Abstract
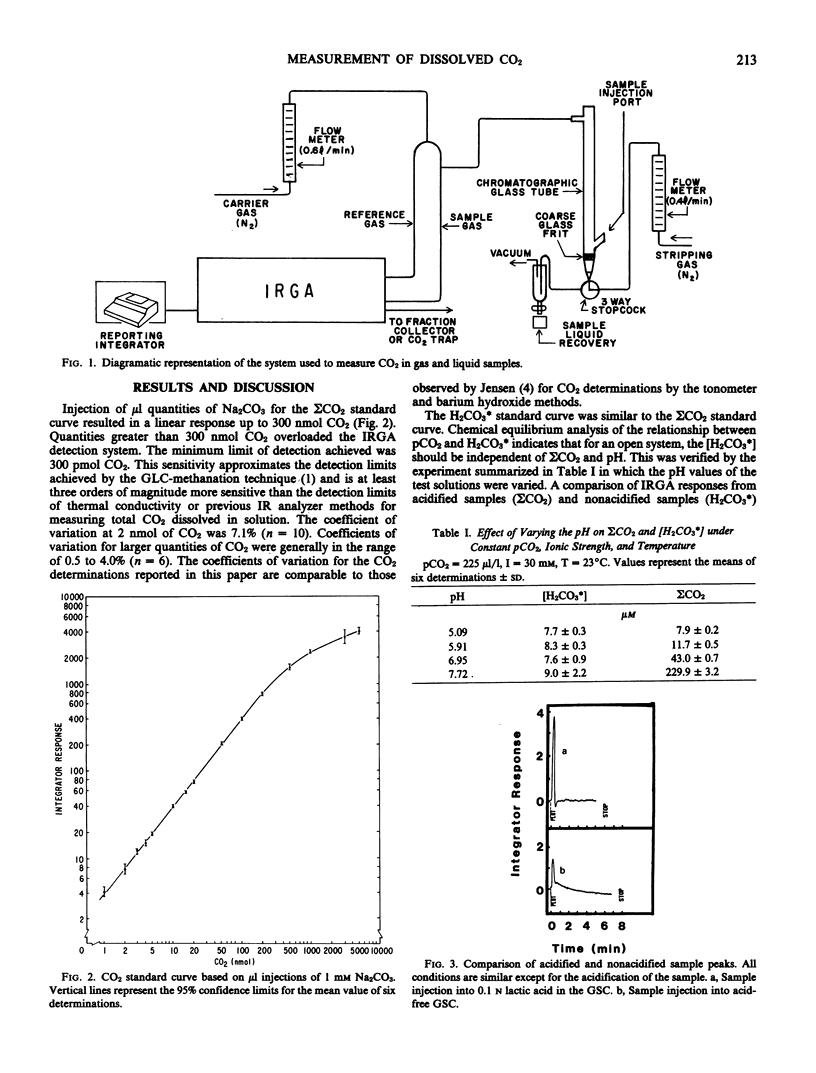
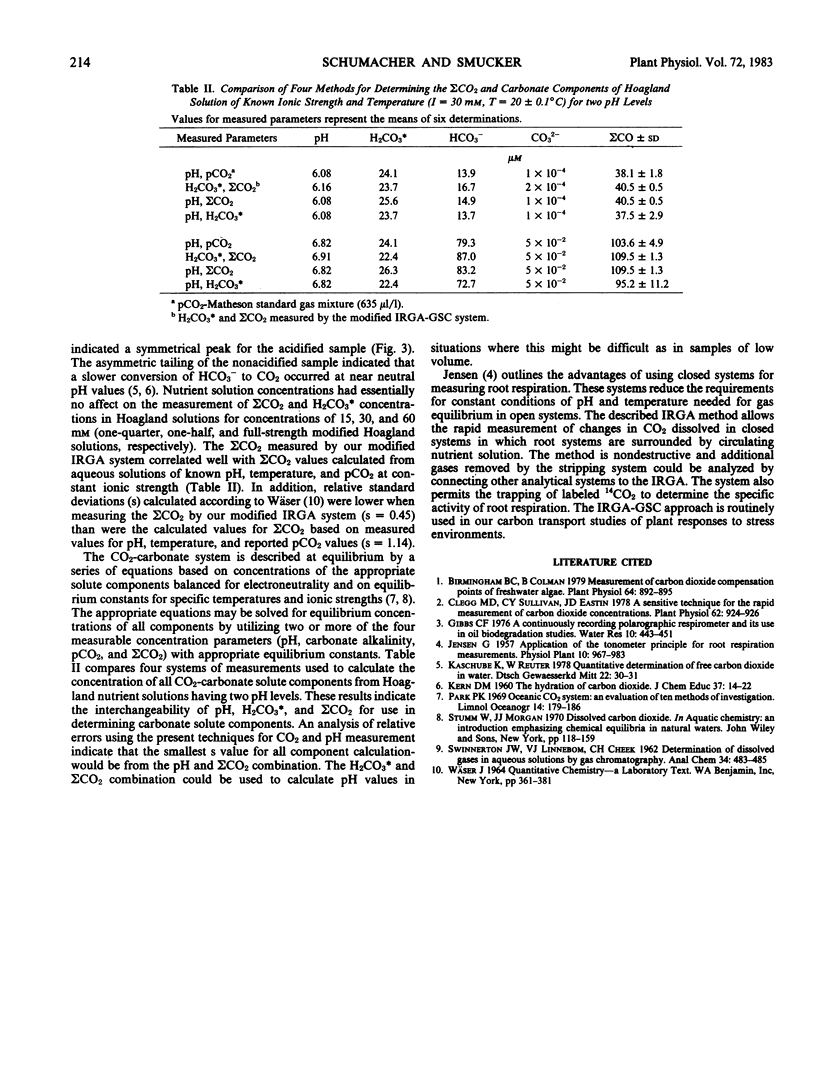
Total dissolved inorganic carbon (ΣCO2) and aqueous carbon dioxide (H2CO3*) in nutrient solutions may be measured by the injection of small gas or liquid samples (1 microliter to 8 milliliters) into a gas stripping column connected in-line with an infrared gas analyzer. The measurement of ΣCO2 in solution requires sample acidification, while H2CO3* and gaseous CO2 are measured without the addition of lactic acid. The standard curve for ΣCO2 was linear up to 300 nanomoles CO2. Maximum sensitivity was approximately 300 picomoles. Measurements of H2CO3* were independent of pH. Consequently, ΣCO2 and H2CO3* could be used to calculate the pH, HCO3−, and CO32− values of nutrient solutions. Injection and complete analyses required from 0.8 to 2 minutes.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birmingham B. C., Colman B. Measurement of carbon dioxide compensation points of freshwater algae. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):892–895. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg M. D., Sullivan C. Y., Eastin J. D. A sensitive technique for the rapid measurement of carbon dioxide concentrations. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):924–926. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


