Abstract
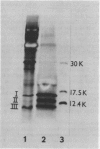
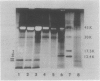
In filaments of the red alga Griffithsia, dead intercalary cells are replaced by the process of cell repair by cell fusion. This process is coordinated by a morphogenetic cell fusion hormone, rhodomorphin, which accelerates cell division and induces the production of a specialized repair cell. We have isolated rhodomorphin from Griffithsia pacifica Kylin and have purified it by concanavalin A affinity chromatography, hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and gel filtration chromatography. This molecule binds specifically to concanavalin A, is proteinase sensitive, and is inactivated by short treatments at temperatures of 50°C or above. It therefore appears that rhodomorphin from G. pacifica is a glycoprotein; its molecular weight, as estimated by gel filtration, is approximately 14,000.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz R., Duntze W. Purification and partial characterization of a factor, a mating hormone produced by mating-type-a cells from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochert G., Yates I. Purification and partial characterization of a glycoprotein sexual inducer from Volvox carteri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1211–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R. C., Jaenicke L. Purification and characterization of the hormone initiating sexual morphogenesis in Volvox carteri f. nagariensis Iyengar. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1050–1054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R. C., O'neil R. M., Miller C. E. L-Glutamic acid as a mediator of sexual morphogenesis in Volvox capensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1025–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waaland S. D., Cleland R. E. Cell repair through cell fusion in the red alga Griffithsia pacifica. Protoplasma. 1974;79(1):185–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02055788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waaland S. D. Evidence for a species-specific cell fusion hormone in red algae. Protoplasma. 1975;86(1-3):253–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01275635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]