Abstract
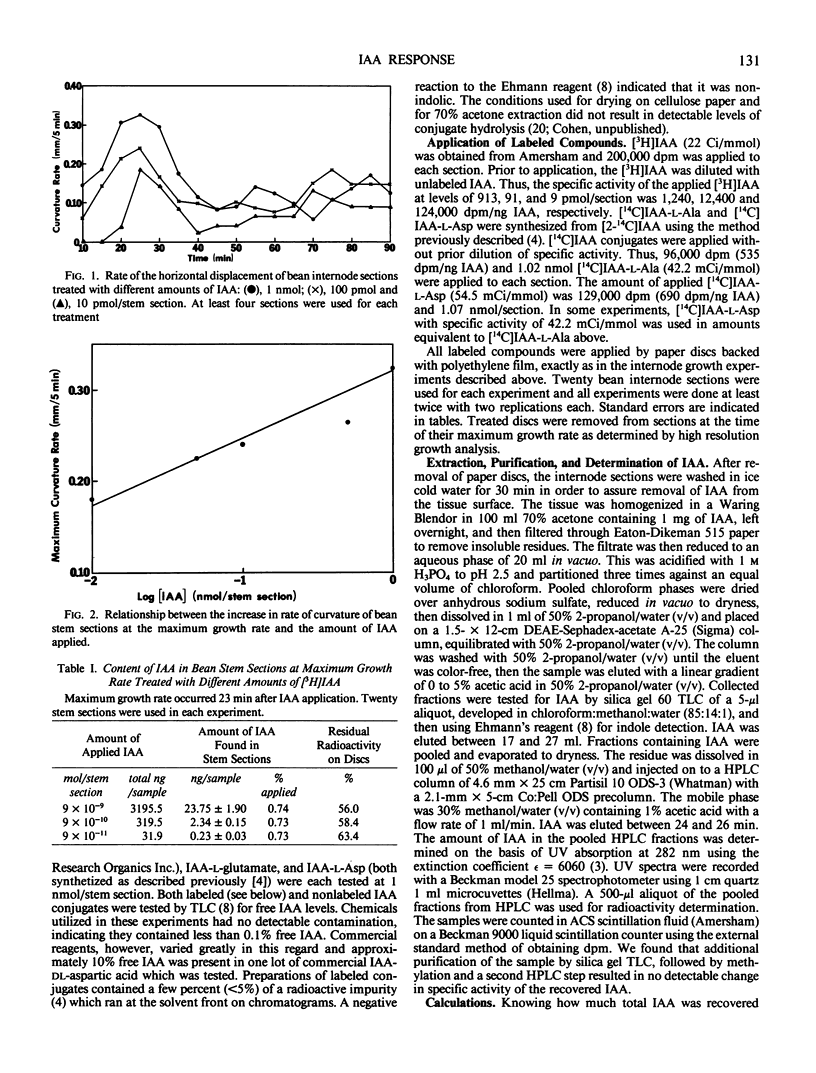
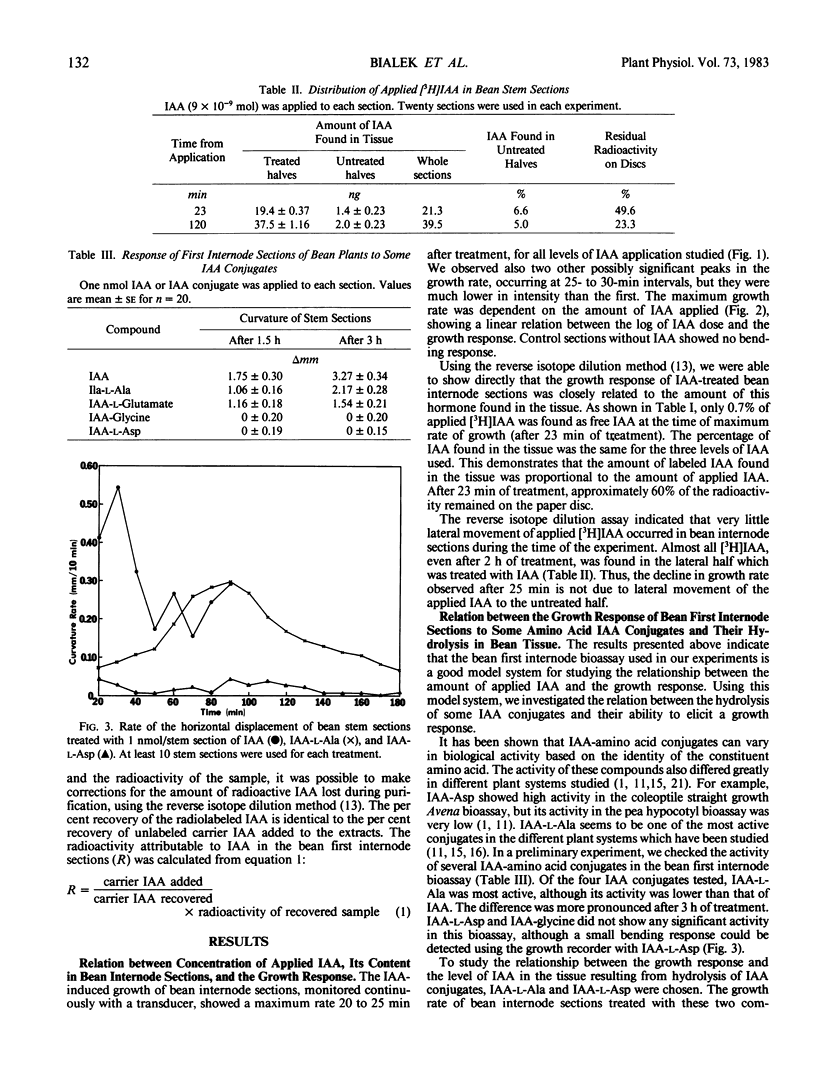
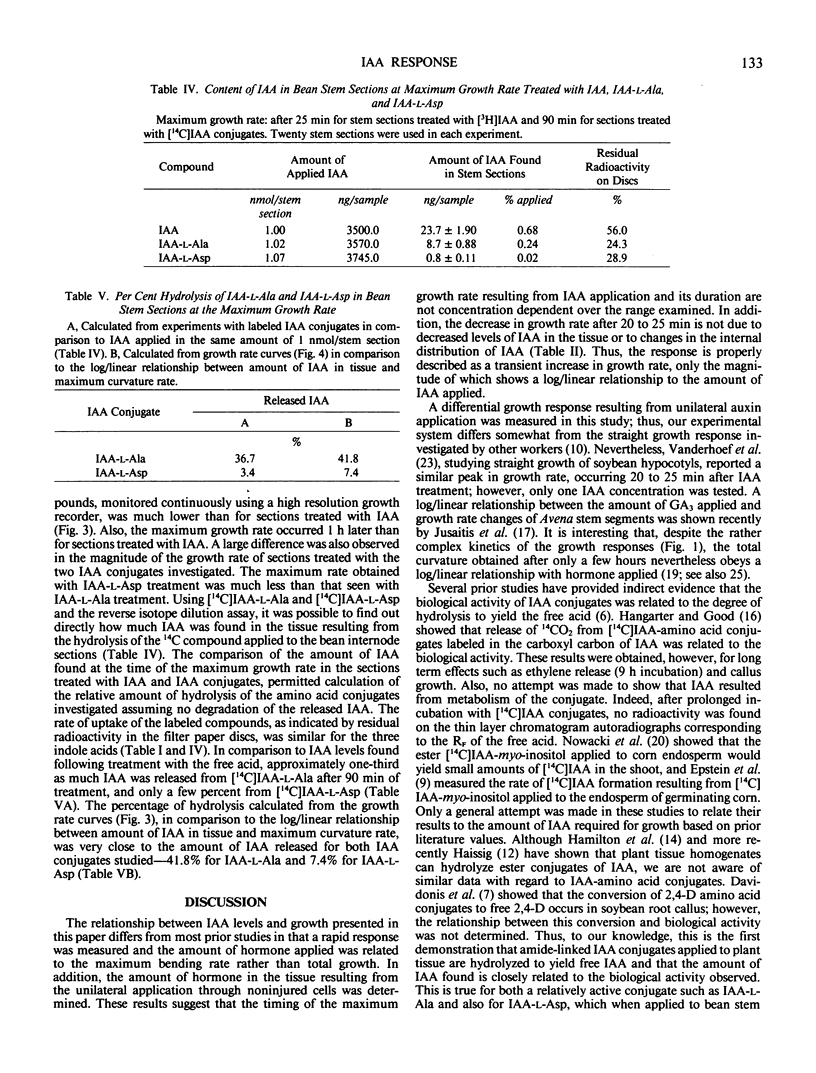
High resolution growth recording techniques and reverse isotope dilution analysis were used to study the relationship between indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) concentration and curvature of excised bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv Bush Burpee Stringless) first internode sections unilaterally treated with hormone. The maximum rate of curvature occurred rapidly (within 25 minutes) and was proportional to the log of the amount of applied IAA recovered in the tissue. The rate of curvature decreased after 30 minutes although little or no lateral migration of applied IAA occurred and tissue levels of IAA increased. The biologic activity of IAA-amino acid conjugates was found to be directly related to the amount of free IAA, resulting from their hydrolysis, which could be recovered from the tissue.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreae W. A., Good N. E. The Formation of Indoleacetylaspartic Acid in Pea Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):380–382. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandurski R. S., Schulze A. Concentrations of Indole-3-acetic Acid and Its Esters in Avena and Zea. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):257–262. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. D. Identification and Quantitative Analysis of Indole-3-Acetyl-l-Aspartate from Seeds of Glycine max L. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):749–753. