Abstract
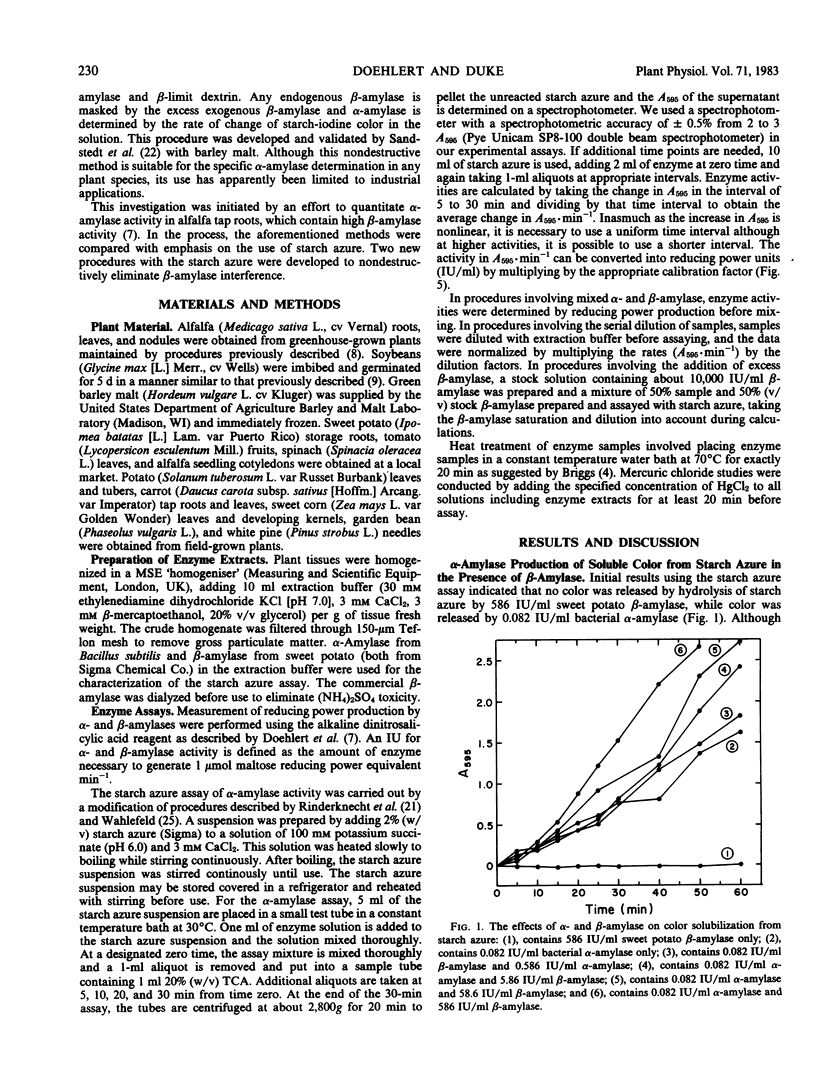
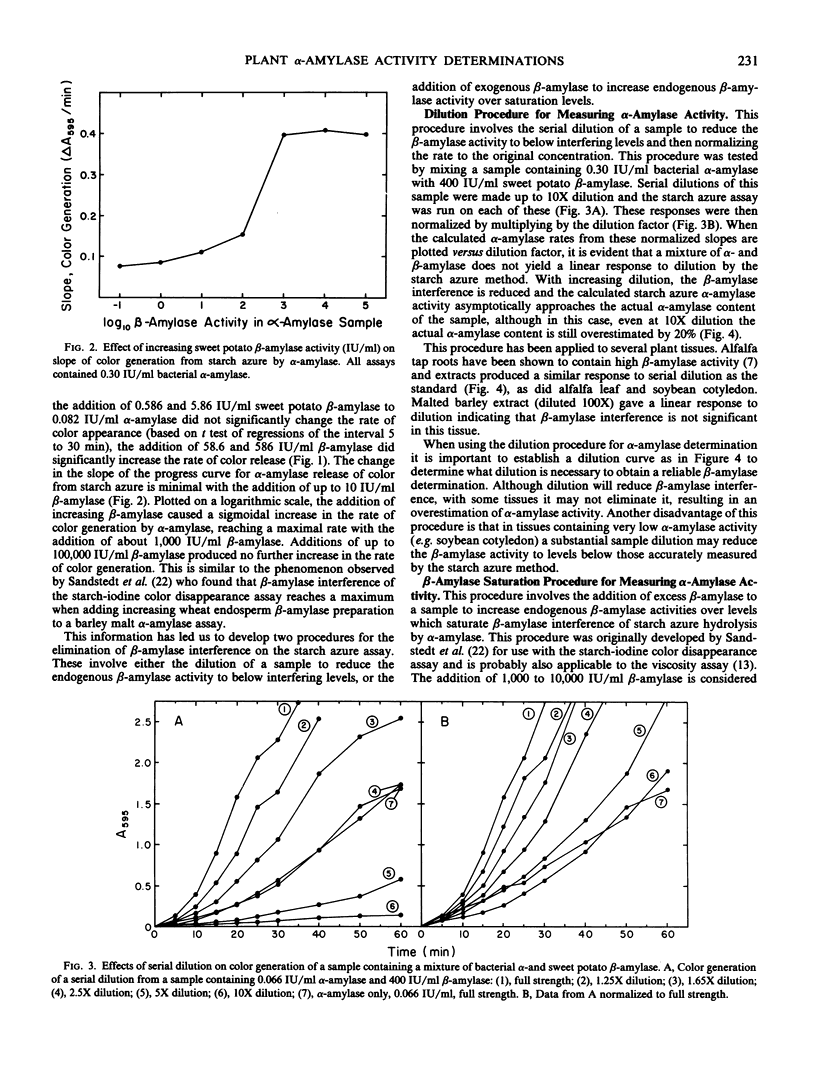
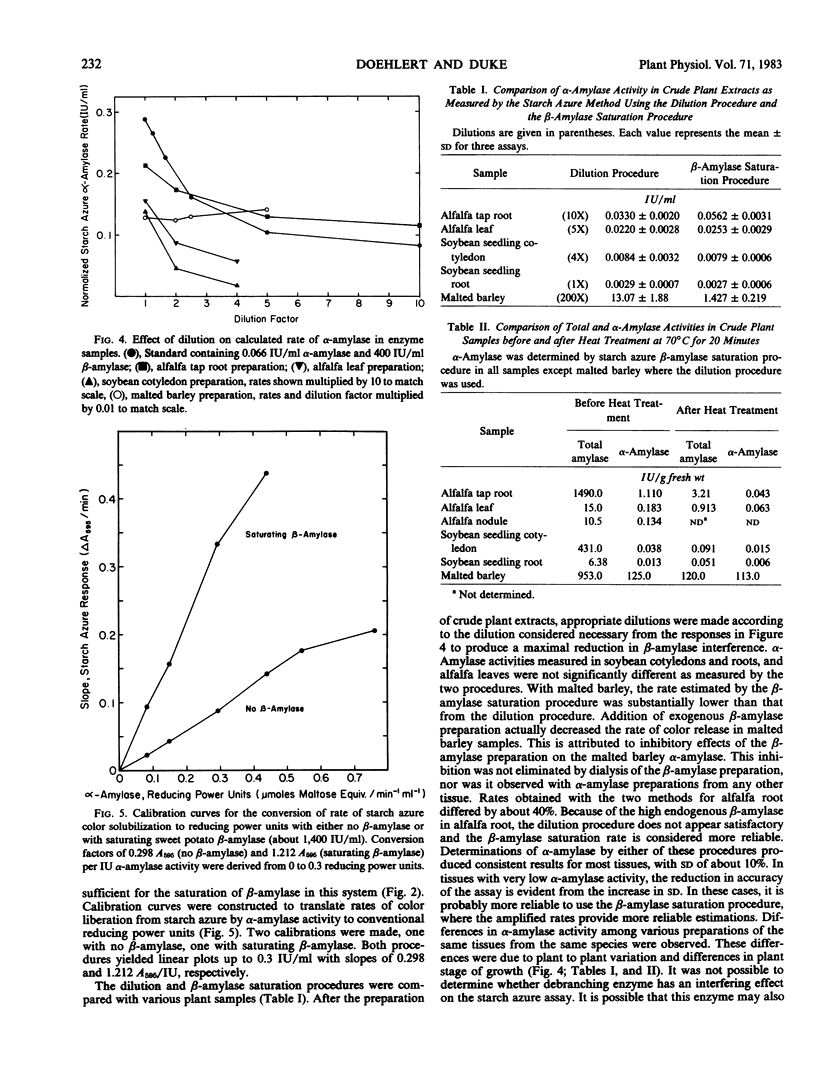
The specific measurement of α-amylase activity in crude plant extracts is difficult because of the presence of β-amylases which directly interfere with most assay methods. Methods compared in this study include heat treatment at 70°C for 20 min, HgCl2 treatment, and the use of the α-amylase specific substrate starch azure. In comparing alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), soybeans (Glycine max [L.] Merr.), and malted barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), the starch azure assay was the only satisfactory method for all tissues. While β-amylase can liberate no color alone, over 10 International units per milliliter β-amylase activity has a stimulatory effect on the rate of color release. This stimulation becomes constant (about 4-fold) at β-amylase activities over 1,000 International units per milliliter. Two starch azure procedures were developed to eliminate β-amylase interference: (a) the dilution procedure, the serial dilution of samples until β-amylase levels are below levels that interfere; (b) the β-amylase saturation procedure, addition of exogenous β-amylase to increase endogenous β-amylase activity to saturating levels. Both