Abstract
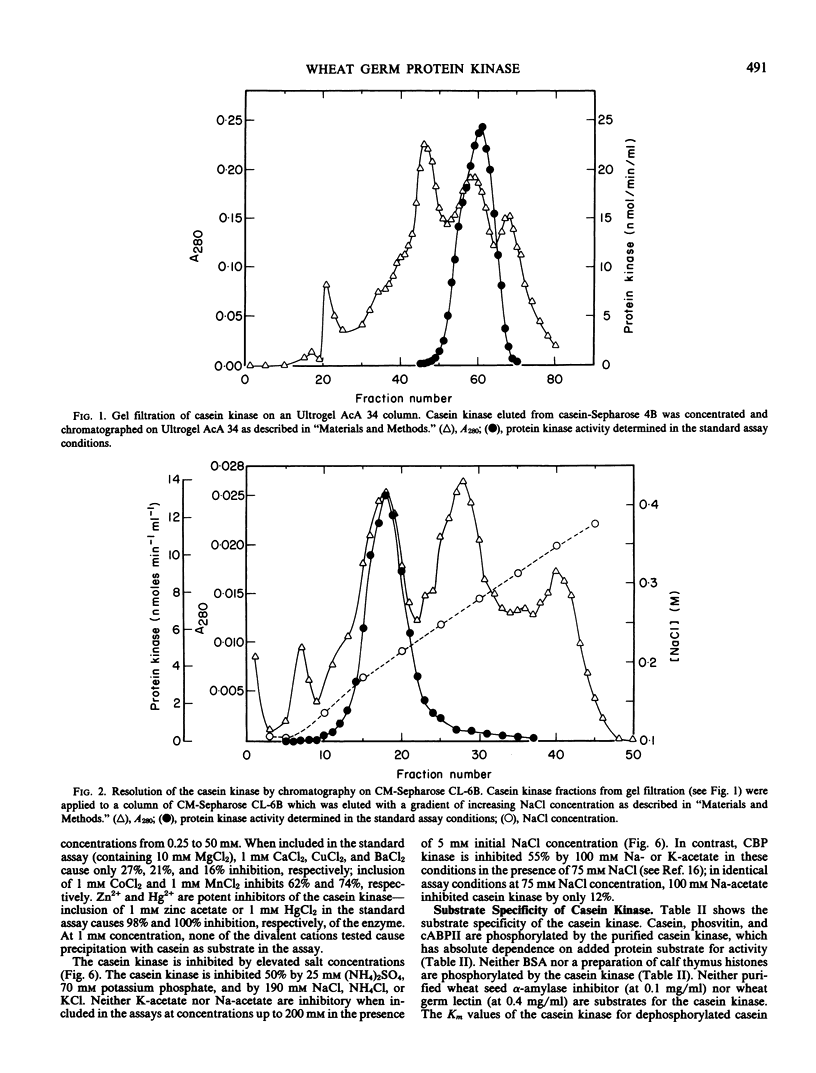
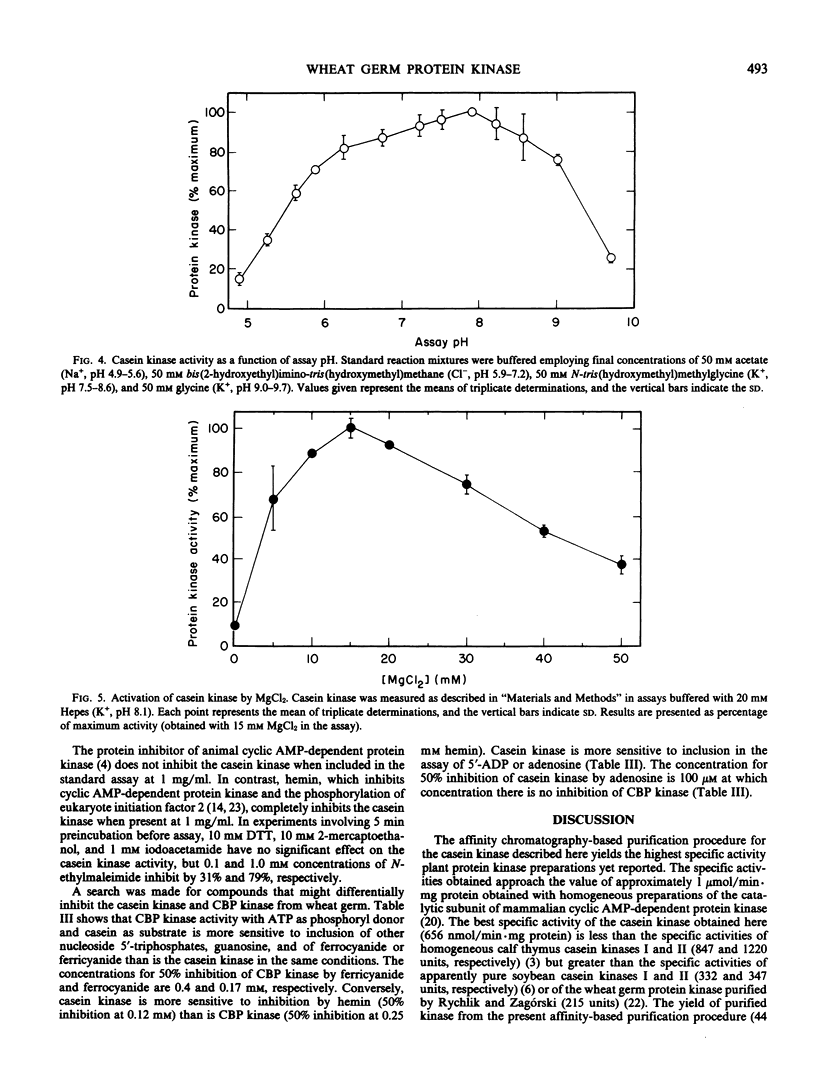
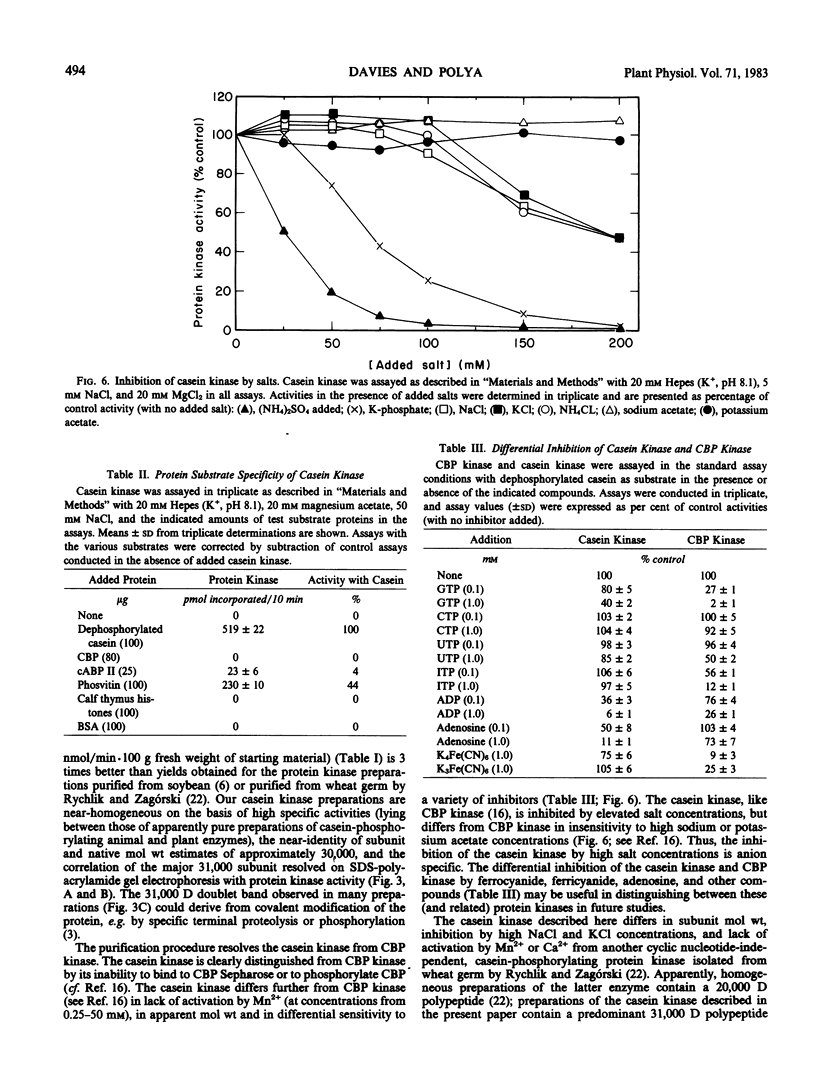
A protein kinase was extensively purified to near-homogeneity from wheat germ by a procedure involving affinity chromatography on casein-Sepharose 4B, gel filtration, and repeated chromatography on carboxymethyl-Sepharose CL-6B. The protein kinase preparations have the highest specific activities (up to 656 nanomoles phosphate incorporated per minute per milligram of protein) yet reported for plant protein kinases. The major polypeptides in purified preparations were revealed as two barely-resolved bands (molecular weight 31,000) on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in subunit-dissociating conditions. The molecular size of the protein kinase as determined from gel filtration is 30,000. The protein kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of casein, phosvitin, and the wheat germ cyclic AMP-binding protein cABPII but not of bovine serum albumin and histones nor of the wheat germ cytokinin-binding protein CBP. The protein kinase has a pH optimum of 7.9 and a Km value for ATP of 10 micromolar. The protein kinase differs from wheat germ CBP kinase in molecular weight, differential sensitivity to inhibitors, and in substrate specificity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahmus M. E. Purification and properties of calf thymus casein kinases I and II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3319–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaille J. G., Peters K. A., Fischer E. H. Isolation and properties of the rabbit skeletal muscle protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3080–3086. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann H., Böcher M., Wagner K. G. Two protein kinases from nuclei of cultured tobacco cells with properties similar to the cyclic nucleotide-independent enzymes (NI and NII) from animal tissue. