., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds : 12. Biosynthesis of alpha-amylase in relation to protein glycosylation. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):147–153. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata S., Okamoto K., Watanabe A., Akazawa T. Enzymic Mechanism of Starch Breakdown in Germinating Rice Seeds: 10. IN VIVO AND IN VITRO SYNTHESIS OF alpha-AMYLASE IN RICE SEED SCUTELLUM. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1314–1318. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Akazawa T. Enzymic Mechanism of Starch Breakdown in Germinating Rice Seeds: 8. Immunohistochemical Localization of beta-Amylase. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):337–340. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Akazawa T. Enzymic Mechanism of Starch Breakdown in Germinating Rice Seeds: 9. DE NOVO SYNTHESIS OF beta-AMYLASE. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jan;65(1):81–84. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanisms of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds: 7. Amylase formation in the epithelium. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):336–340. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Murai T., Eguchi G., Okamoto M., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds : 11. Ultrastructural changes in scutellar epithelium. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):905–911. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]