procedures yield linear calibrations up to 0.3 International units per milliliter. These two procedures produced statistically identical results with most tissues, but not for all tissues. Differences between the two methods with some plant tissues was attributed to inaccuracy with the dilution procedure in tissues high in β-amylase activity or inhibitory effects of the commercial β-amylase. The β-amylase saturation procedure was found to be preferable with most species. The heat treatment was satisfactory only for malted barley, as α-amylases in alfalfa and soybeans are heat labile. Whereas HgCl2 proved to be a potent inhibitor of β-amylase activity at concentrations of 10 to 100 micromolar, these concentrations also partially inhibited α-amylase in barley malt. The reported α-amylase activities in crude enzyme extracts from a number of plant species are apparently the first specific measurements reported for any plant tissues other than germinating cereals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilderback D. E. A Simple Method to Differentiate between alpha- and beta-Amylase. Plant Physiol. 1973 Mar;51(3):594–595. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doehlert D. C., Duke S. H., Anderson L. Beta-Amylases from Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1096–1102. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke S. H., Schrader L. E., Miller M. G. Low Temperature Effects on Soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr. cv. Wells) Mitochondrial Respiration and Several Dehydrogenases during Imbibition and Germination. Plant Physiol. 1977 Nov;60(5):716–722. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano B. O., Varner J. E. Enzymic degradiation of starch granules in the cotyledons of germinating peas. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jun;44(6):886–892. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.6.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Greenberg E., Kuhn D. N., Preiss J. Subcellular localization of the starch degradative and biosynthetic enzymes of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):187–192. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Preiss J. Starch Degradation in Spinach Leaves: ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE AMYLASES AND R-ENZYME OF SPINACH LEAVES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):870–876. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Wilding P., Haverback B. J. A new method for the determination of alpha-amylase. Experientia. 1967 Oct 15;23(10):805–805. doi: 10.1007/BF02146851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


