Abstract
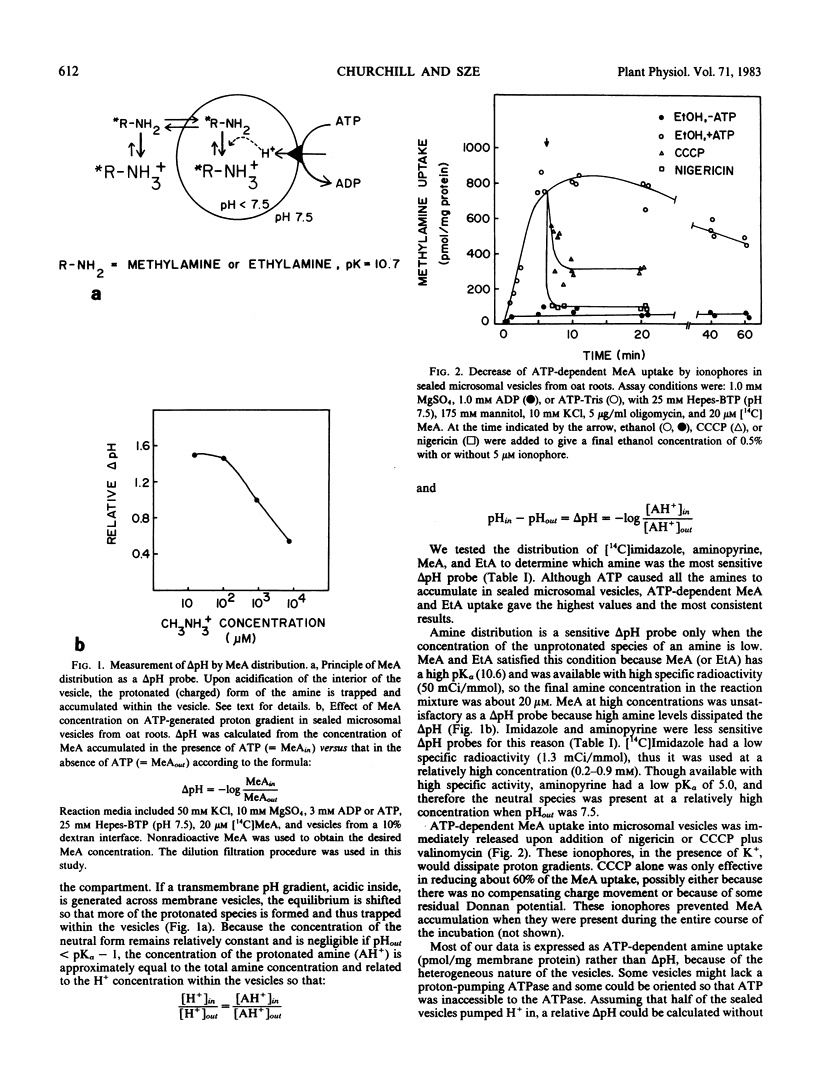
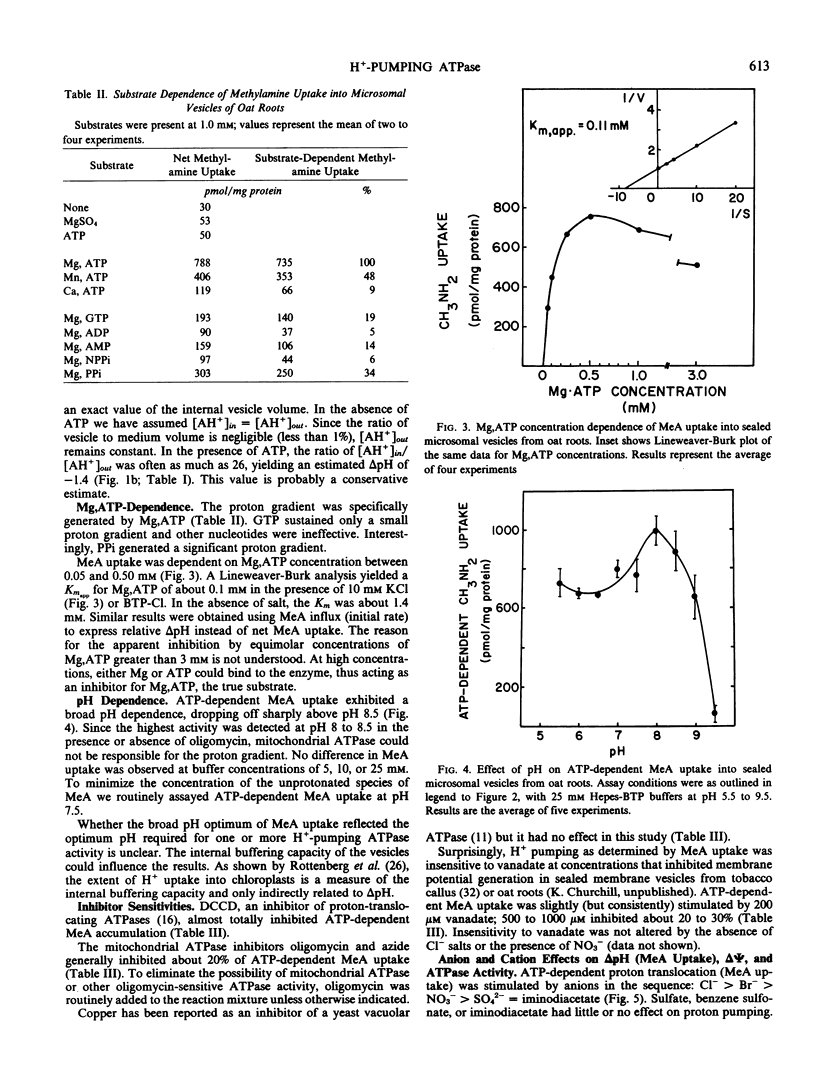
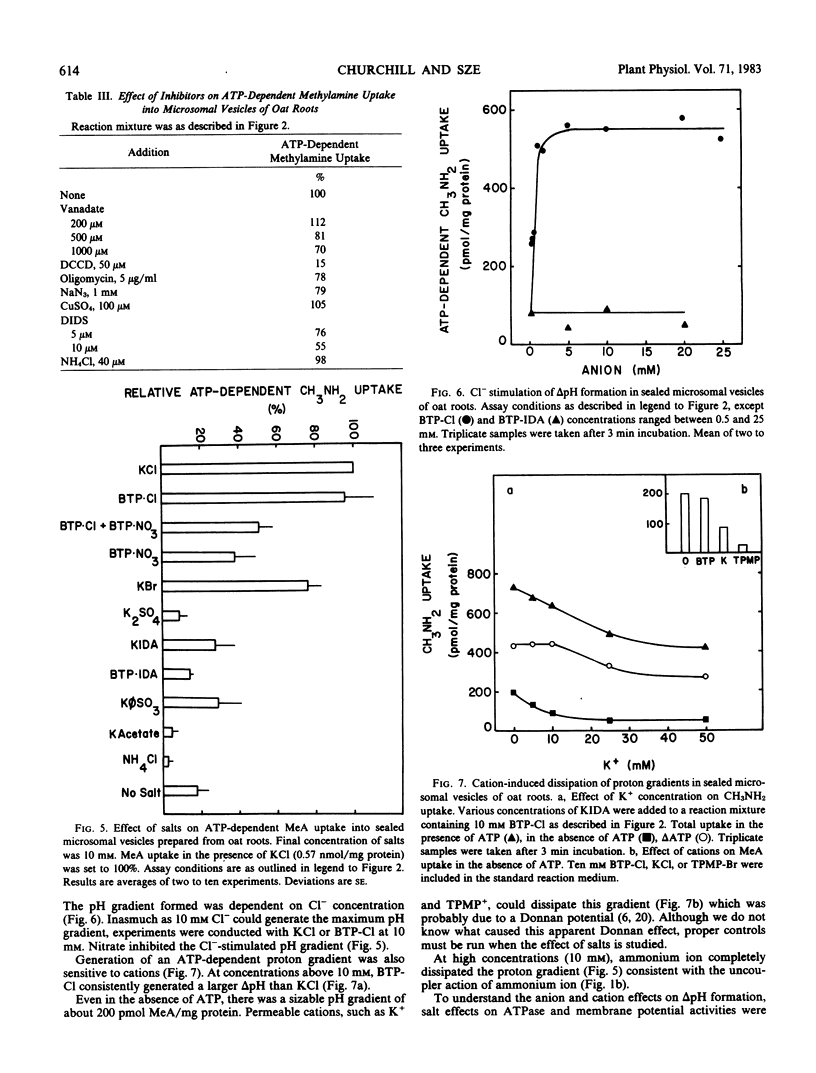
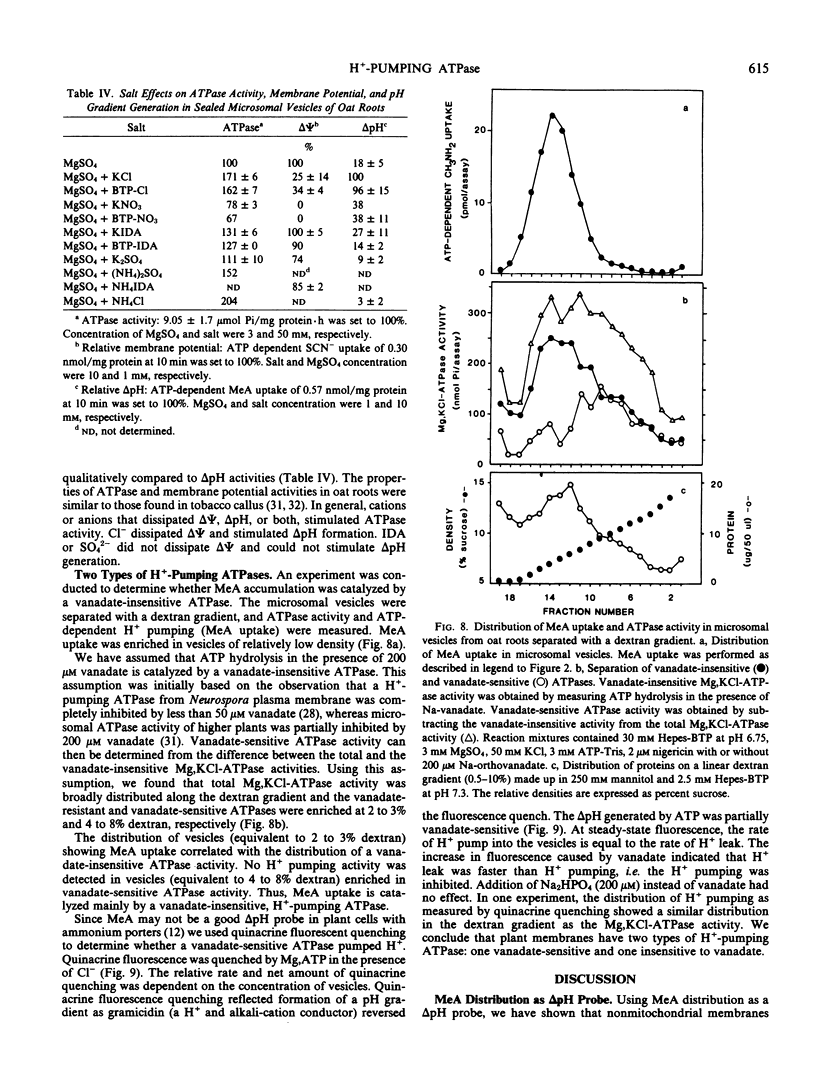
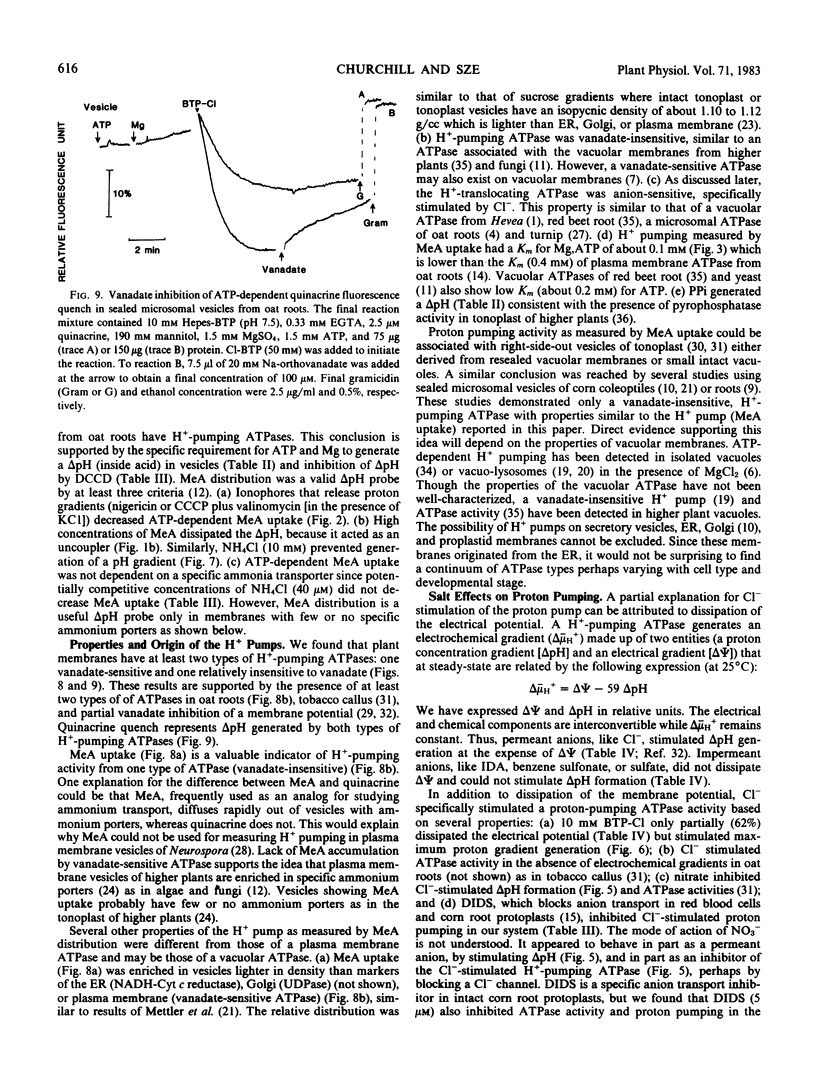
H+-pumping ATPases were detected in microsomal vesicles of oat (Avena sativa L. var Lang) roots using [14C]methylamine distribution or quinacrine fluorescent quenching. Methylamine (MeA) accumulation into vesicles and quinacrine quench were specifically dependent on Mg,ATP. Both activities reflected formation of a proton gradient (ΔpH) (acid inside) as carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, nigericin (in the presence of K+), or gramicidin decreased MeA uptake or increased quinacrine fluorescence. The properties of H+ pumping as measured by MeA uptake were characterized. The Kmapp for ATP was about 0.1 millimolar. Mg,GTP and Mg, pyrophosphate were 19% and 30% as effective as Mg,ATP. MeA uptake was inhibited by N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and was mostly insensitive to oligomycin, vanadate, or copper. ATP-dependent MeA was stimulated by anions with decreasing order of potency of Cl− > Br− > NO3− > SO42−, iminodiacetate, benzene sulfonate. Anion stimulation of H+ pumping was caused in part by the ability of permeant anions to dissipate the electrical potential and in part by a specific requirement of Cl− by a H+ -pumping ATPase. A pH gradient, probably caused by a Donnan potential, could be dissipated by K+ in the presence or absence of ATP. MeA uptake was enriched in vesicles of relatively