Abstract
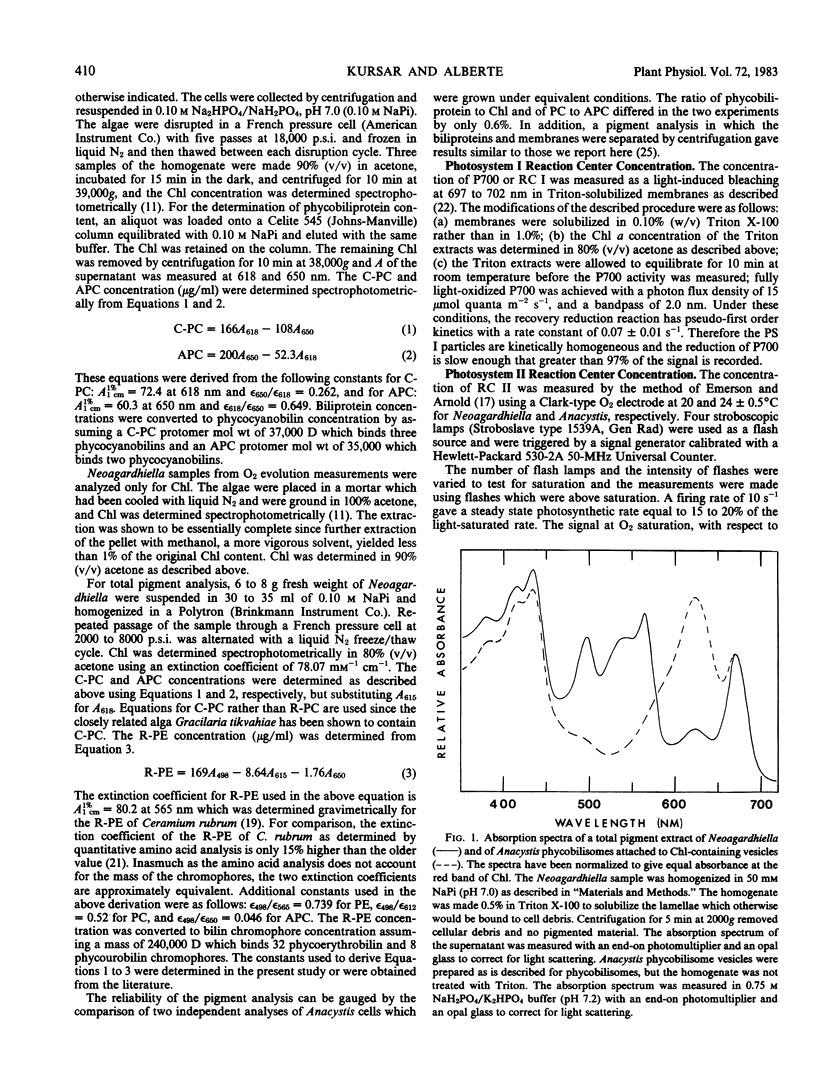
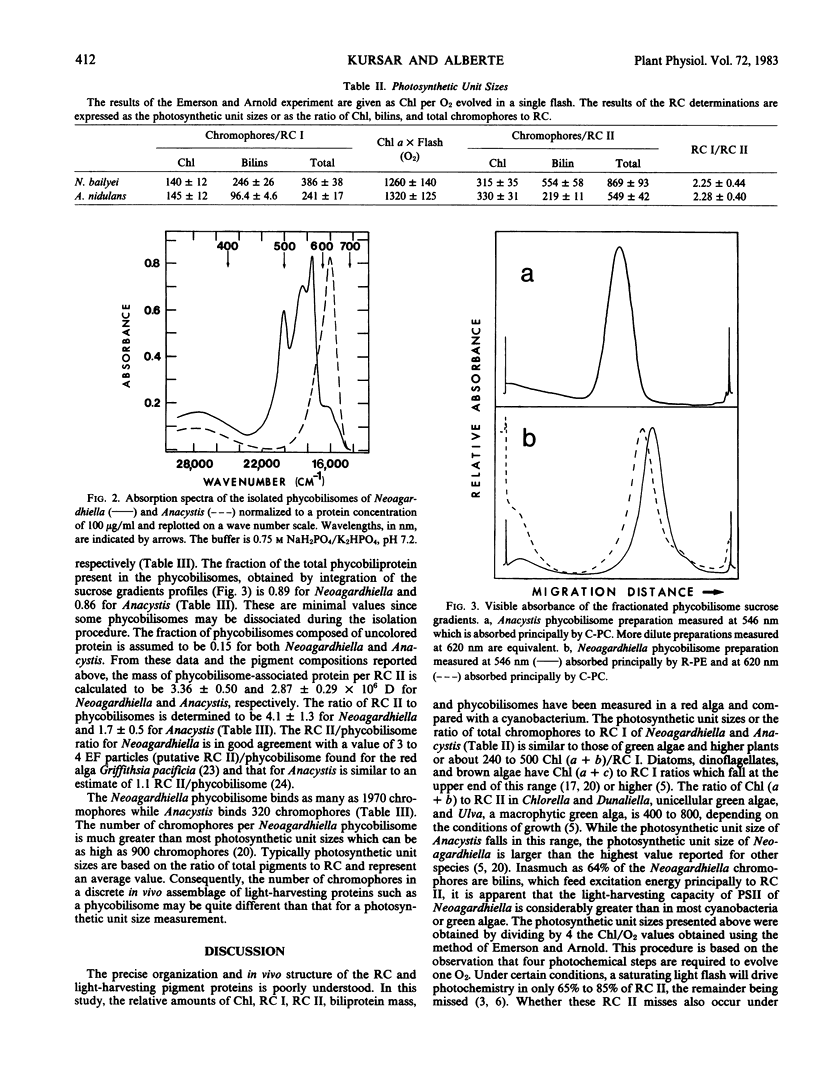
The relative concentration of biliproteins, phycobilisomes, chlorophyll a, and reaction centers I and II are reported for Neoagardhiella bailyei, a macrophytic red alga collected in the field and compared with Anacystis nidulans, a cyanobacterium cultured in the laboratory. The ratios of chlorophyll to reaction center I, of chlorophyll to reaction center II, and the mass of phycobiliprotein per reaction center II are quite similar in Neoagardhiella and Anacystis, supporting the concept that the red algal chloroplast is derived from a cyanobacterial progenitor. The ratios of reaction center I to reaction center II are about 2.3 in both species. The Anacystis phycobilisome has about 40% of the mass of the Neoagardhiella phycobilisome, 4.9 and 14.9 × 106 daltons, respectively. The reaction center II/phycobilisome ratio is about 1.7 in Anacystis and 4.1 in Neoagardhiella. Phycobilisome size and physical restrictions on phycobilisome packing may be a major constraint on the reaction center II-phycobilisome association and the assembly of the photosynthetic membrane in both the red algae and cyanobacteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diner B. A., Wollman F. A. Biosynthesis of Photosystem II Reaction Centers, Antenna and Plastoquinone Pool in Greening Cells of Cyanidium caldarium Mutant III-C. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):26–29. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diner B. A., Wollman F. A. Functional Comparison of the Photosystem II Center-Antenna Complex of a Phycocyanin-less Mutant of Cyanidium caldarium with That of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):20–25. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski P. G., Owens T. G., Ley A. C., Mauzerall D. C. Effects of growth irradiance levels on the ratio of reaction centers in two species of marine phytoplankton. Plant Physiol. 1981 Oct;68(4):969–973. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.4.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N., Apell G. S., Hixson C. S., Bryant D. A., Rimon S., Brown D. M. Biliproteins of cyanobacteria and Rhodophyta: Homologous family of photosynthetic accessory pigments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):428–431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. U., Berns D. S. Letter: Sequences of the N-terminus portions of biliproteins. J Mol Evol. 1975 Jul 11;5(2):153–163. doi: 10.1007/BF01732519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melis A., Brown J. S. Stoichiometry of system I and system II reaction centers and of plastoquinone in different photosynthetic membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4712–4716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J., Graham J. R., Wang R. T. Light Harvesting in Anacystis nidulans Studied in Pigment Mutants. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1144–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCARRA P. PURIFICATION AND N-TERMINAL ANALYSES OF ALGAL BILIPROTEINS. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj0940171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren J., Pählman S., Glad M., Hjertén S. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography on non-charged Sepharose derivatives. Binding of a model protein, related to ionic strength, hydrophobicity of the substituent, and degree of substitution (determined by NMR). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 18;412(1):51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa J. A., Alberte R. S., Thornber J. P. The P700-chlorophyll a-protein. Isolation and some characteristics of the complex in higher plants. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):388–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


