Abstract
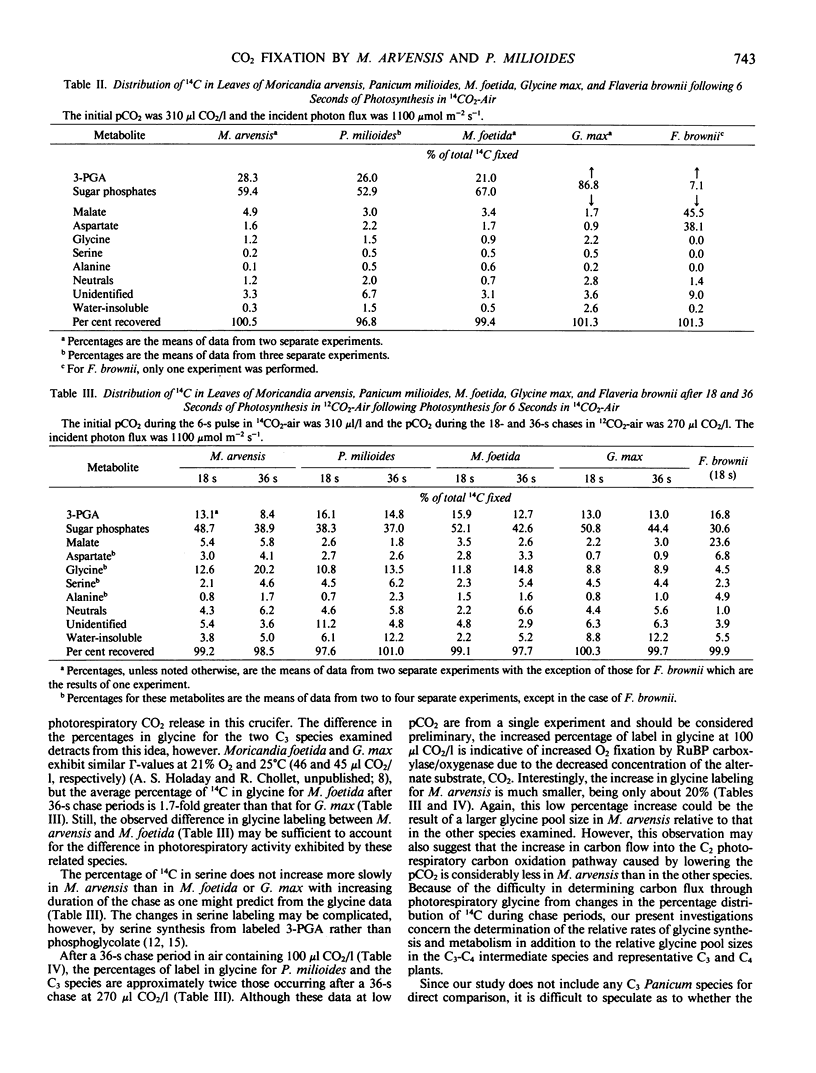
The distribution of 14C in photosynthetic metabolites of two naturally occurring higher plants with reduced photorespiration, Moricandia arvensis and Panicum milioides, in pulse and pulse-chase 14CO2 incorporation experiments was similar to that for the C3 species, M. foetida and Glycine max. After 6 seconds of 14CO2 incorporation, only about 6% of the total 14C fixed was in malate and aspartate in both M. arvensis and P. milioides. The apparent turnover of the C4 acids was very slow, and malate accumulated during the day in M. arvensis. Thus, C4 acid metabolism by M. arvensis and P. milioides had no significant role in photosynthetic carbon assimilation under the conditions of our experiments (310 microliters CO2 per liter, 21% O2, 1100 or 1900 micromoles photon per square meter per second, 27°C).