low density and showed a parallel distribution with vanadate-insensitive ATPase activity on a continuous dextran gradient. ΔpH as measured by quinacrine quench was partially vanadate-sensitive. These results show that plant membranes have at least two types of H+ -pumping ATPases. One is vanadate-sensitive and probably enriched in the plasma membrane. One is vanadate-resistant, anion-sensitive and has many properties characteristic of a vacuolar ATPase. These results are consistent with the presence of electrogenic H+ pumps at the plasma membrane and tonoplast of higher plant cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cretin H. The proton gradient across the vacuo-lysosomal membrane of lutoids from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis. I. Further evidence for a proton-translocating ATPase on the vacuo-lysosomal membrane of intact lutoids. J Membr Biol. 1982;65(3):175–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01869961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Bennett A. B., Spanswick R. M. Localization of a proton-translocating ATPase on sucrose gradients. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakinuma Y., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Properties of H+-translocating adenosine triphosphatase in vacuolar membranes of SAccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10859–10863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. The transport of NH3 and NH4+ across biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 9;639(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Forte J. G. A study of H+ transport in gastric microsomal vesicles using fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hodges T. K. Characterization of Plasma Membrane-associated Adenosine Triphosphase Activity of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):6–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M. Isolation of Functionally Intact Rhodoplasts from Griffithsia monilis (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):5–8. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. Inhibition of anion transport in corn root protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):435–438. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnett P. E., Beechey R. B. Inhibitors of the ATP synthethase system. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:472–518. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin B., Blasco F. Further evidence for the proton pumping work of tonoplast ATPase from Hevea latex vacuome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):354–361. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin B., Marin-Lanza M., Komor E. The protonmotive potential difference across the vacuo-lysosomal membrane of Hevea brasiliensis (rubber tree) and its modification by a membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 15;198(2):365–372. doi: 10.1042/bj1980365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven J. A., Farquhar G. D. Methylammonium Transport in Phaseolus vulgaris Leaf Slices. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):859–863. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Grunwald T., Avron M. Determination of pH in chloroplasts. I. Distribution of ( 14 C) methylamine. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):54–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungie J. M., Wiskich J. T. Salt-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase from Smooth Microsomes of Turnip. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):1064–1068. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A. Proton translocation catalyzed by the electrogenic ATPase in the plasma membrane of Neurospora. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2925–2931. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. G., Cleland R. E. Evidence for a Cl-Stimulated MgATPase Proton Pump in Oat Root Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):798–803. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze H. Characterization of nigericin-stimulated ATPase from sealed microsomal vesicles of tobacco callus. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):498–505. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze H., Churchill K. A. Mg/KCl-ATPase of plant plasma membranes is an electrogenic pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5578–5582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze H. Nigericin-stimulated ATPase activity in microsomal vesicles of tobacco callus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5904–5908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


