Abstract
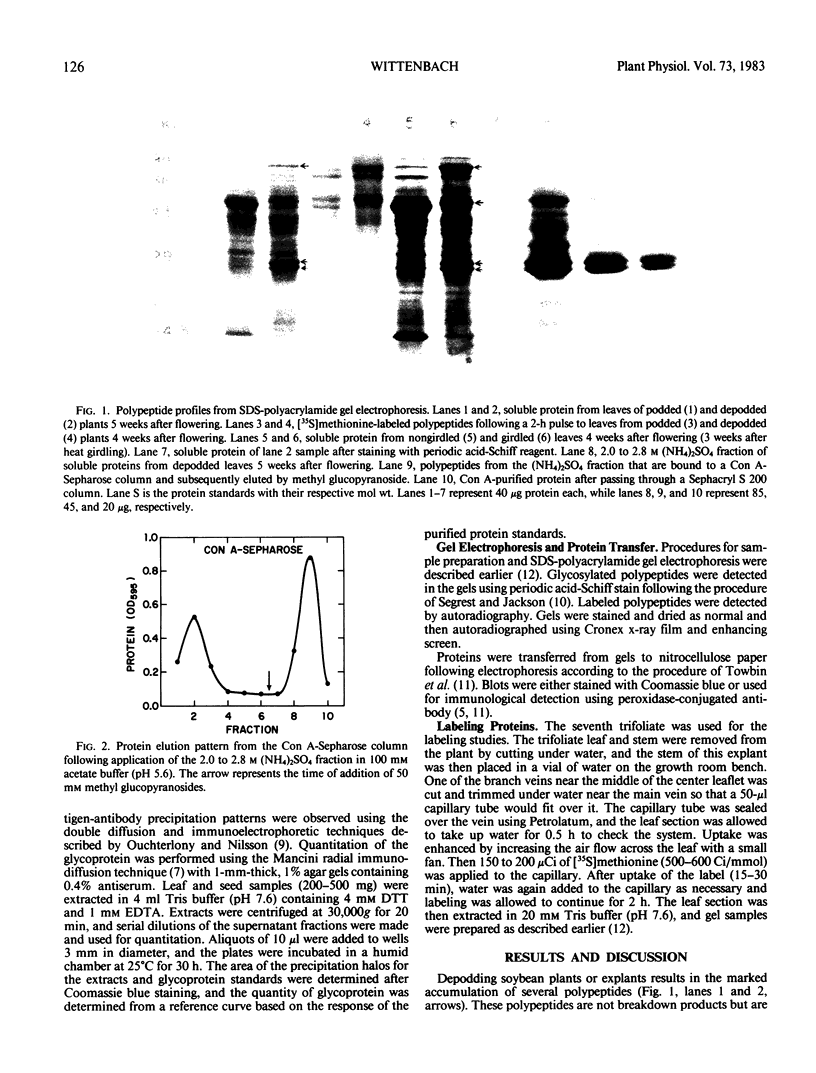
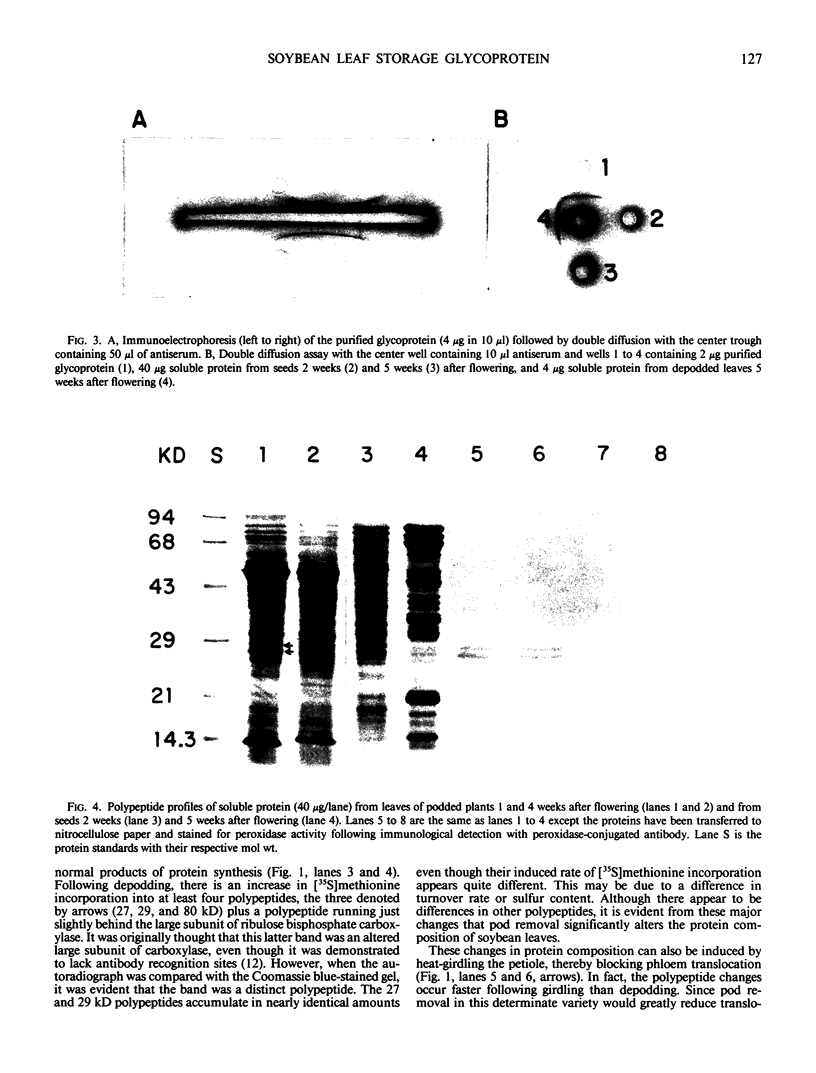
Removing the pods from soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr. cv Wye) plants induces a change in leaf function which is characterized by a change in the leaf soluble protein pattern. The synthesis of at least four polypeptides (∼27, 29, 54, and 80 kilodaltons) is enhanced, and these polypeptides accumulate to levels comprising over 50% of the soluble protein. Heat girdling the petiole also causes the accumulation of these polypeptides, suggesting that the signal for changing leaf function may be associated with inhibition of phloem transport. The 27 and 29 kilodalton polypeptides are glycosylated and have been purified to greater than 90% by (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, concanavilin A affinity, and gel filtration chromatography. These peptides appear to comprise a single protein. Mouse antiserum has been prepared against this glycoprotein and has been used to check for cross-reactivity with seed proteins and to quantitate changes with leaf development. No cross-reactivity was observed with seed soluble proteins from several stages of development. Quantitation showed the highest content in podded plants at, and shortly following, flowering, with levels subsequently declining in conjunction with seed growth. In depodded plants, the level of glycoprotein continued to increase following flowering and accounted for 45% of the soluble leaf protein by 4 weeks after depodding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Franceschi V. R., Wittenbach V. A., Giaquinta R. T. Paraveinal Mesophyll of Soybean Leaves in Relation to Assimilate Transfer and Compartmentation : III. Immunohistochemical Localization of Specific Glycopeptides in the Vacuole after Depodding. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):586–589. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal M. H., Brun W. A., Brenner M. L. Effects of Sink Removal on Photosynthesis and Senescence in Leaves of Soybean (Glycine max L.) Plants. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):394–397. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenbach V. A. Effect of pod removal on leaf senescence in soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1544–1548. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]