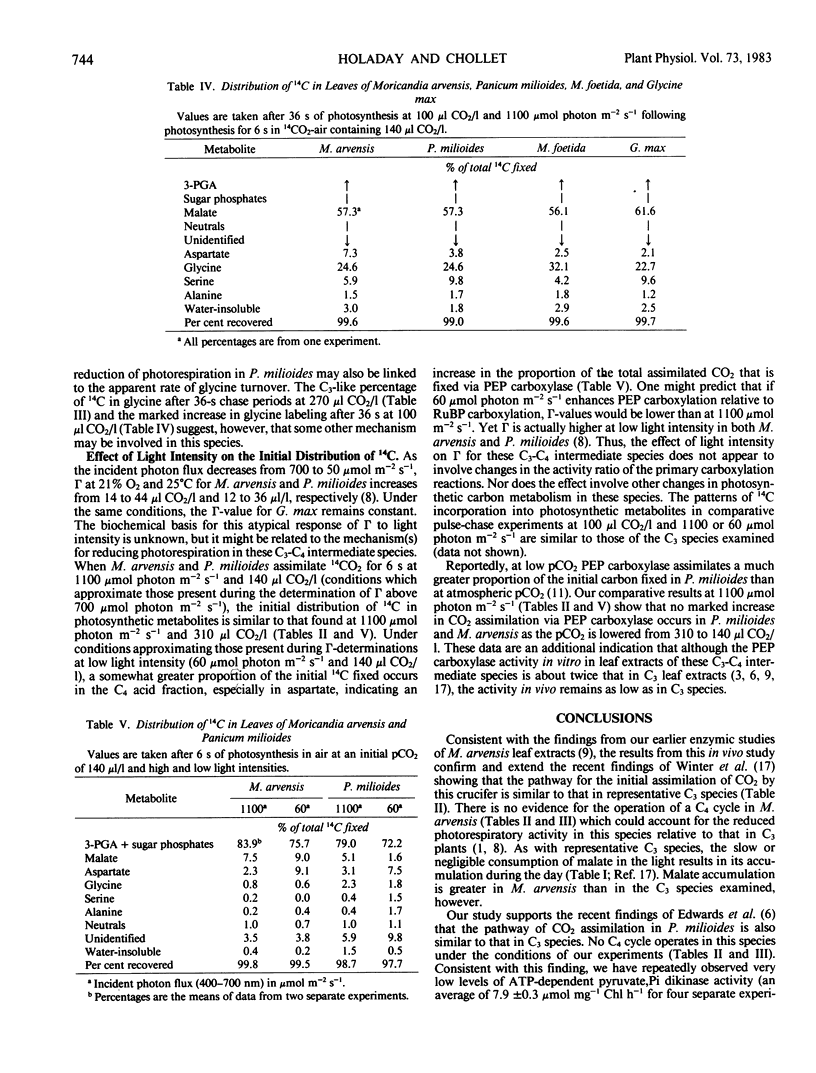
After a 36-second chase period in air containing 270 microliters CO2 per liter, about 20% of the total 14C fixed was in glycine with M. arvensis, as compared to 15% with M. foetida, 14% with P. milioides, and 9% with G. max. After a 36-second chase period in 100 microliters CO2 per liter, the percentage in glycine was about twice that at 270 microliters CO2 per liter in the C3 species and P. milioides, but only 20% more 14C was in glycine in M. arvensis. These data suggest that either the photorespiratory glycine pool in M. arvensis is larger than in the other species examined or the apparent turnover rate of glycine and the flow of carbon into glycine during photorespiration are less in M. arvensis. An unusual glycine metabolism in M. arvensis may be linked to the mechanism of photorespiratory reduction in this crucifer.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chollet R., Anderson L. L. Cyanate modification of essential lysyl residues in the catalytic subunit of tobacco ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 7;525(2):455–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D. Mechanism of C4 photosynthesis in Chloris gayana: pool sizes and kinetics of 14CO2 incorporation into 4-carbon and 3-carbon intermediates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90601-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon W. H., Holaday A. S., Black C. C. Diurnal Changes in Metabolite Levels and Crassulacean Acid Metabolism in Kalanchoë daigremontiana Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1002–1007. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler D. P., Mayne B. C., Ray T. B., Goldstein L. D., Brown R. H., Black C. C. Biochemical components of the photosynthetic CO2 compensation point of higher plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1439–1446. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt S. G., Plaut Z., Bassham J. A. Steady-state photosynthesis in alfalfa leaflets: effects of carbon dioxide concentration. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):230–234. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathnam C. K., Chollet R. Photosynthetic carbon metabolism in Panicum milioides, a C3-C4 intermediate species: evidence for a limited C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 6;548(3):500–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C. Chemical inhibition of the glycolate pathway in soybean leaf cells. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):461–466. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter K., Usuda H., Tsuzuki M., Schmitt M., Edwards G. E., Thomas R. J., Evert R. F. Influence of Nitrate and Ammonia on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Leaf Anatomy of Moricandia arvensis. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):616–625. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


