Abstract
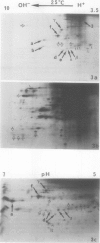
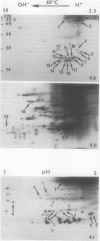
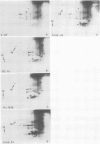
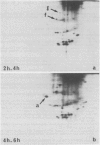
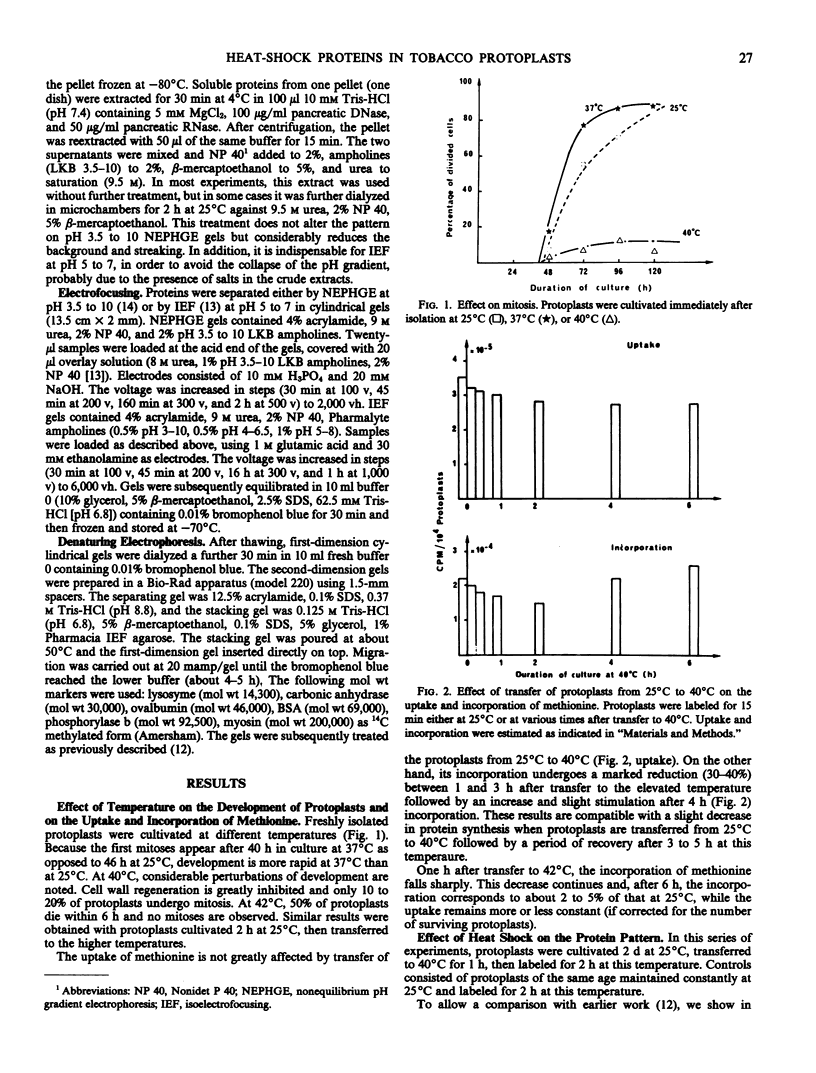
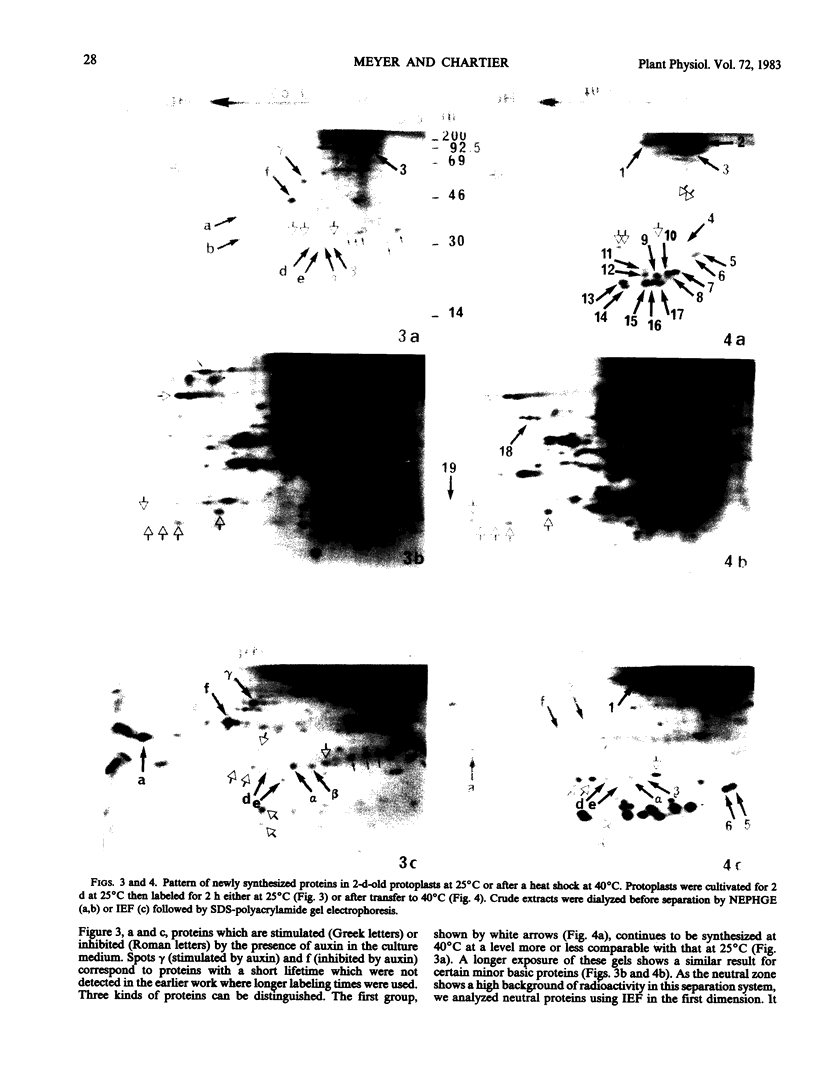
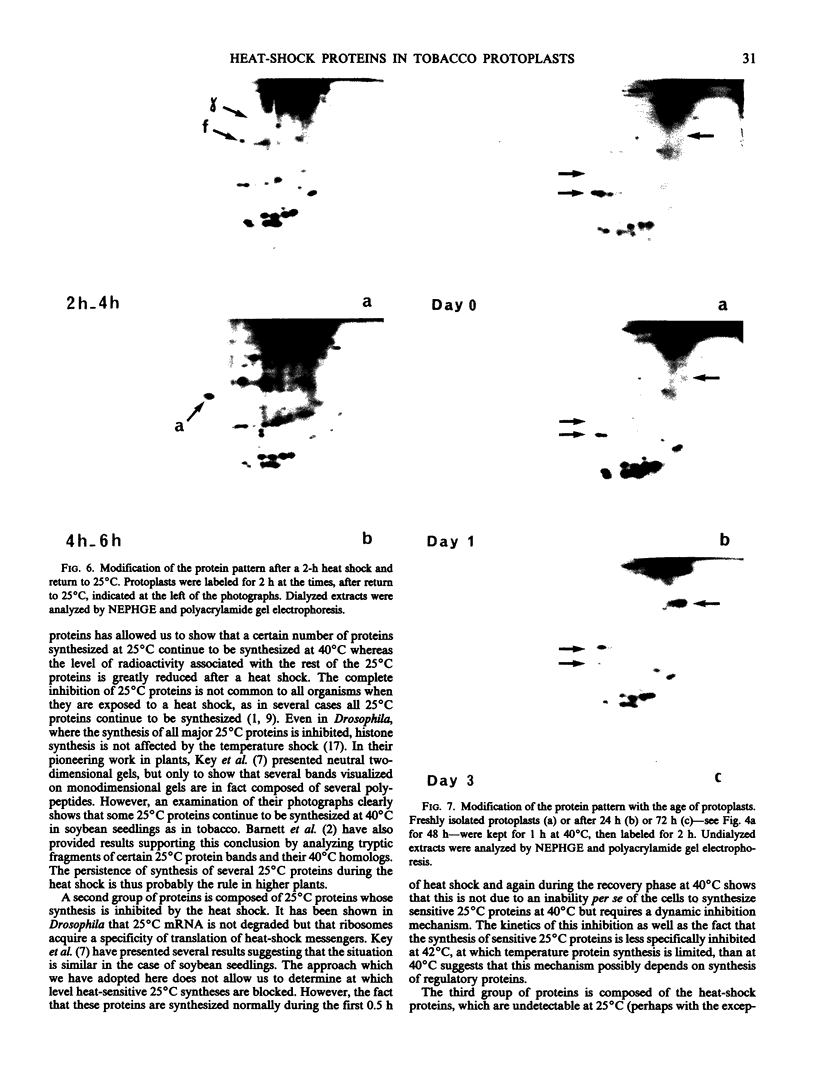
We have studied modifications in the pattern of proteins synthesized by tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum var Maryland) mesophyll protoplasts when they are transferred from 25°C to 40°C. The synthesis of one group of proteins is practically unaffected by the heat shock. On the other hand, the synthesis of most other 25°C proteins is greatly reduced, while specific heat-shock proteins appear: 17 stable, neutral, major proteins, which are synthesized throughout the culture period at the higher temperature and which correspond to those observed in other organisms, and two basic proteins with a short lifetime and which are synthesized only during the first 2 hours of heat shock. We suggest that these latter proteins are regulatory peptides which intervene in the inhibition of 25°C syntheses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson B. G. Synthesis of heat-shock proteins by cells undergoing myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):666–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Amalric F., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Zalta J. P. Effects of heat shock on gene expression and subcellular protein distribution in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1739–1747. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findly R. C., Pederson T. Regulated transcription of the genes for actin and heat-shock proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):323–328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D., Lin L. Heat shock response in a cellular slime mold, Polysphondylium pallidum. Dev Biol. 1980 Sep;79(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger C., Benecke B. J. In vitro translation of Drosophila heat-shock and non--heat-shock mRNAs in heterologous and homologous cell-free systems. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. Regulation of protein synthesis during heat shock. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):311–314. doi: 10.1038/293311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Y., Chartier Y. Hormonal Control of Mitotic Development in Tobacco Protoplasts: TWO-DIMENSIONAL DISTRIBUTION OF NEWLY-SYNTHESIZED PROTEINS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1273–1278. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Pardue M. L. Translational control in lysates of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3353–3357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater A., Cato A. C., Sillar G. M., Kioussis J., Burdon R. H. The pattern of protein synthesis induced by heat shock of HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Pardue M. L., Penman S. Messenger RNA in heat-shocked Drosophila cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 5;109(4):559–587. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Translational control of protein synthesis in response to heat shock in D. melanogaster cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Tanguay R. M. Heat-shock induced proteins present in the cell nucleus of Chironomus tentans salivary gland. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):501–503. doi: 10.1038/281501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Southgate R., Tissières A., Levis R., Gehring W. A DNA segment isolated from chromosomal site 67B in D. melanogaster contains four closely linked heat-shock genes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]