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 25;137(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. P., Key J. L. Histone Kinase from Soybean Hypocotyls: PURIFICATION, PROPERTIES, AND SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITIES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):360–367. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazuś B., Szurmak B., Buchowicz J. Phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo of the wheat embryo RNA polymerase II. Acta Biochim Pol. 1980;27(1):9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Guilfoyle T. J., Key J. L. Isolation and Characterization of a Chromatin-associated Protein Kinase from Soybean. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jun;61(6):1023–1030. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.6.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Guilfoyle T. J., Key J. L. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a casein kinase from cauliflower nuclei. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):434–437. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Key J. L. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-enhanced Phosphorylation of Soybean Nuclear Proteins. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):190–198. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S., de Haro C. Regulation of protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:549–580. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polya G. M., Bowman J. A. Resolution and Properties of Two High Affinity Cyclic Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-Binding Proteins from Wheat Germ. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):577–584. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polya G. M., Davies J. R. Resolution and properties of a protein kinase catalyzing the phosphorylation of a wheat germ cytokinin-binding protein. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):482–488. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall D. D., Rubin P. M. Plant Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: II. ATP-Dependent Inactivation and Phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jan;59(1):1–3. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S. Isolation of a translational inhibitor from wheat germ with protein kinase activity that phosphorylates initiation factor eIF-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):1124–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Rangel-Aldao R., Erlichman J. Soluble cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases: review of the enzyme isolated from bovine cardiac muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1977;12:39–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Kupidlowska E., Nowak E., Zagórski W. Wheat germ protein kinase affects the translation of Brome Mosaic virus ribonucleic acid in vitro. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5249–5255. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Zagórski W. Purification and characterisation of adenosine-3',5'-phosphate-independent protein kinase from wheat germ. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):653–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., de Haro C., Datta A., Ochoa S. Translational control by protein kinase in Artemia salina and wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4356–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süss K. H. Identification of chloroplast thylakoid phosphoproteins. Evidence for the absence of phosphoryl-polypeptide intermediates in the ATPase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 30;102(2):724–729. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]