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidonis G. H., Hamilton R. H., Mumma R. O. Metabolism of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid (2,4-D) in Soybean Root Callus : EVIDENCE FOR THE CONVERSION OF 2,4-D AMINO ACID CONJUGATES TO FREE 2,4-D. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):537–540. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann A. The van urk-Salkowski reagent--a sensitive and specific chromogenic reagent for silica gel thin-layer chromatographic detection and identification of indole derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1977 Feb 11;132(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Cohen J. D., Bandurski R. S. Concentration and Metabolic Turnover of Indoles in Germinating Kernels of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):415–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feung C. S., Hamilton R. H., Mumma R. O. Metabolism of Indole-3-acetic Acid: IV. Biological Properties of Amino Acid Conjugates. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jan;59(1):91–93. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. L., Bandurski R. S. Movement of Indole-3-acetic Acid and Tryptophan-derived Indole-3-acetic Acid from the Endosperm to the Shoot of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):425–429. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. H. Isolation of indole-3-acetic acid from corn kernels & etiolated corn seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1961 May;36(3):354–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.3.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hangarter R. P., Good N. E. Evidence That IAA Conjugates Are Slow-Release Sources of Free IAA in Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1424–1427. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hangarter R. P., Peterson M. D., Good N. E. Biological activities of indoleacetylamino acids and their use as auxins in tissue culture. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):761–767. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jusaitis M., Paleg L. G., Aspinall D. The Influence of Gibberellic Acid and Temperature on the Growth Rate of Avena sativa Stem Segments. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):532–539. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowacki J., Bandurski R. S. Myo-Inositol Esters of Indole-3-acetic Acid as Seed Auxin Precursors of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):422–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves W. K., Hollenberg S. M. Metabolism of Exogenous Indoleacetic Acid to Its Amide Conjugates in Cucumis sativus L. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):283–286. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhoef L. N., Lu T. Y., Williams C. A. Comparison of Auxin-induced and Acid-induced Elongation in Soybean Hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):1004–1007. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldrum J. D., Davies E. Subcellular Localization of IAA Oxidase in Peas. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1303–1307. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


